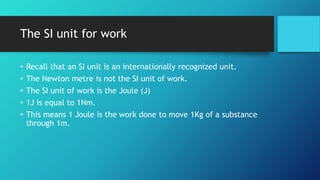
This document discusses the meaning, units, and SI unit of measurement for work. Work is defined as the product of the applied force and the distance moved in the direction of the force. The unit for force is the Newton (N), the unit for distance is the meter (m), and therefore the unit for work is the Newton meter (Nm). However, the standard SI unit for work is the Joule (J), where 1 Joule is equal to the work done by a 1 Newton force to move an object 1 meter.