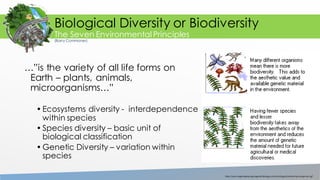
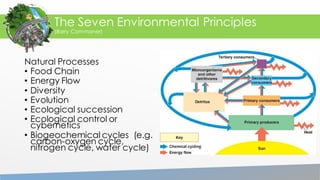
The document outlines the seven environmental principles proposed by Barry Commoner, emphasizing the interconnectedness of ecosystems and the importance of biodiversity. It discusses the significance of sustainable development and natural resource management, highlighting the need for conservation practices and ecological technology. The document also reflects on the role of humans as stewards of the environment, urging responsible management of natural resources to ensure future sustainability.