This document discusses the human sensory system and how sensory information is processed in the nervous system. It covers:
1. How sensory receptors detect different types of energy (light, sound, touch, temperature) and convert it into action potentials.
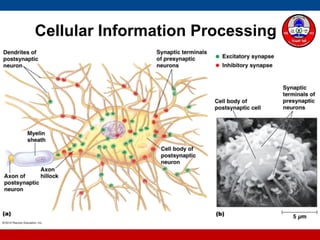
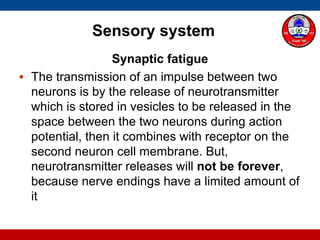
2. How action potentials travel along sensory neurons to the spinal cord and brain for analysis. Sensory information can be urgent and travel along myelinated fibers.
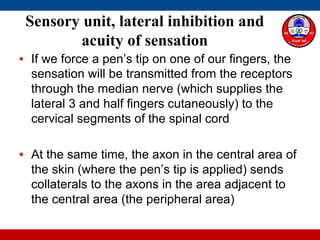
3. How the number and distribution of receptors impacts our ability to detect and differentiate stimuli.
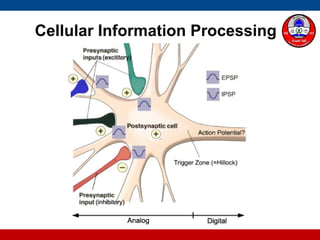
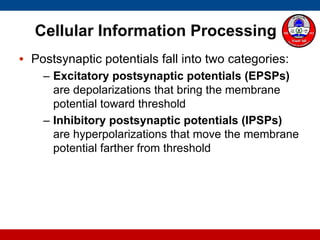
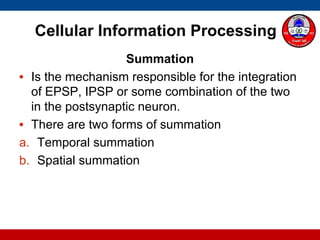
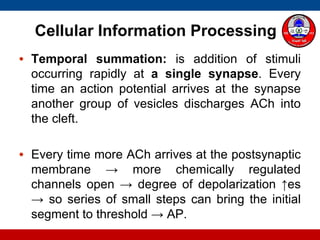
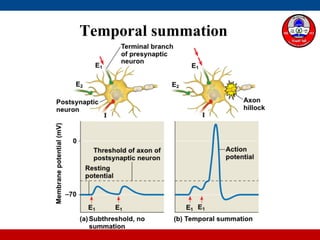
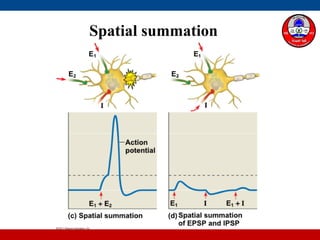
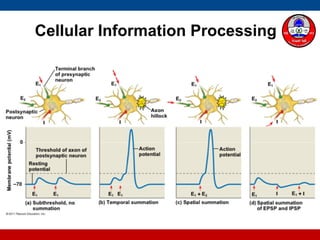
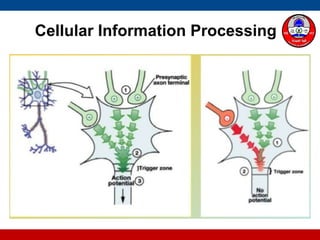
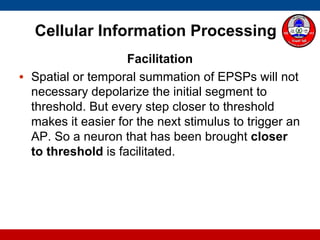
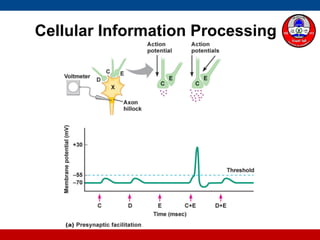
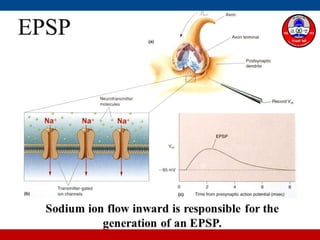
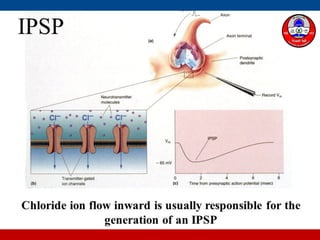
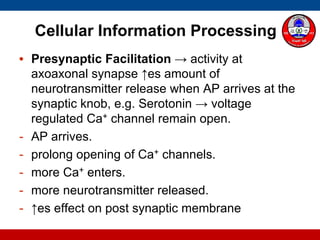
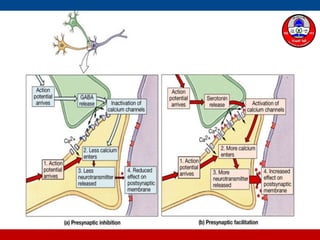
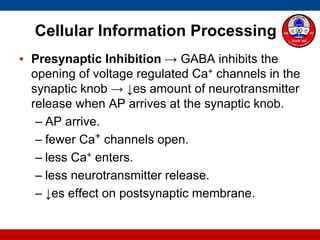
4. How summation (temporal and spatial) of excitatory and inhibitory postsynaptic potentials integrates sensory information at the cellular level in the central nervous system.