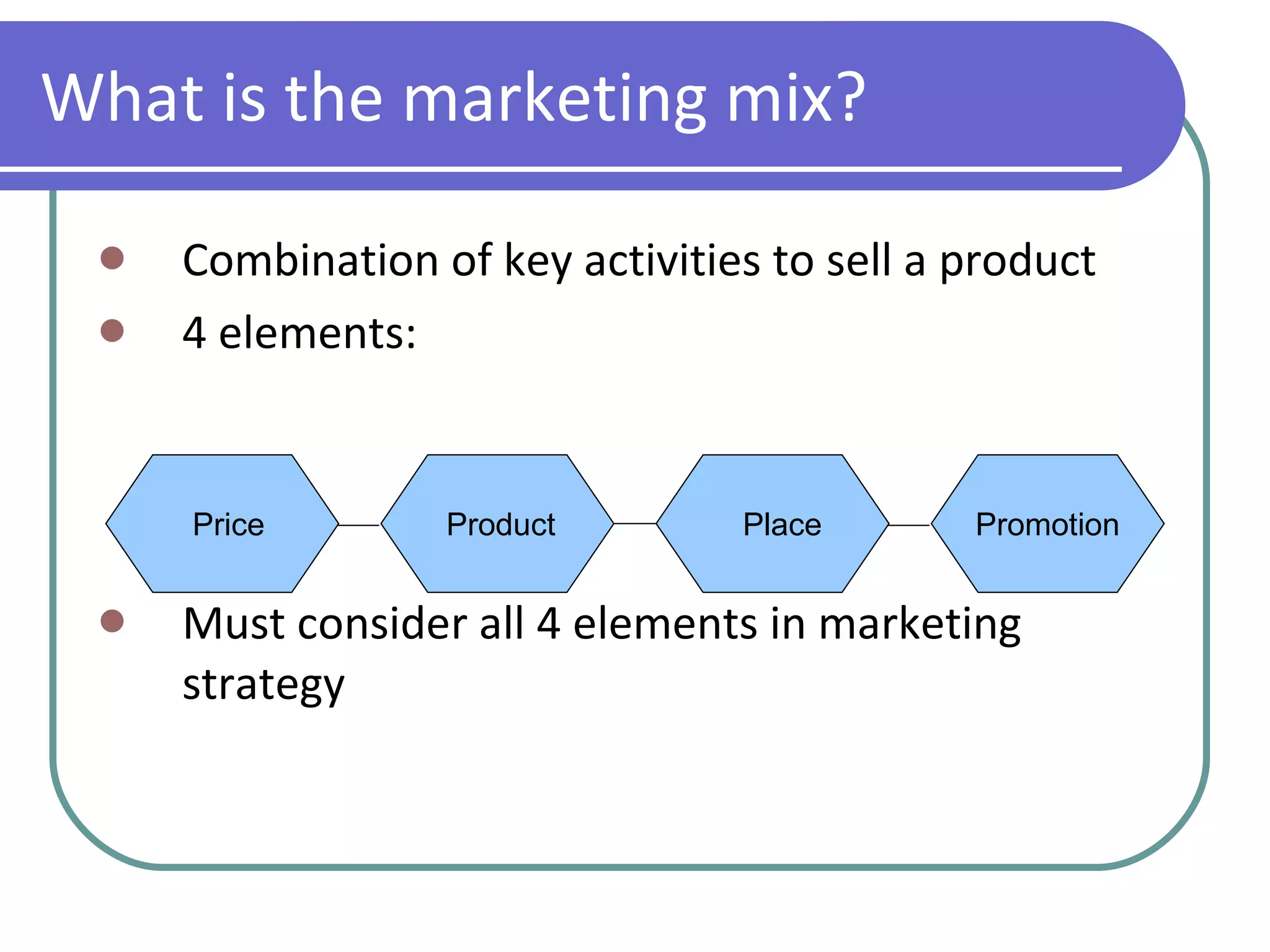
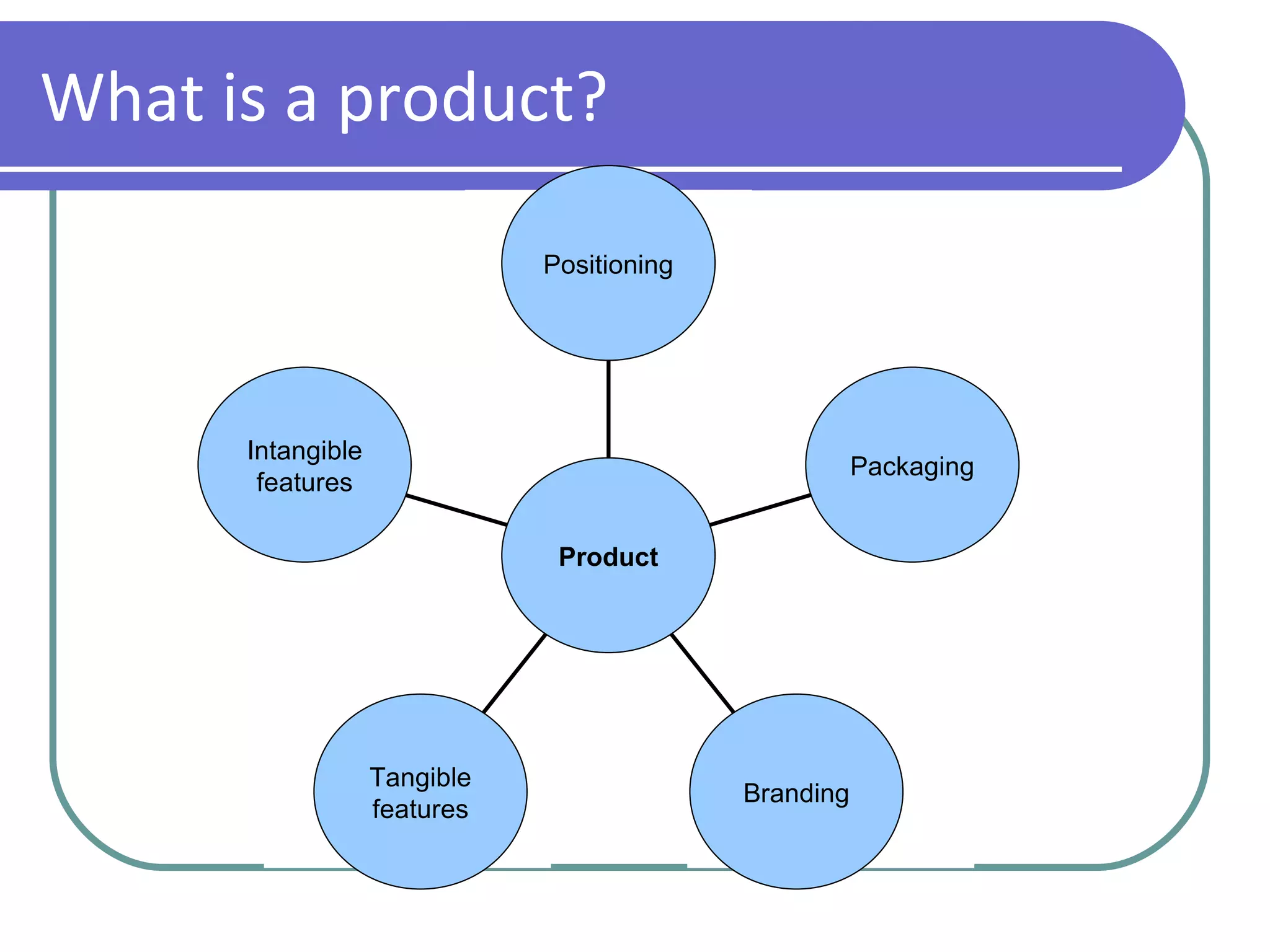
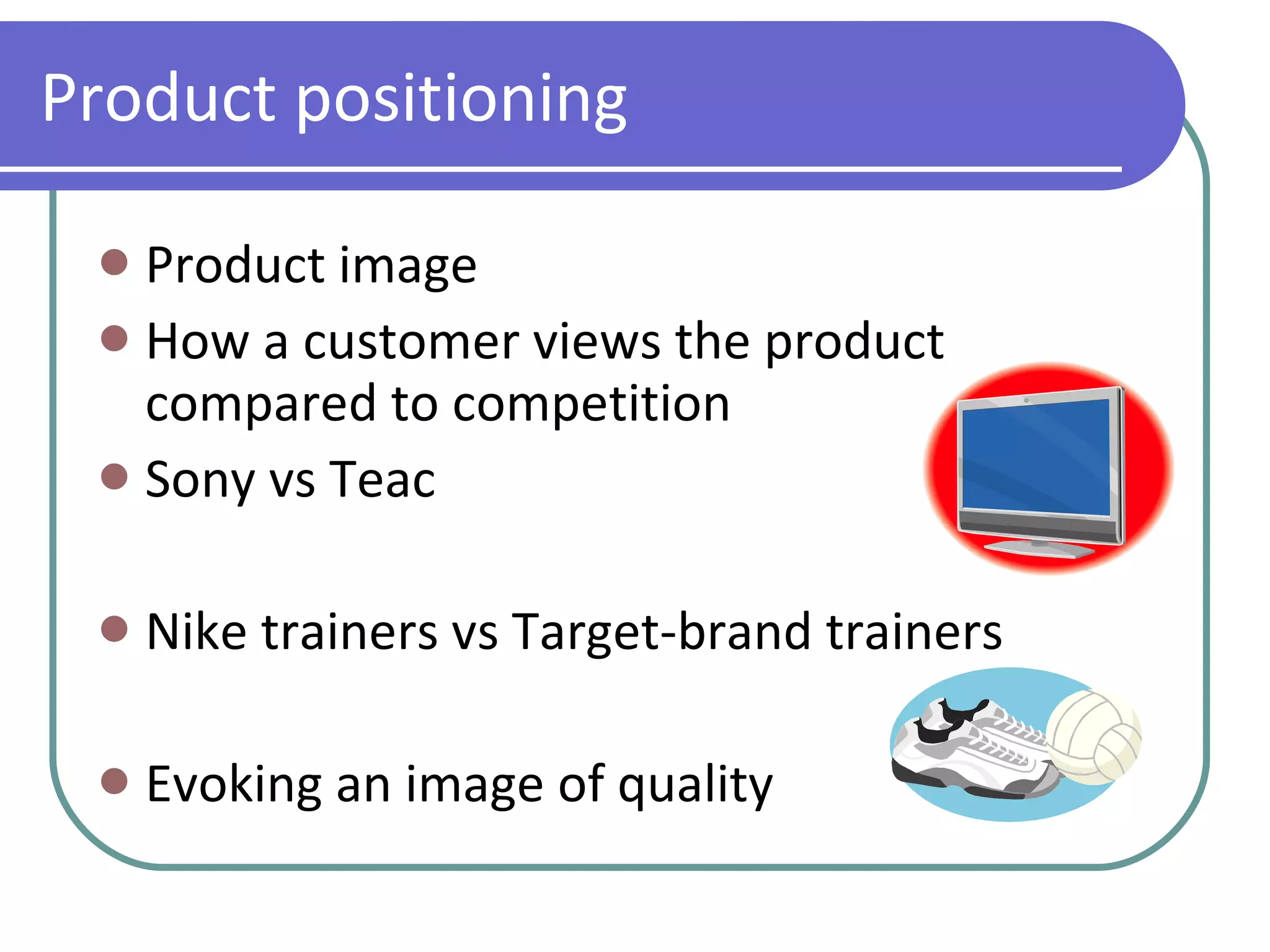
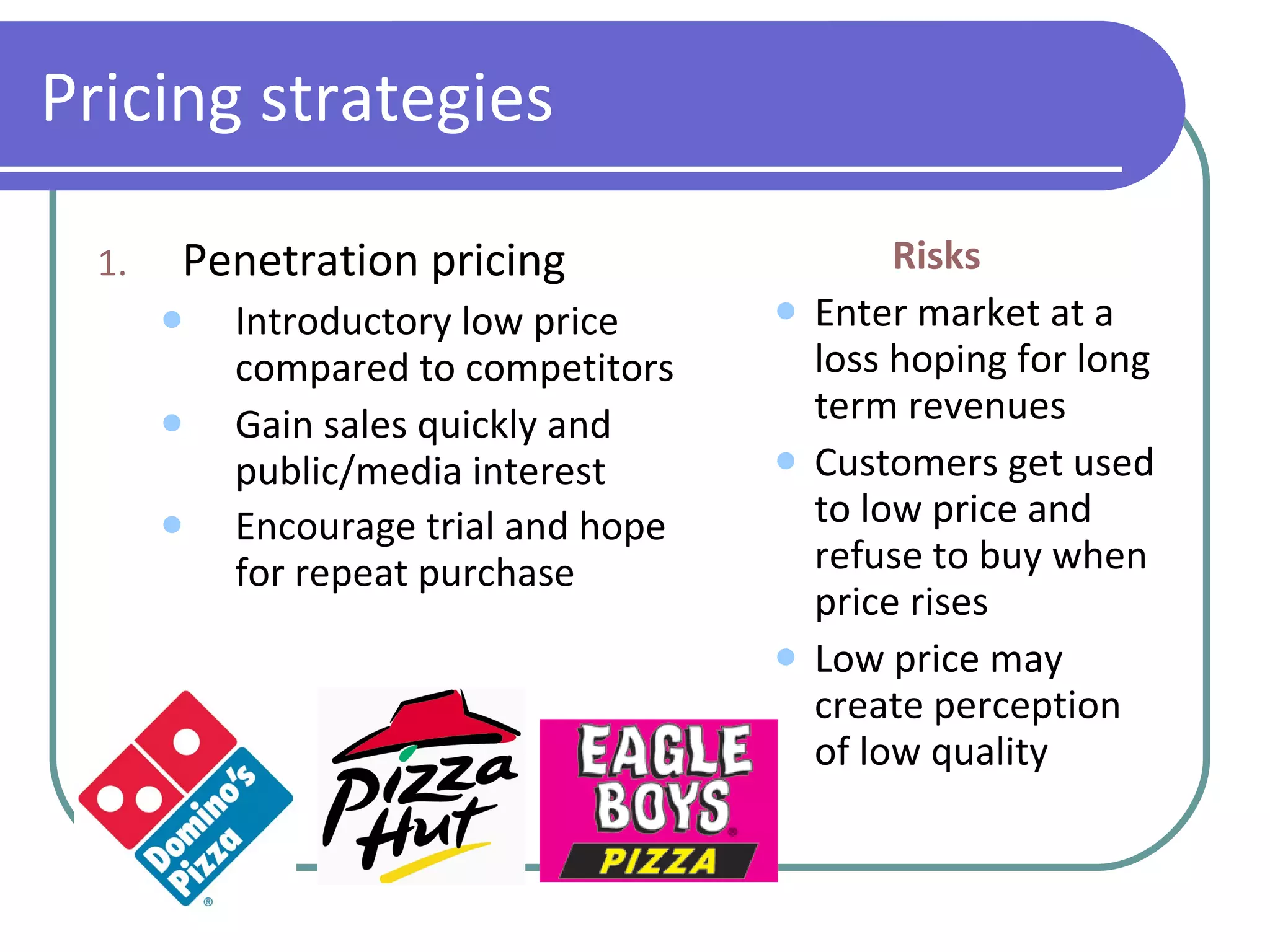
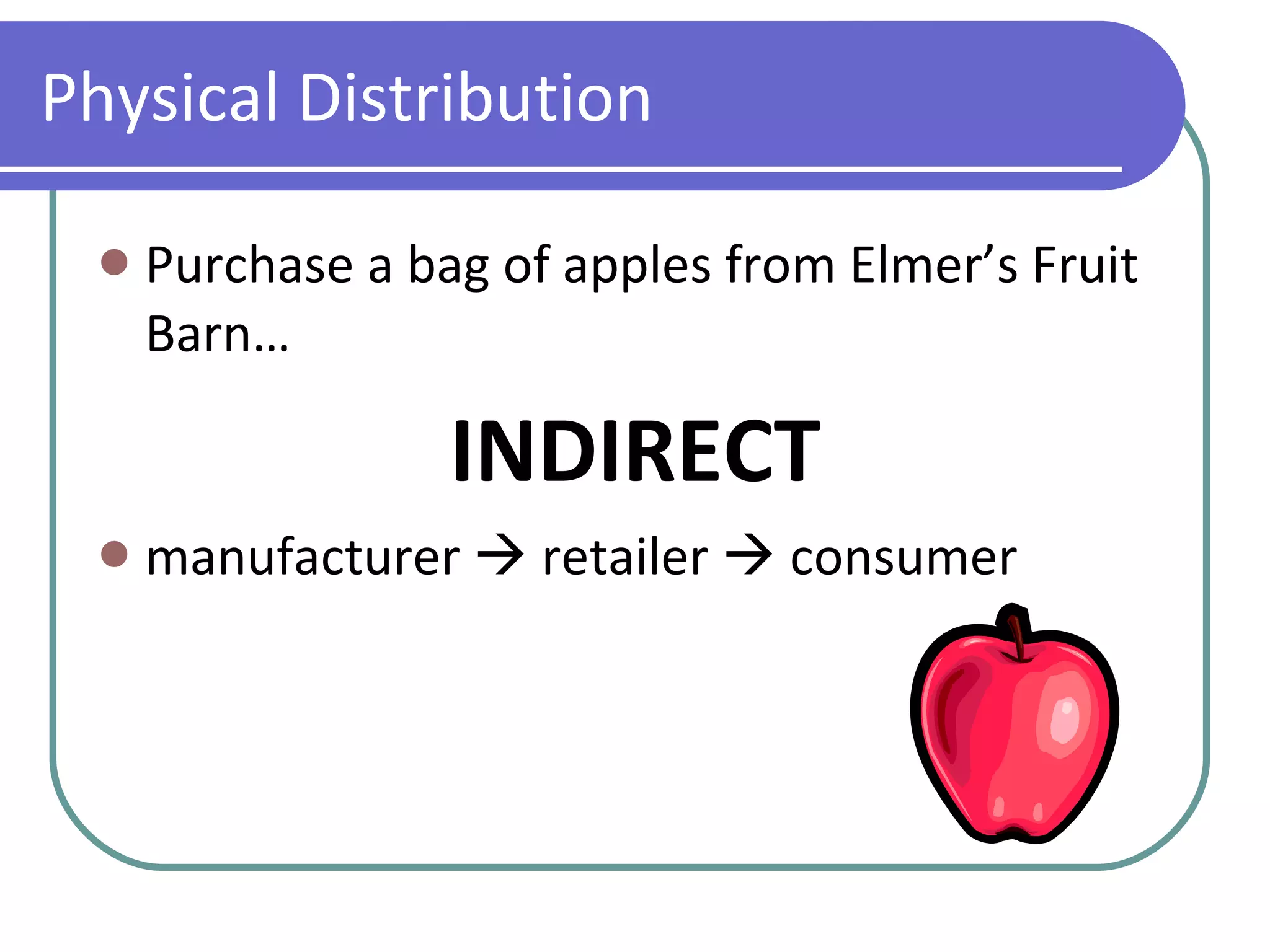
The marketing mix consists of 4 key elements used to sell a product: product, price, place, and promotion. A product includes both tangible features like packaging as well as intangible features like branding. Price is used both to make a profit and influence consumer perceptions of quality. Place refers to how the product reaches customers through distribution channels. Promotion communicates information about the product through advertising, public relations, sales promotions, and direct marketing.