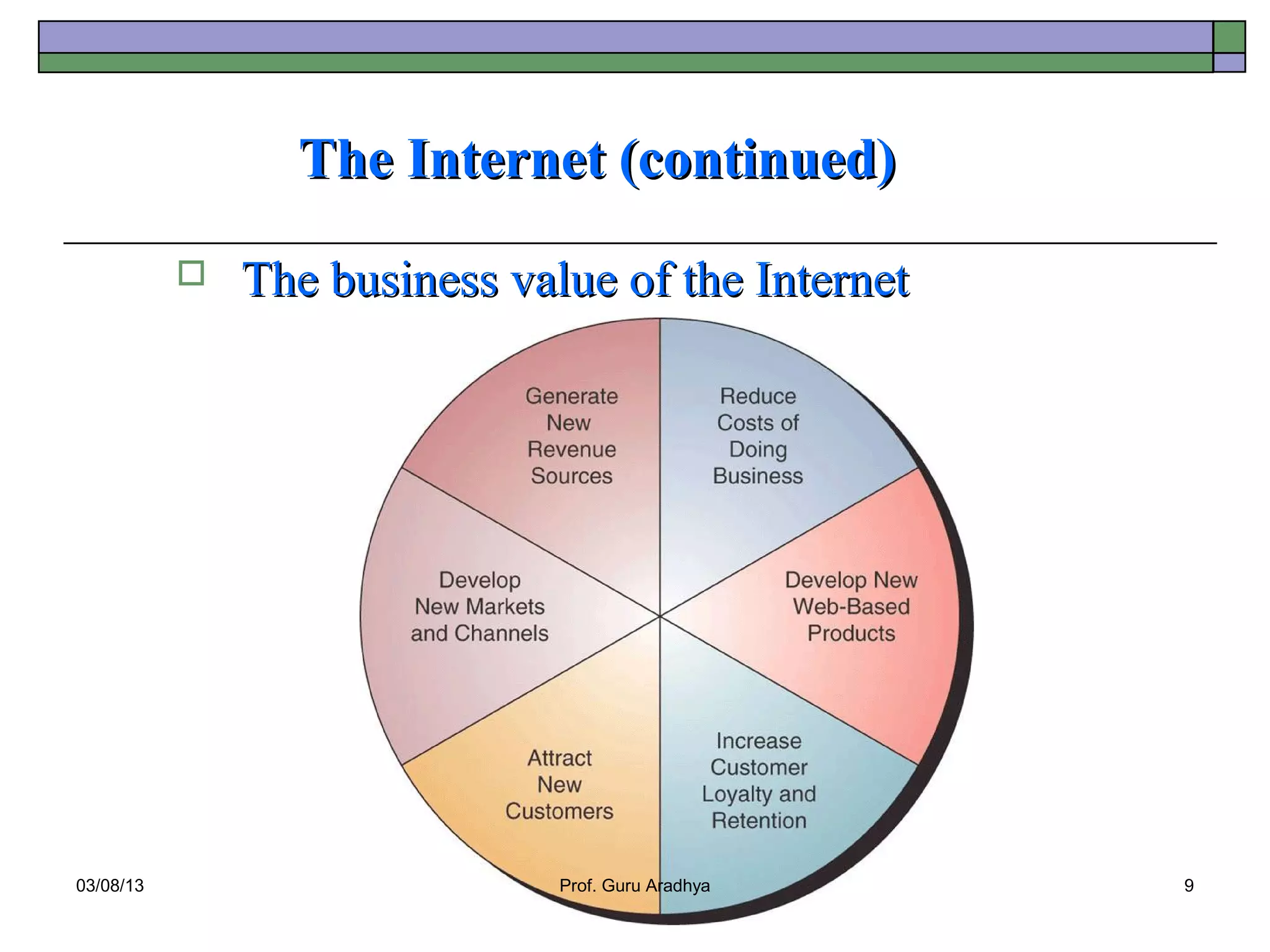
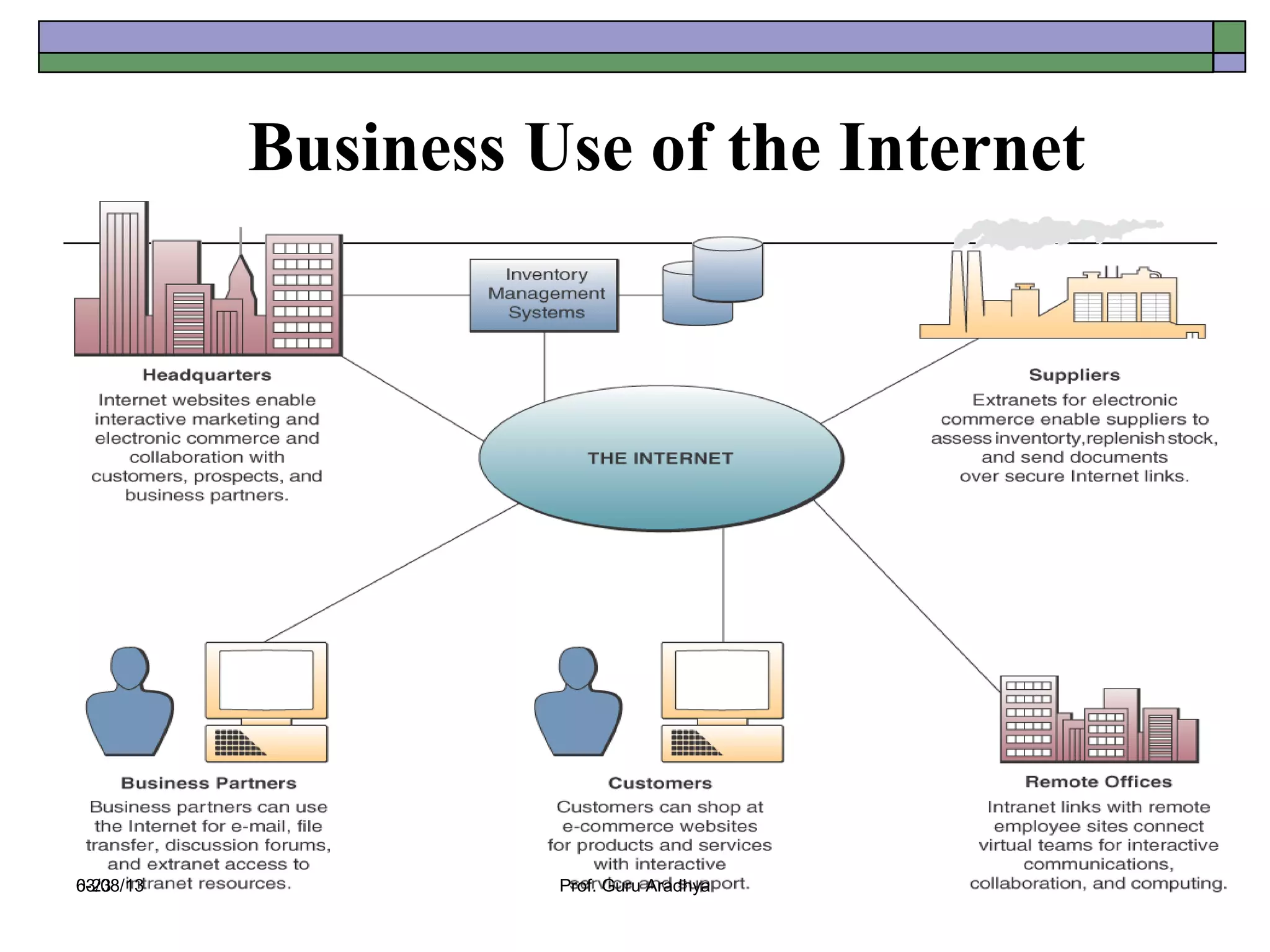
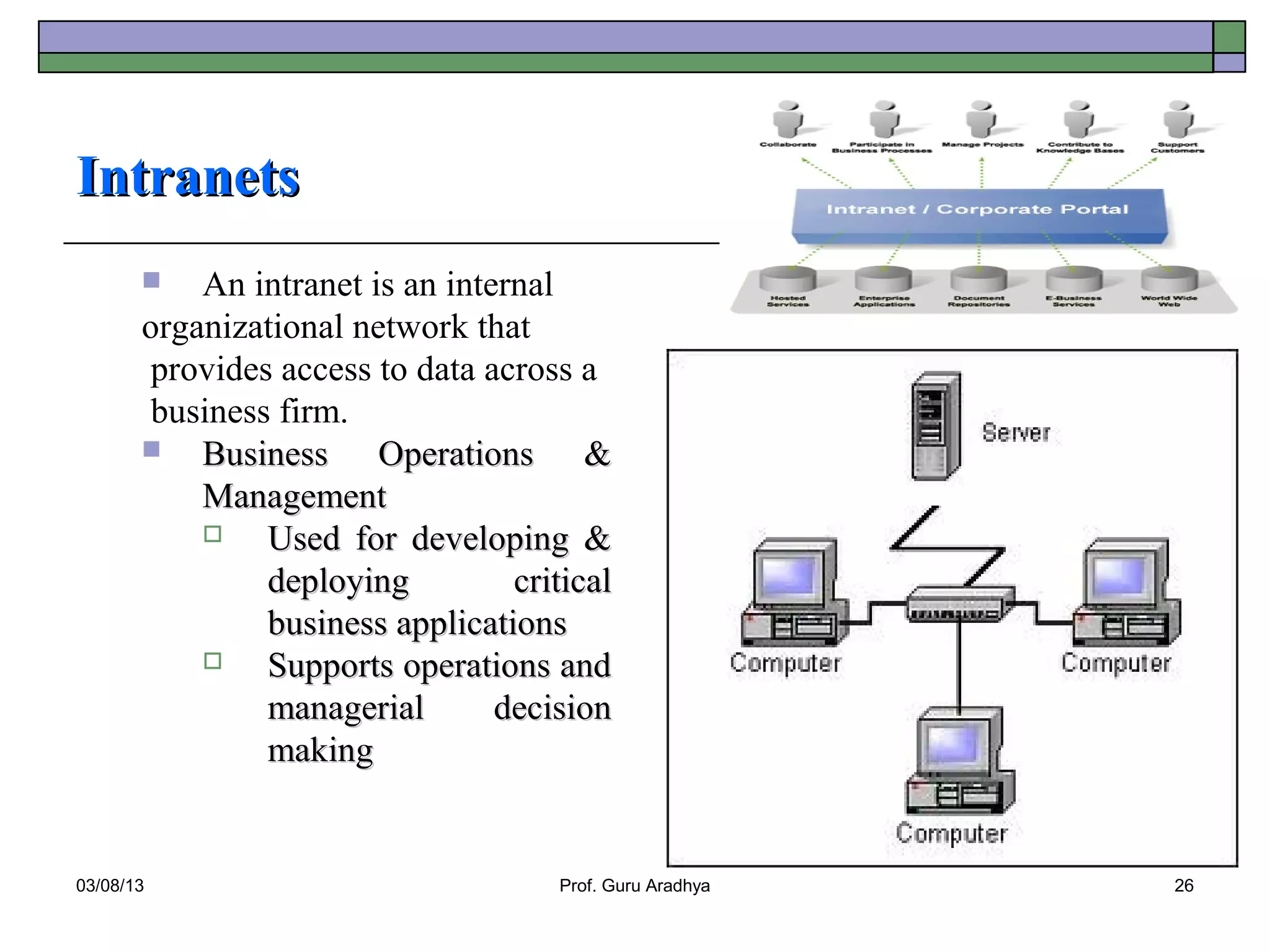
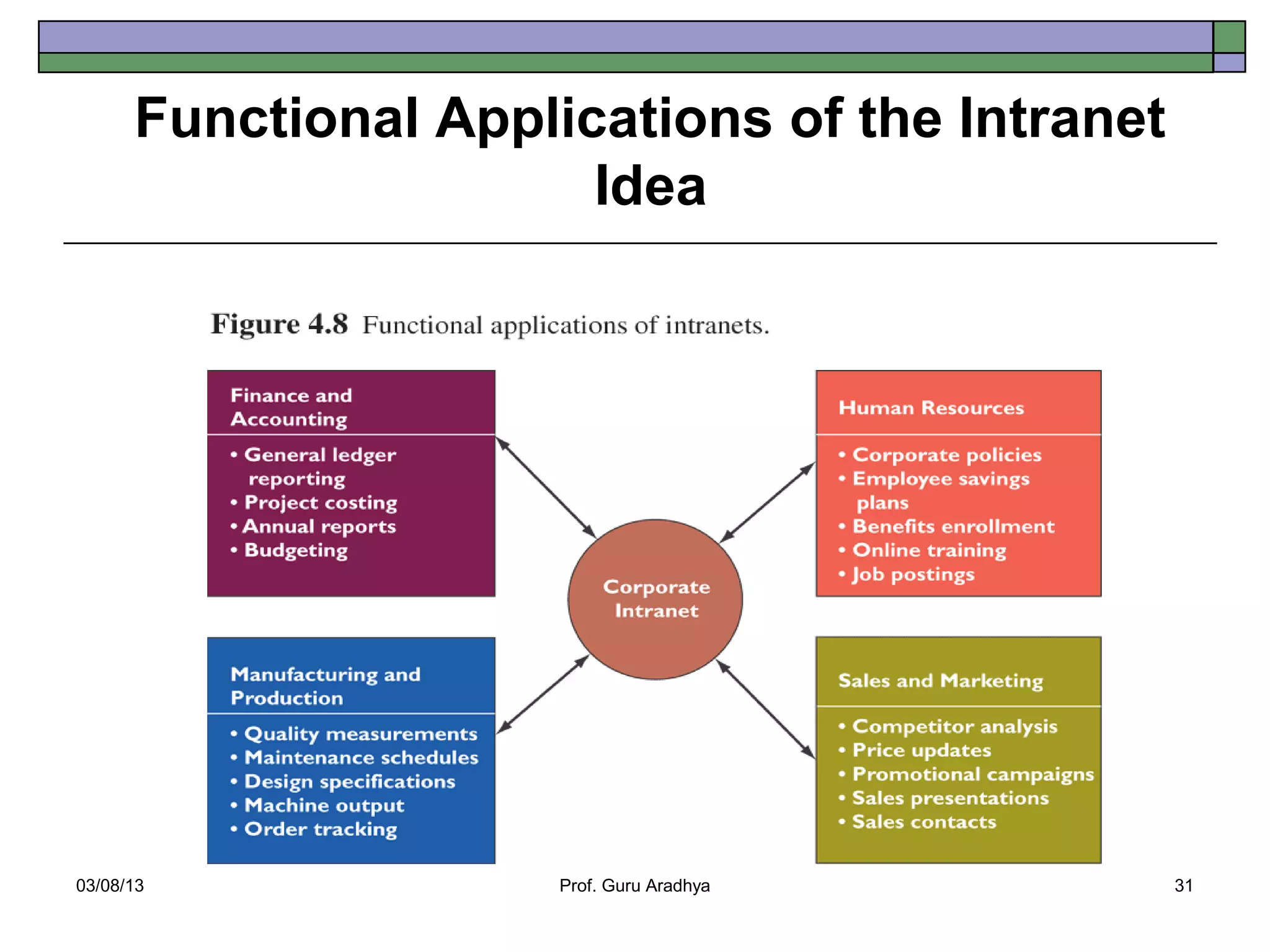
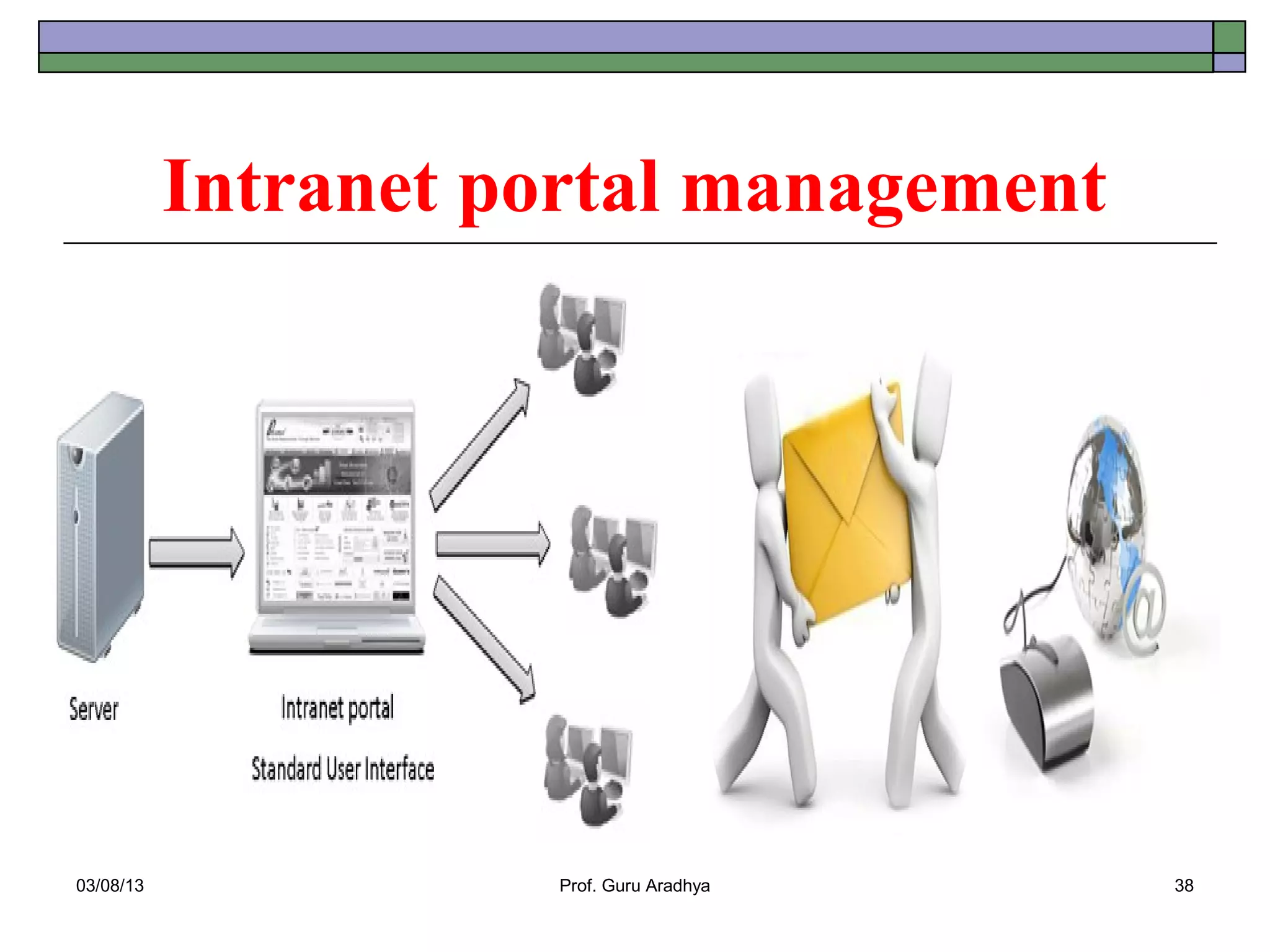
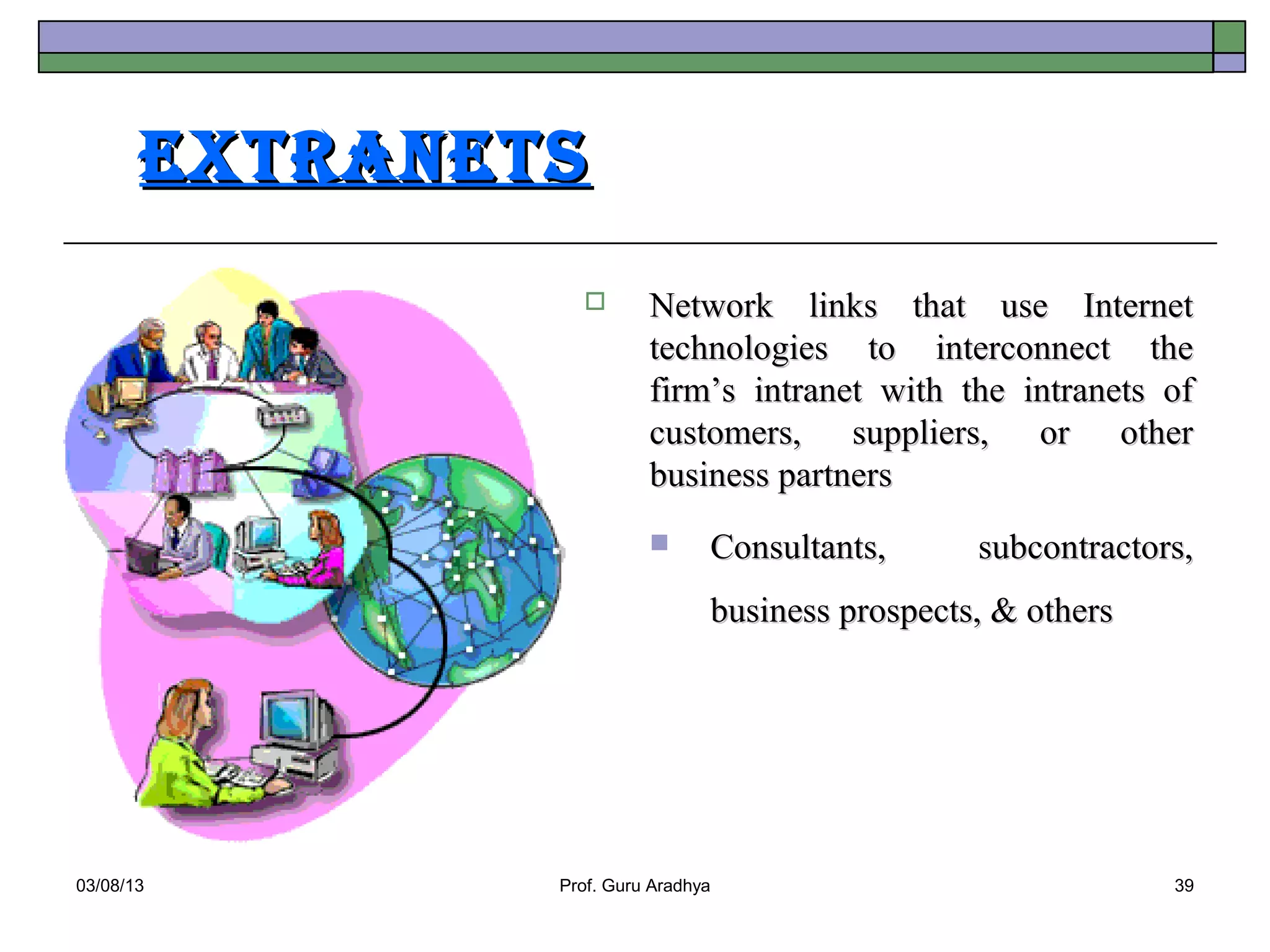
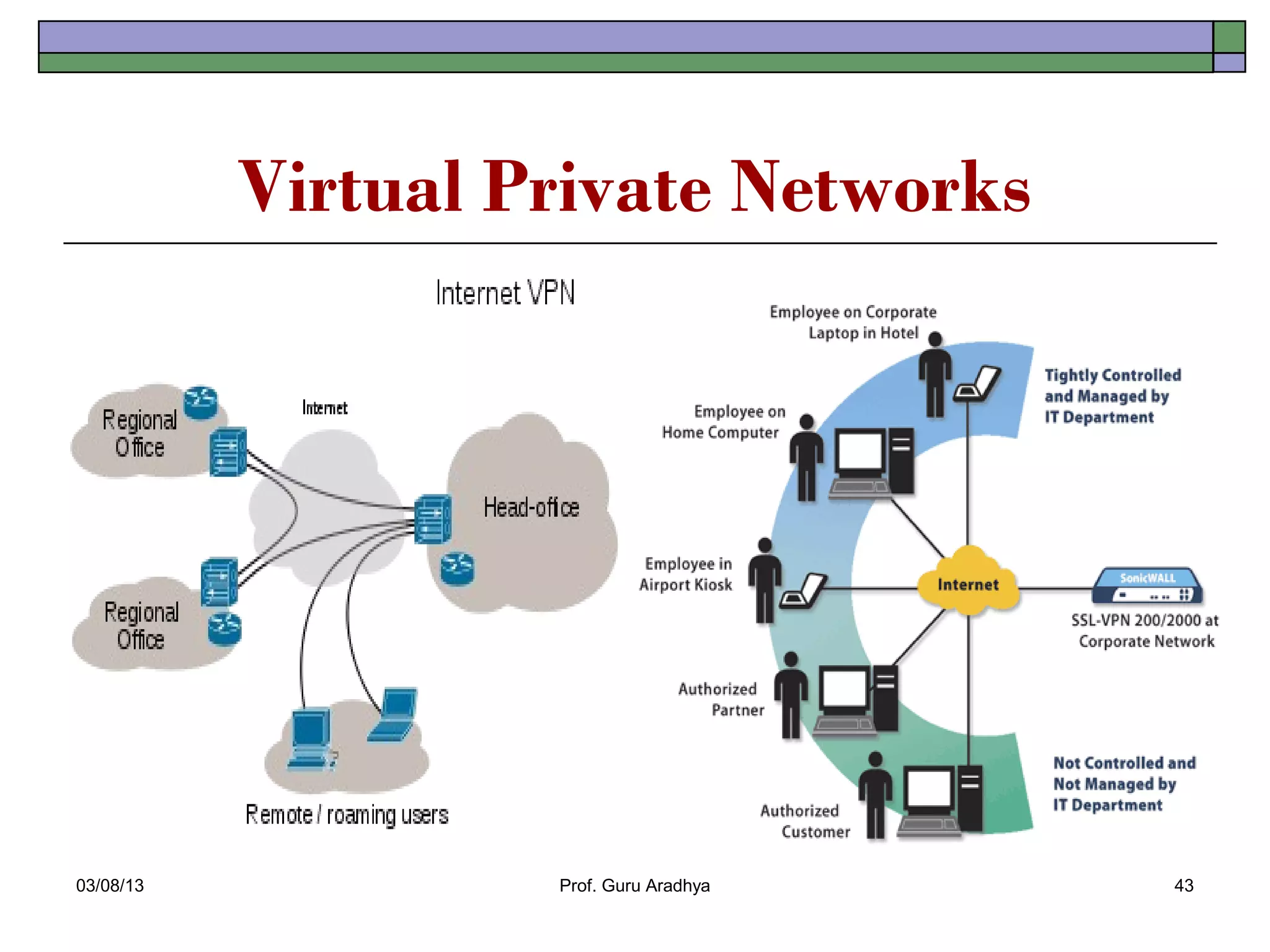
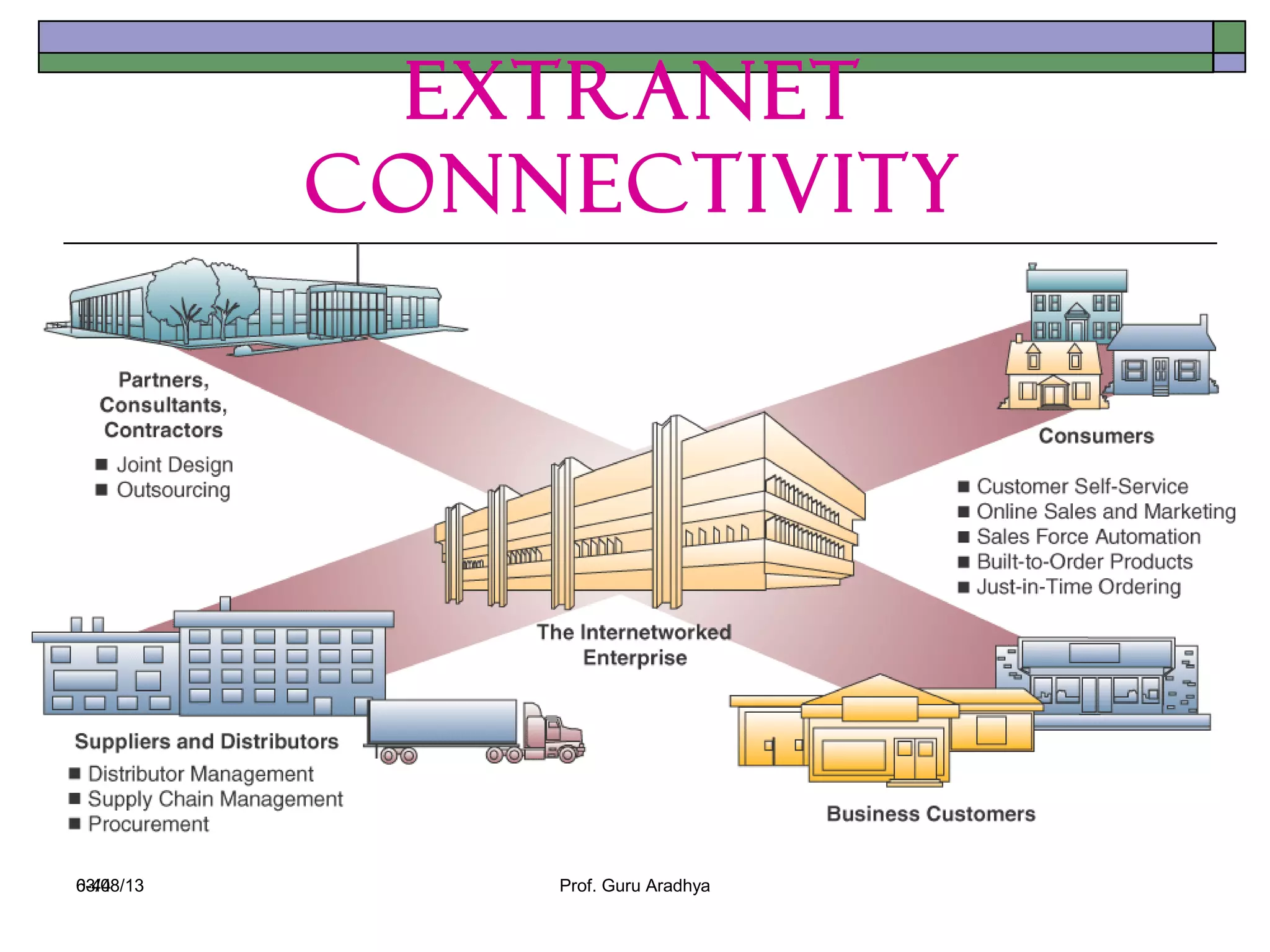
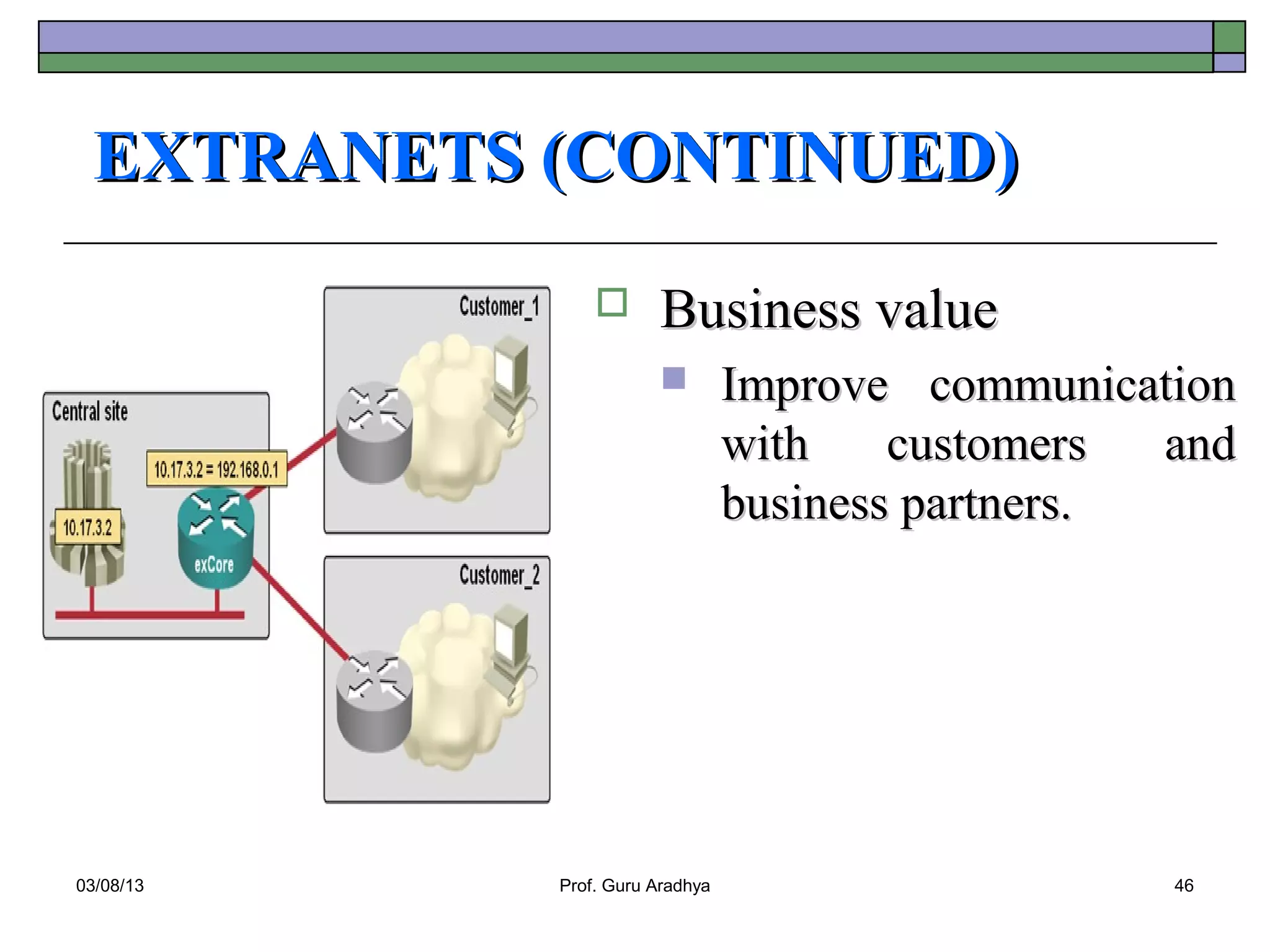
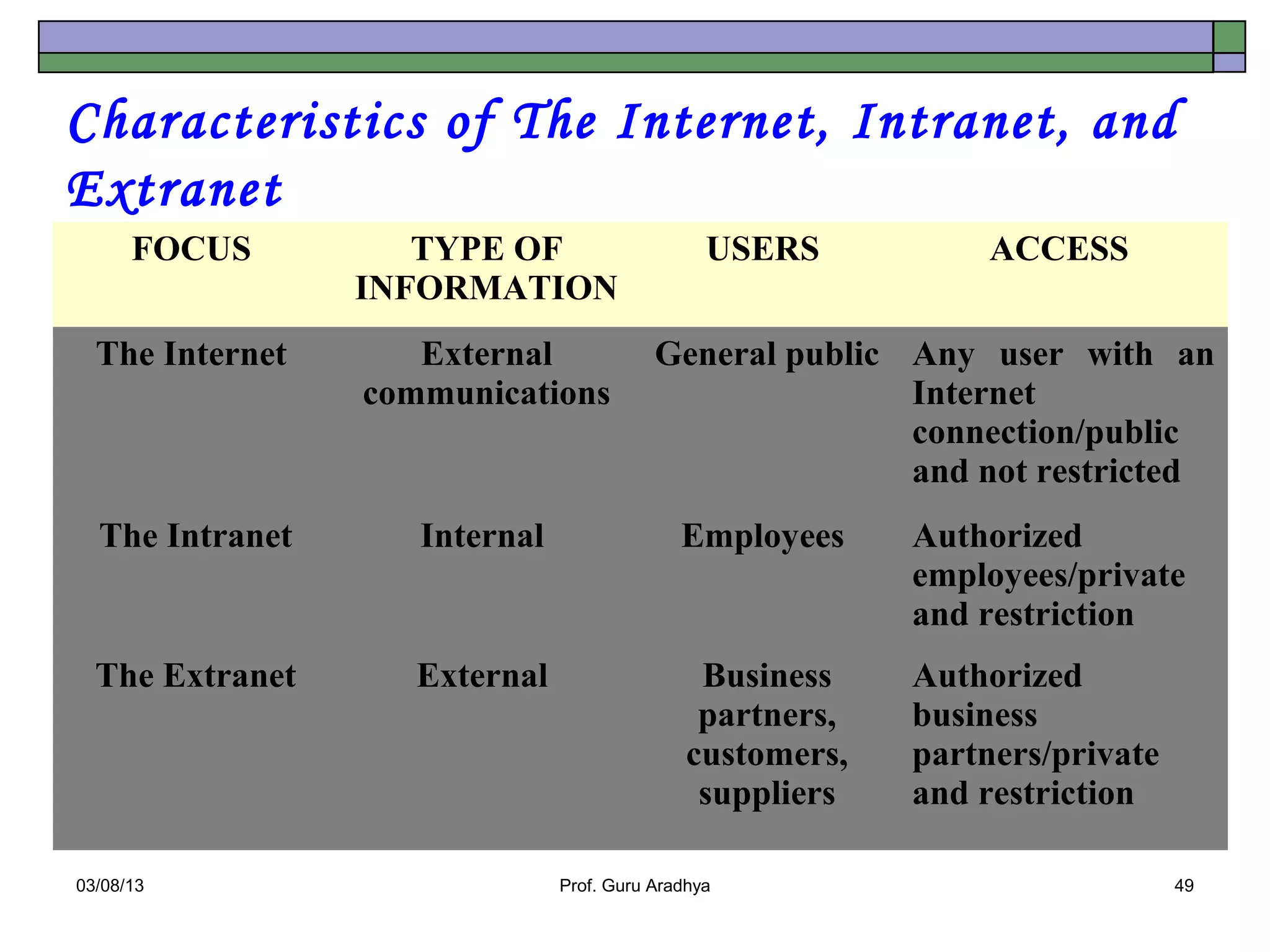
The document discusses the history and evolution of telecommunication networks and the Internet. It describes how the Internet has grown from a few servers in 1991 to over 46 million today. It also outlines several popular Internet applications like email, browsing the World Wide Web, and various online communication tools. Finally, it discusses the business value of networks like the Internet, intranets, and extranets in enabling communication, collaboration and sharing information.