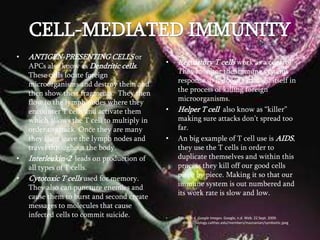
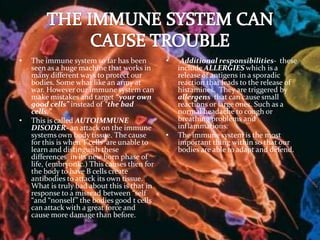
The immune system has two main types of defenses - nonspecific defenses that provide immediate protection and specific defenses that provide long-lasting protection. Nonspecific defenses include phagocytes that destroy foreign particles and an inflammatory response that isolates infections. Specific defenses involve lymphocytes that recognize specific pathogens and produce targeted responses like antibodies or cytotoxic T cells. While the immune system protects the body, it can sometimes mistakenly attack the body's own tissues, causing autoimmune disorders.