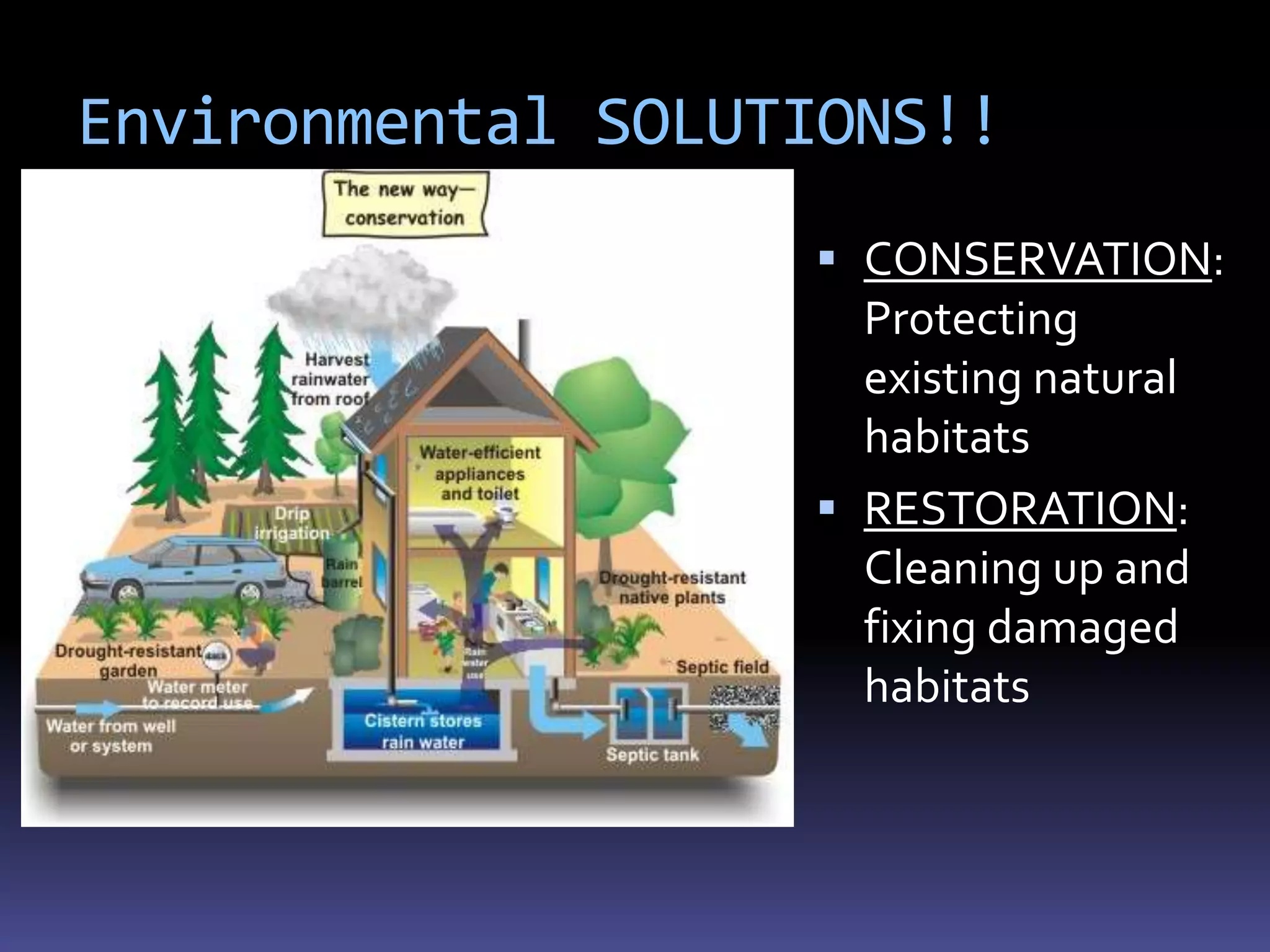
The document discusses how humans impact the environment and various environmental issues. It notes that as the human population has increased from 10 million to over 6 billion in 10,000 years, our impact on the environment has also increased. Some key environmental issues discussed include air and water pollution, global warming, soil damage, and ecosystem disruption which can harm biodiversity. Solutions mentioned are conservation efforts to protect habitats and restoration to repair damaged areas.