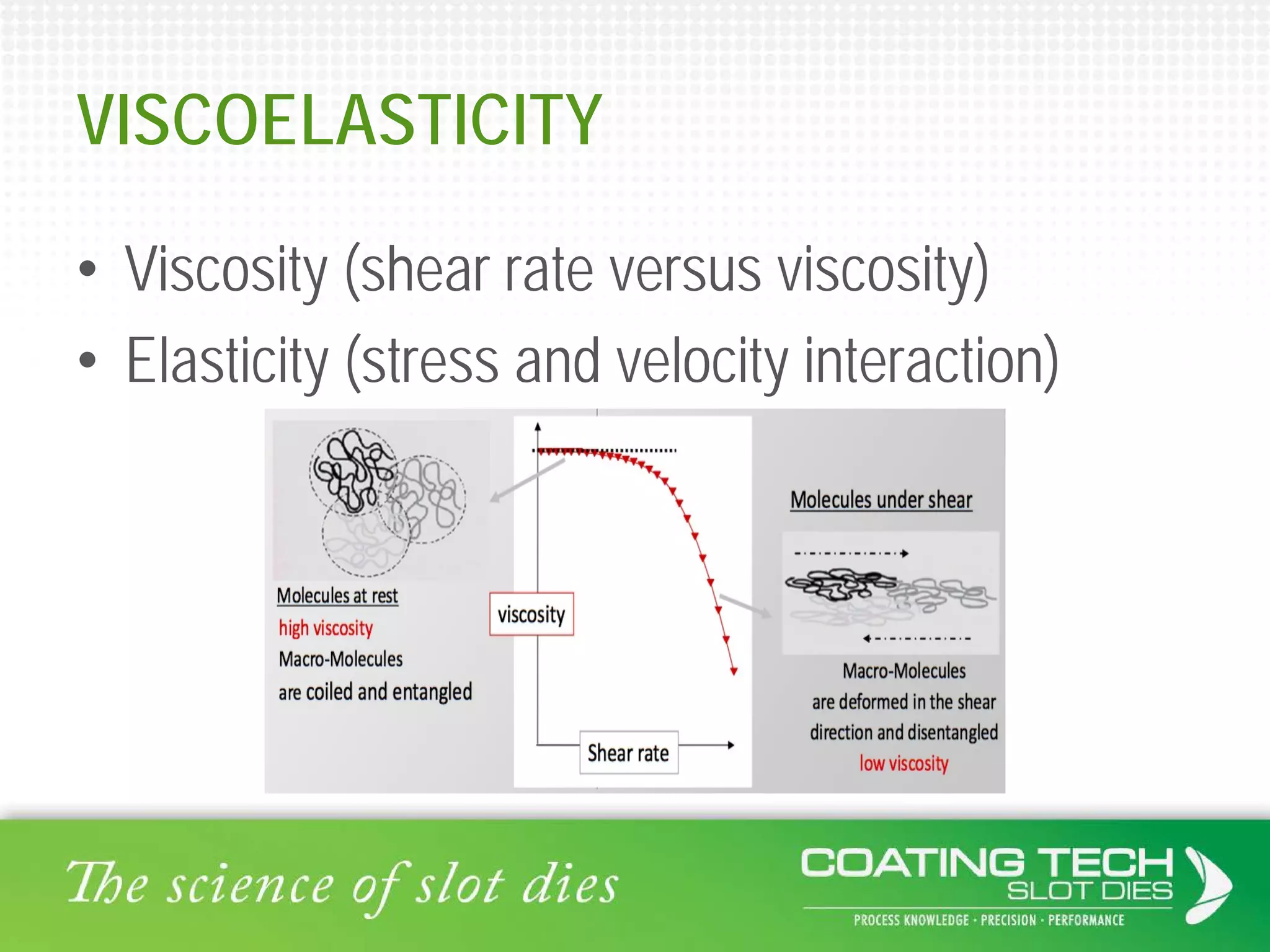
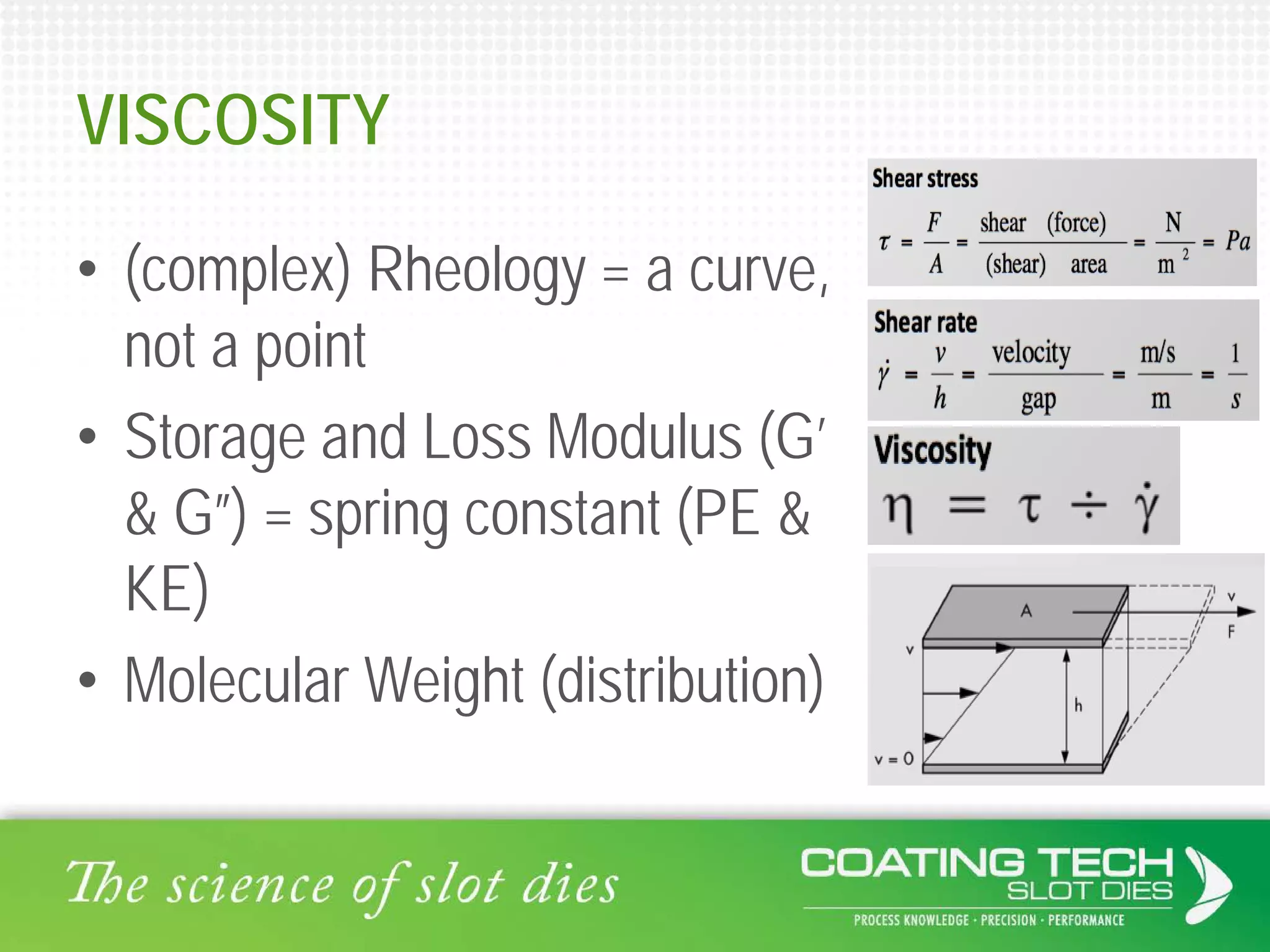
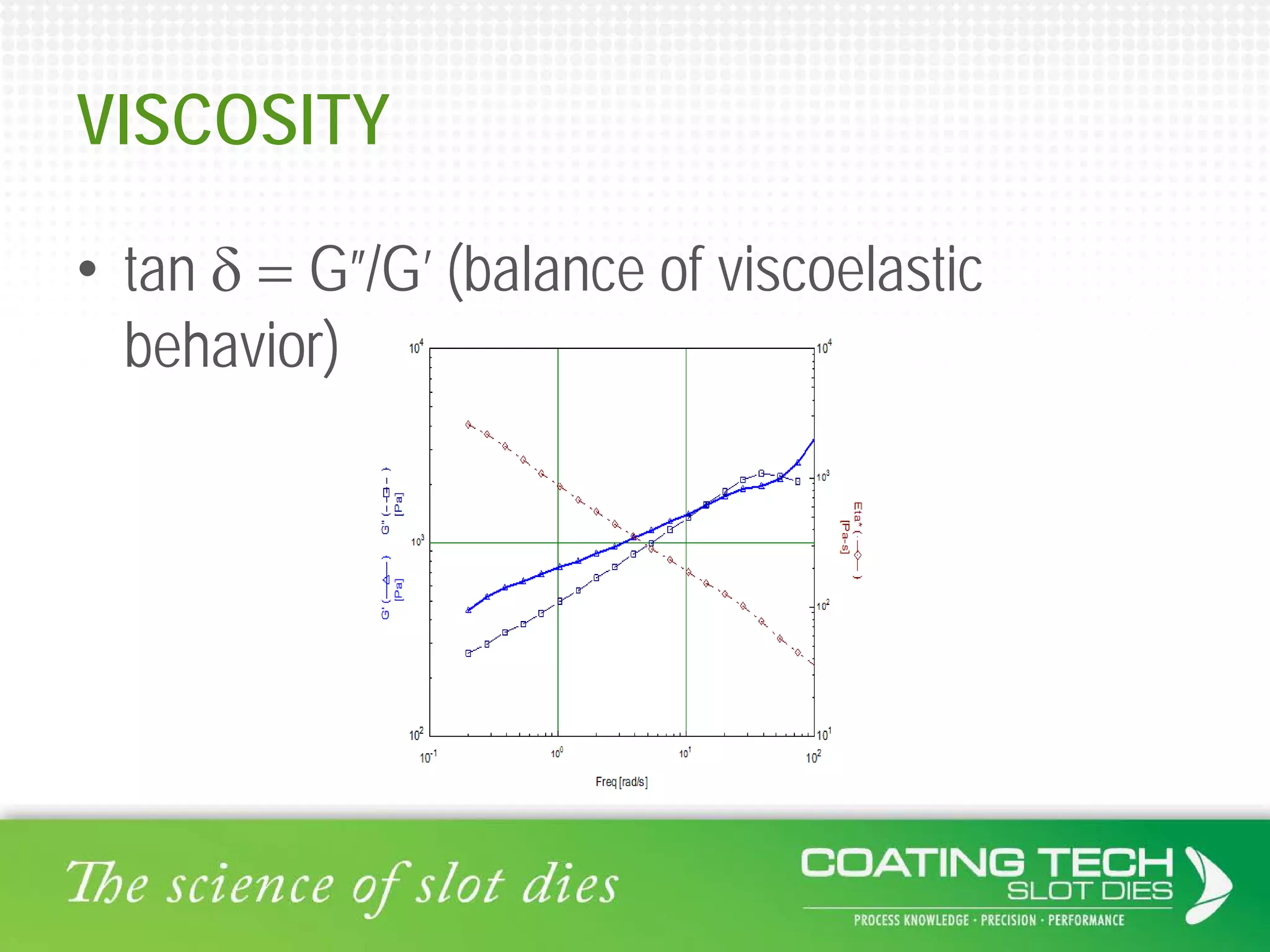
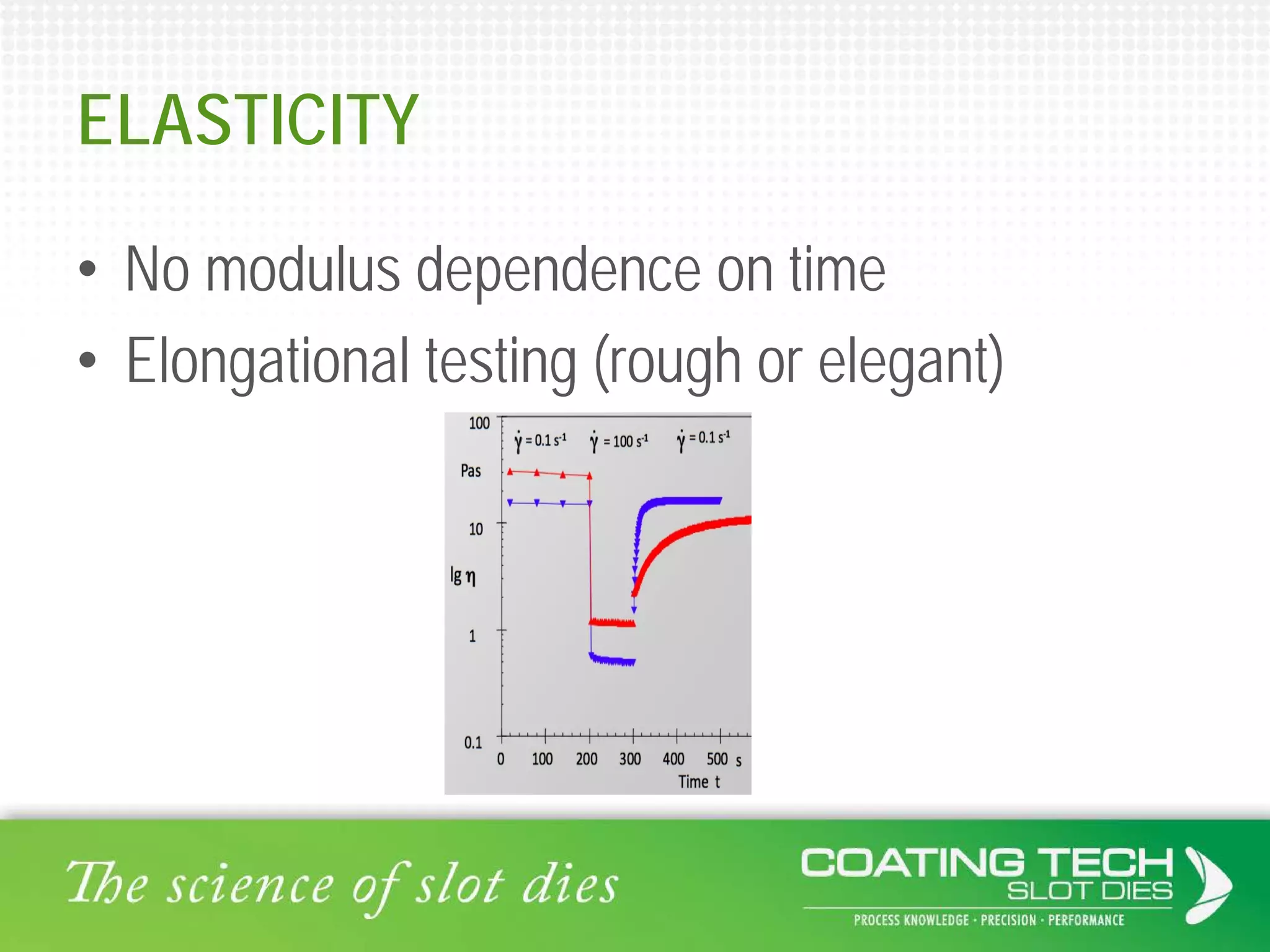
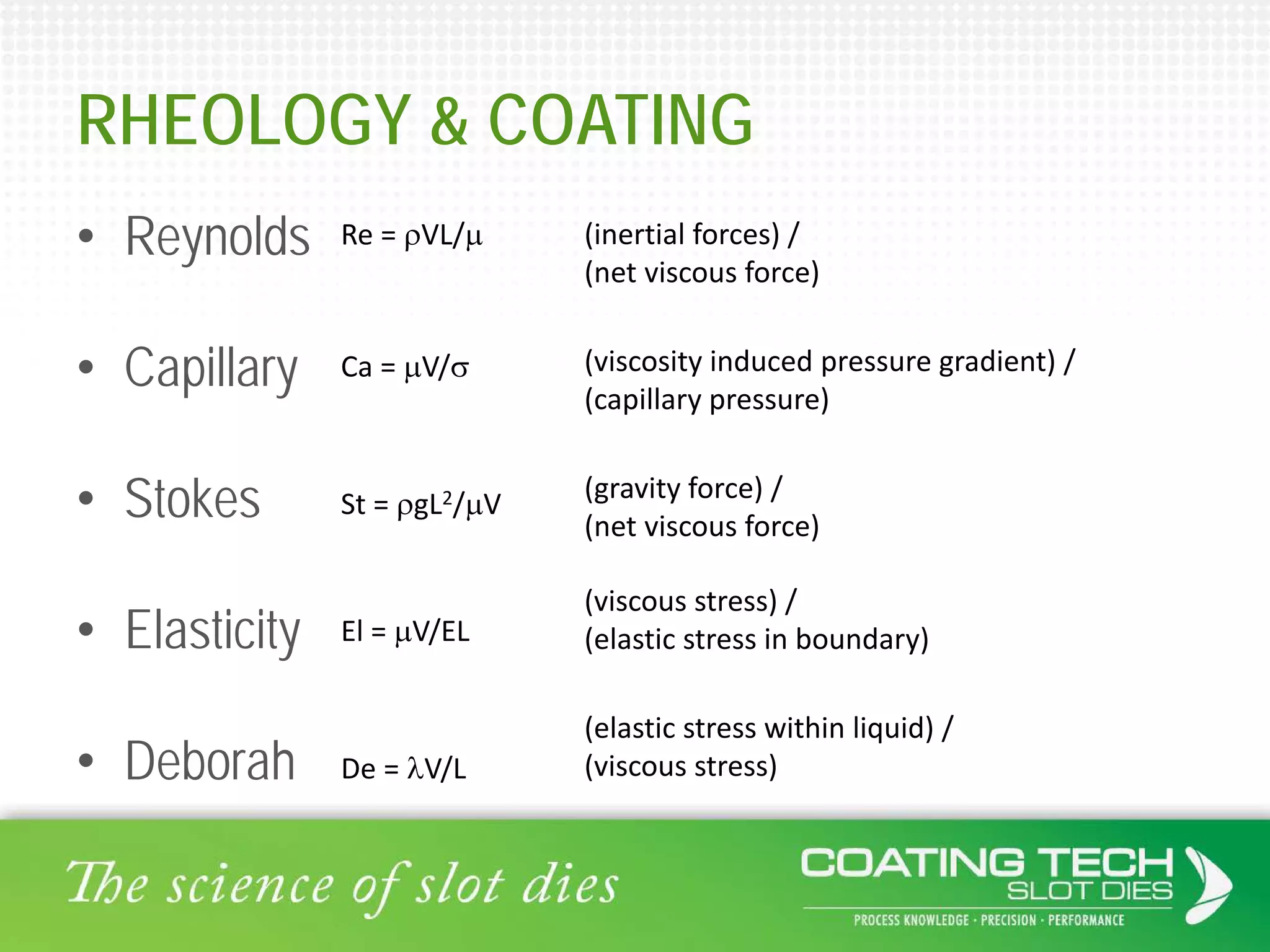
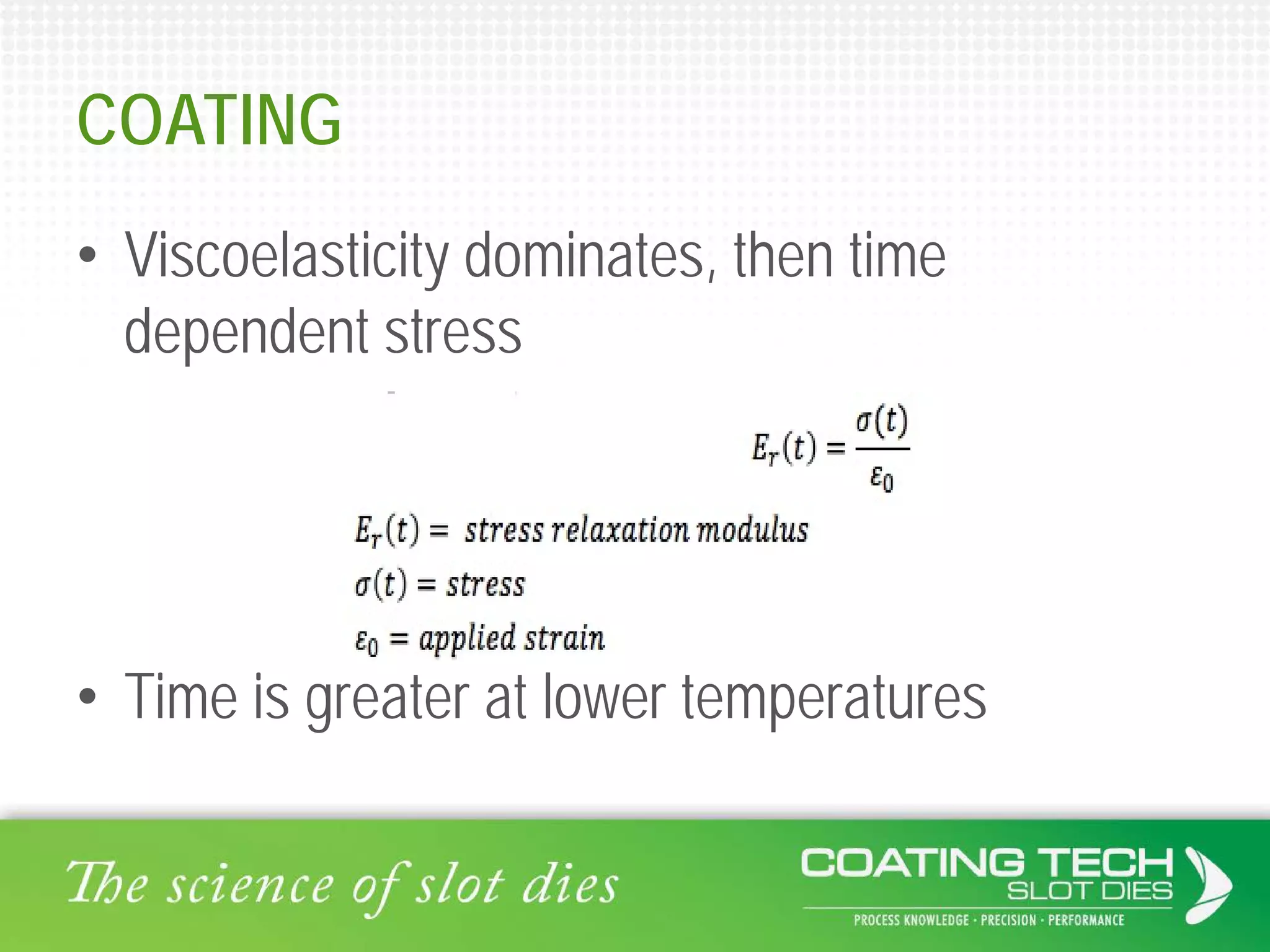
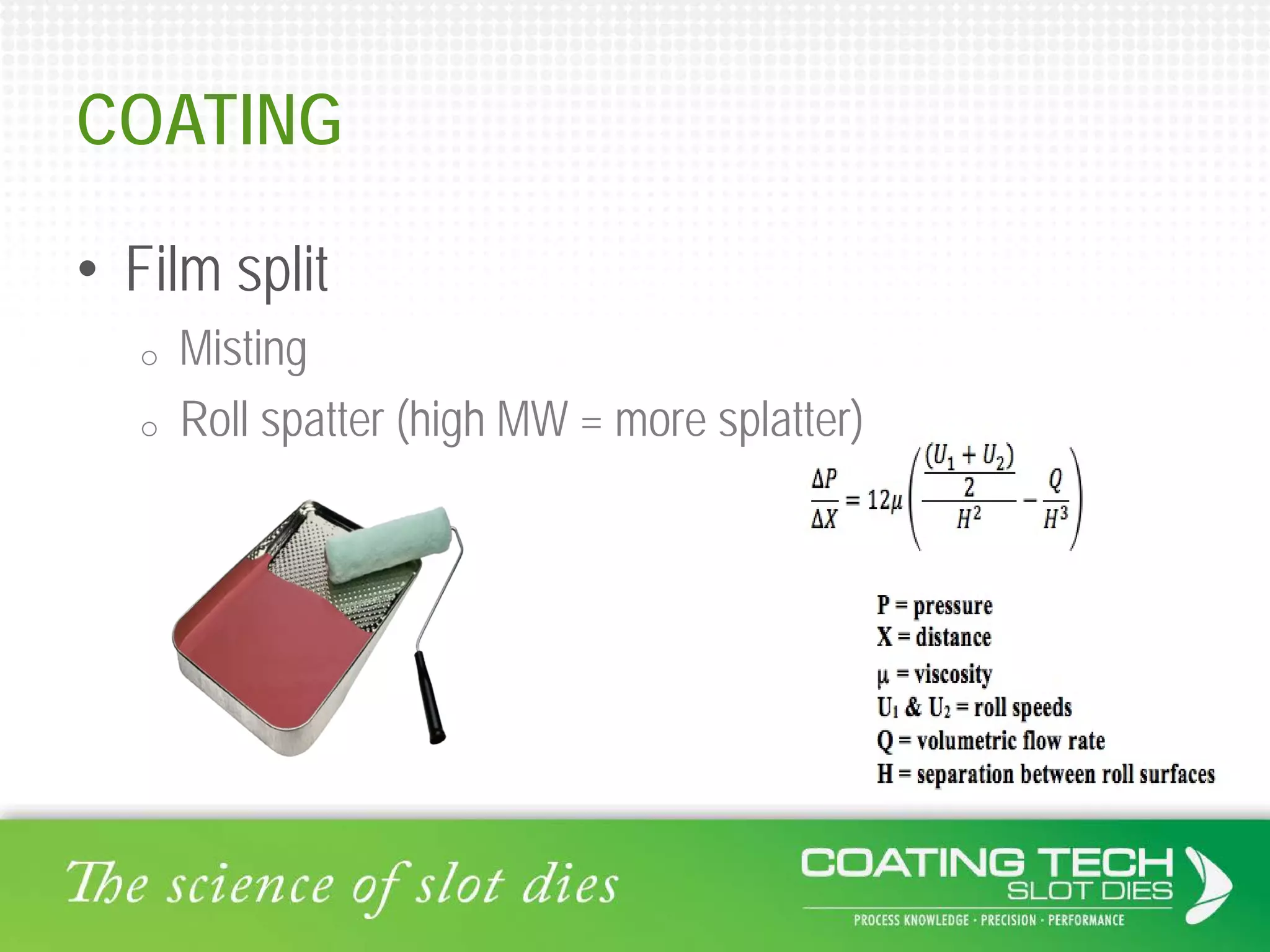
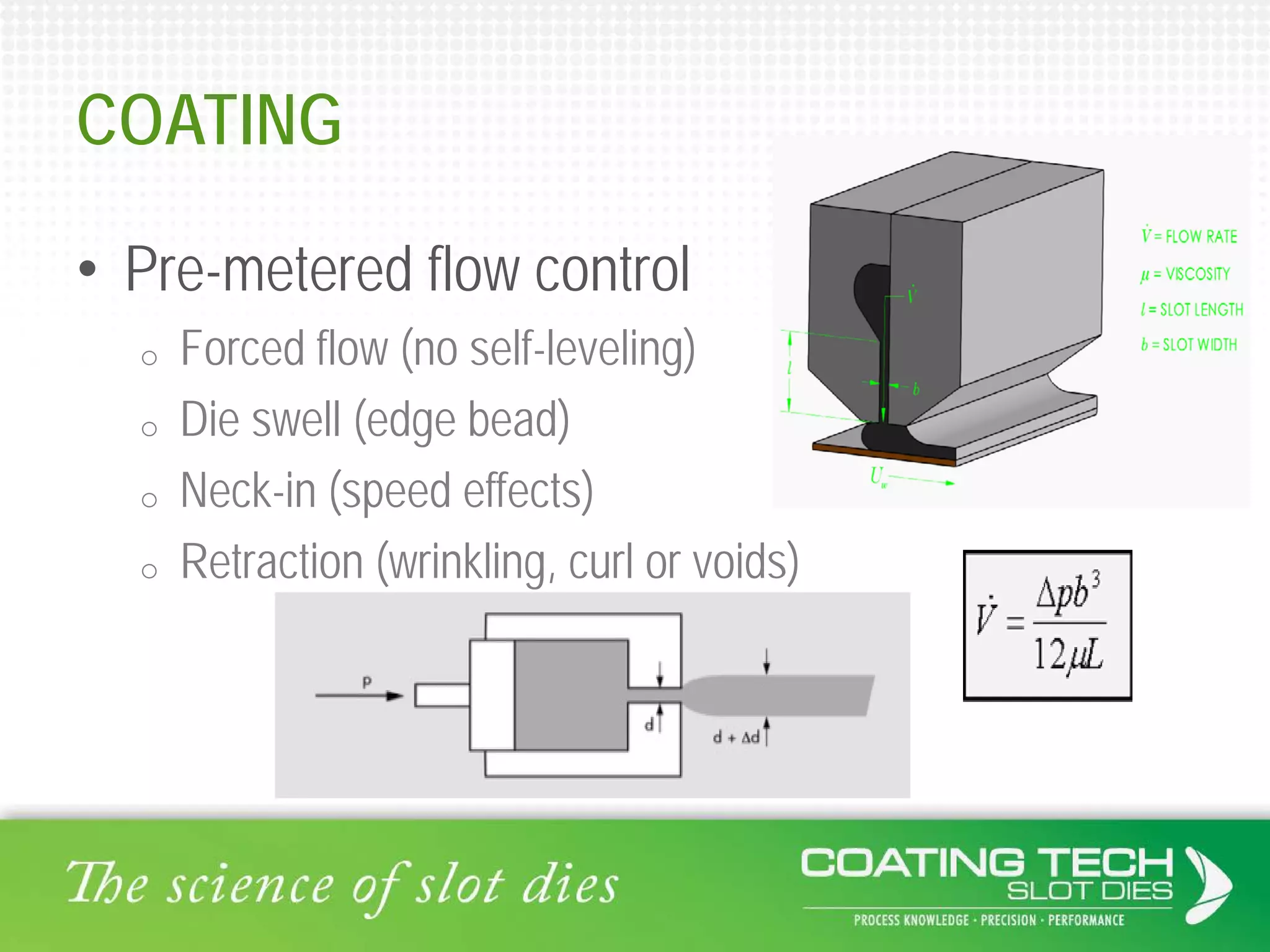
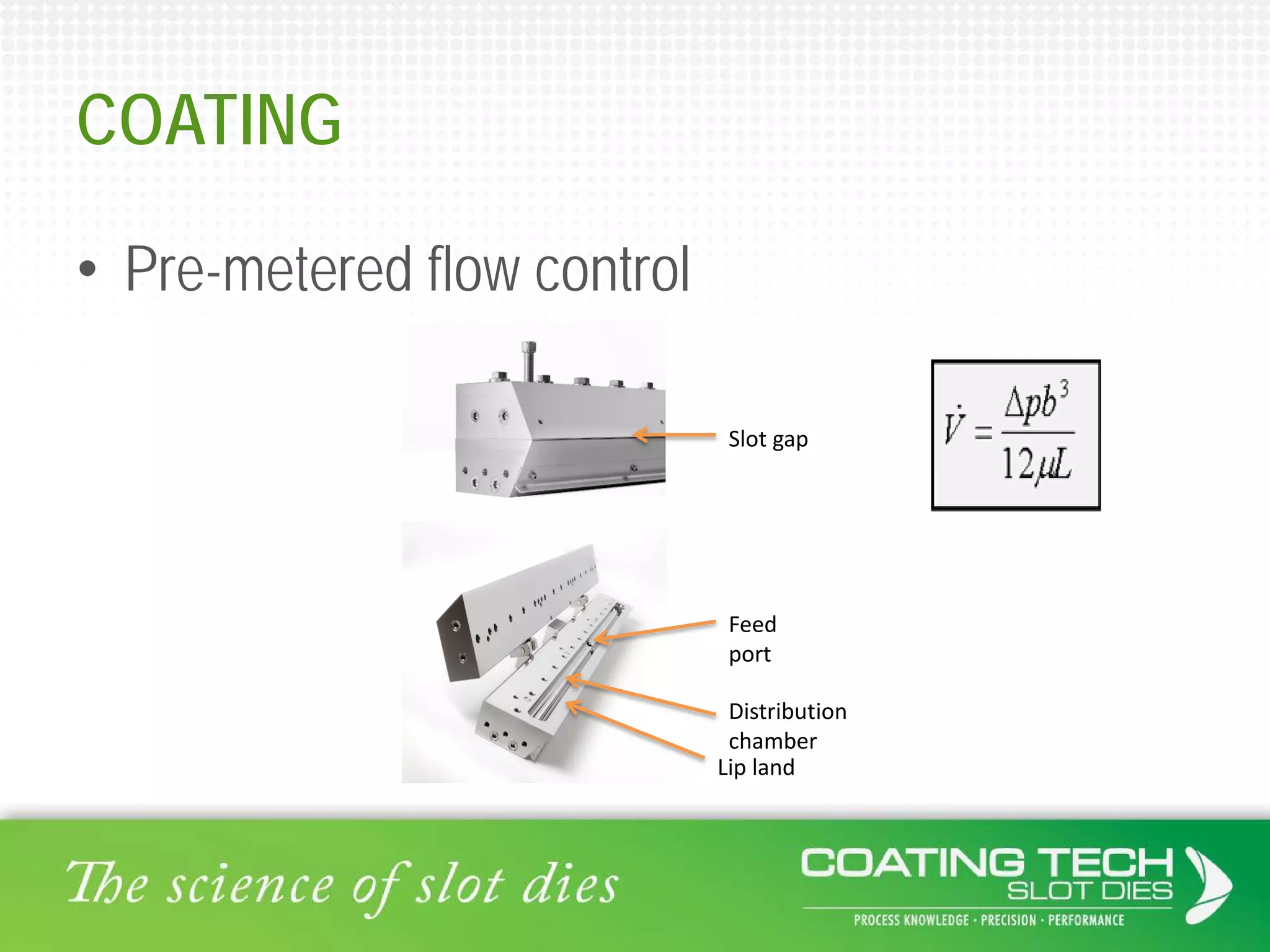
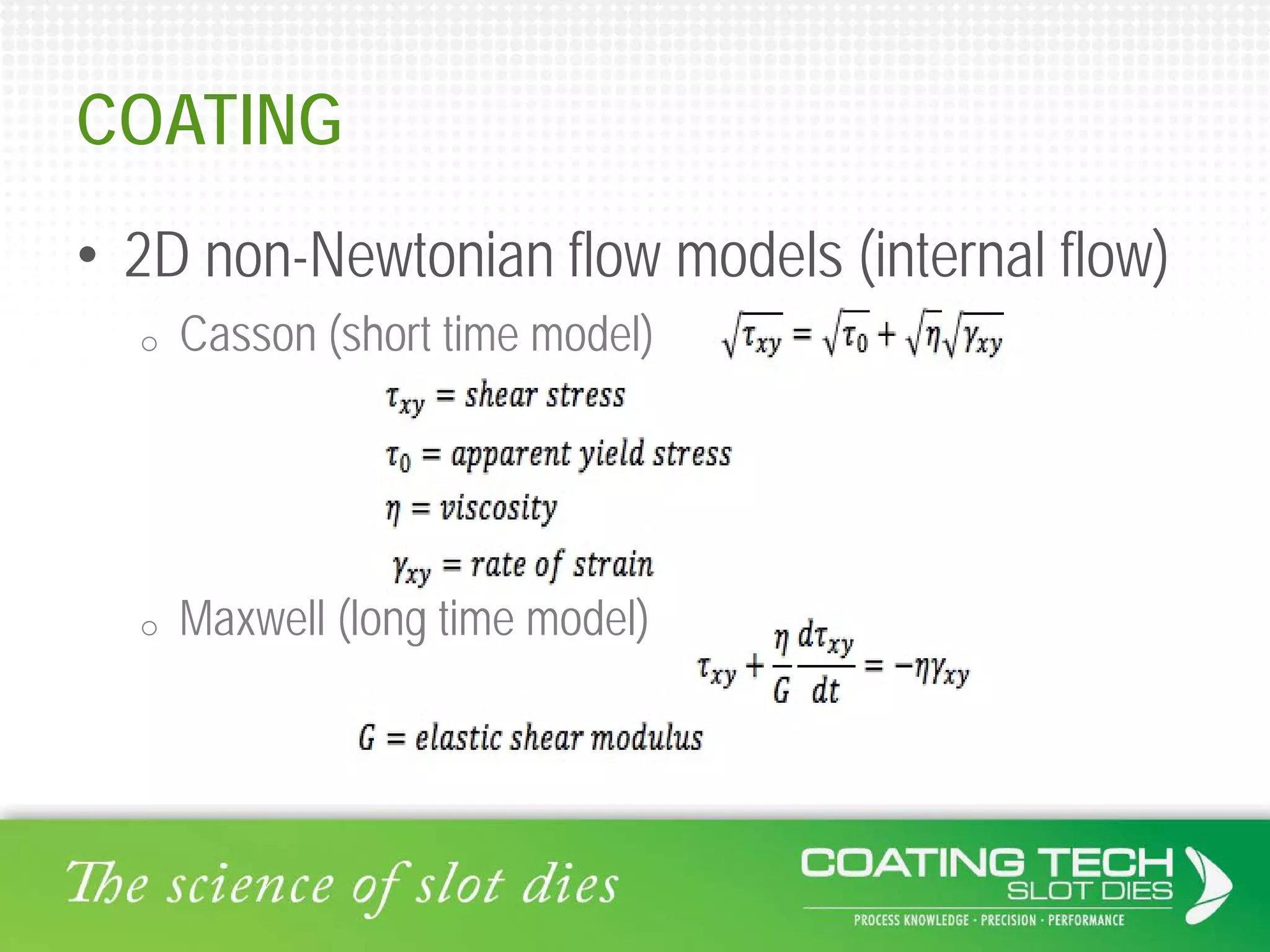
The document discusses the complex viscoelastic behavior affecting coating properties, including viscosity, elasticity, and their time-dependent nature. It emphasizes the significance of various models and conditions that impact coating defects and solutions to mitigate issues like ribbing and voids. Ultimately, it concludes that understanding viscoelasticity is crucial for optimizing coating processes.