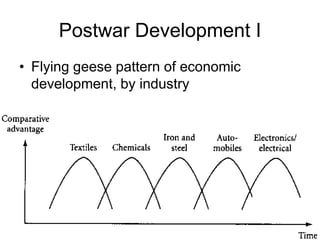
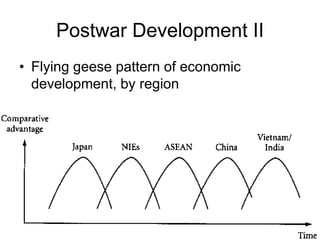
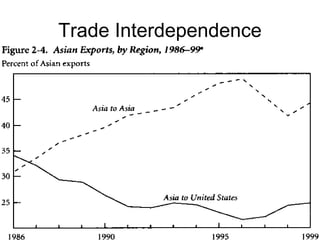
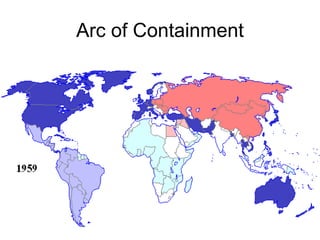
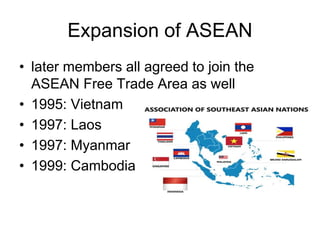
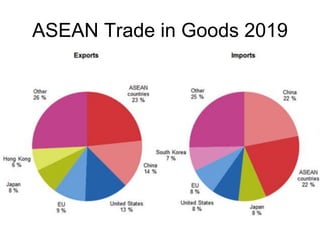
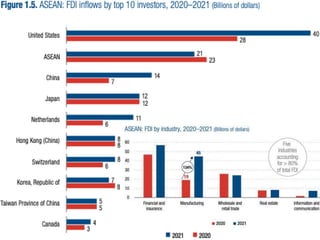
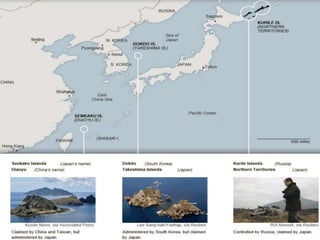
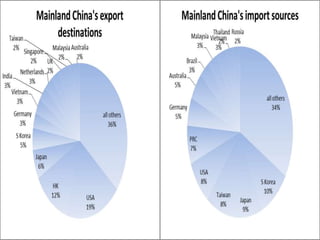
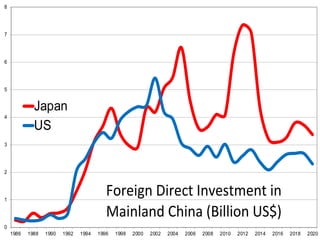
This document discusses Asian regionalism, focusing on ASEAN and Northeast Asia. It provides an overview of ASEAN, including its founding, expansion, and key economic agreements. ASEAN has 10 member states and over $3 trillion in collective GDP. The document also examines Northeast Asia, covering the political difficulties in the region due to histories of war and disputes. However, countries like China, Japan, and South Korea now have significant economic interdependence, with China and Japan being each other's top trade partners importing over $100 billion from each other annually.