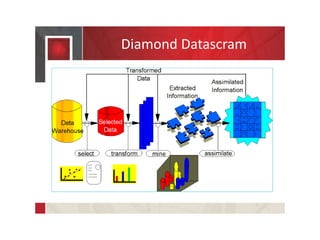
The document discusses the launch of Diamond Datascram, a software solution designed to identify and manage dark and redundant data for businesses. It also outlines various privacy issues related to technology companies, cybersecurity strategies, intellectual property protections, and employment agreements. Additionally, it emphasizes the importance of compliance with regulatory standards and effective human resources policies.