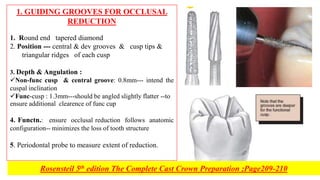
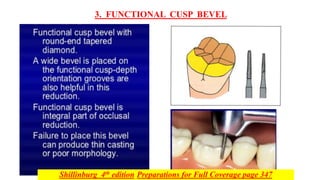
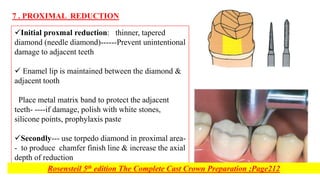
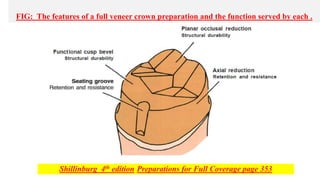
This document discusses full coverage crown preparations. It begins by explaining the advantages of full coverage crowns over partial coverage, as supported by laboratory studies. Contraindications and indications for full coverage crowns are then outlined. The main advantages are strength, retention, and ability to modify form and occlusion, while the main disadvantages are removal of large amounts of tooth structure and potential adverse effects. Special considerations for bevels and chamfer width are described to prevent thin castings and conserve tooth structure. The preparation technique is then explained in detail through multiple steps including occlusal and axial reduction, finishing, and additional retentive features. Evaluation of the preparation is important to detect and correct any errors that could compromise retention.