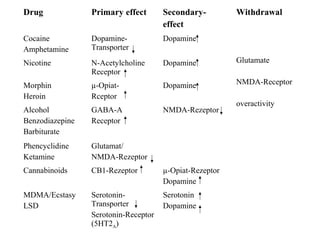
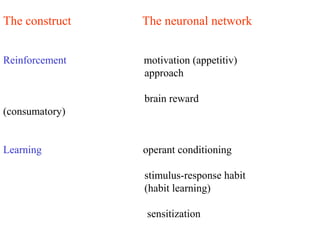
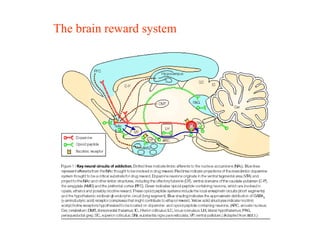
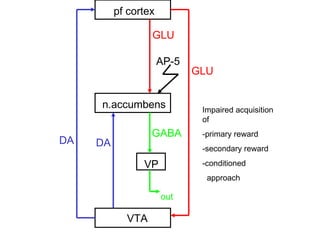
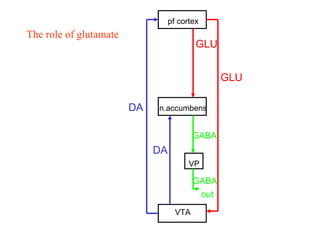
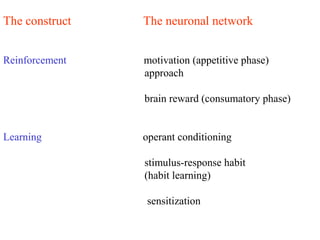
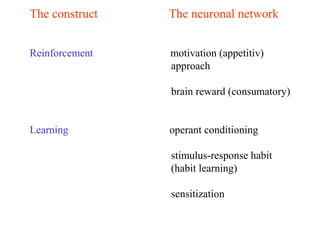
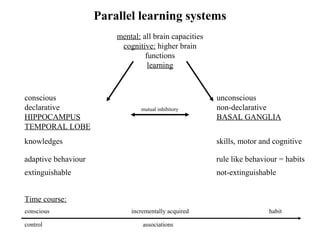
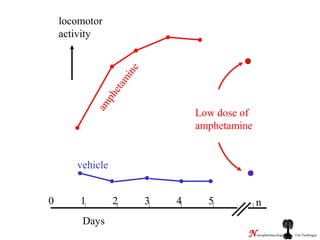
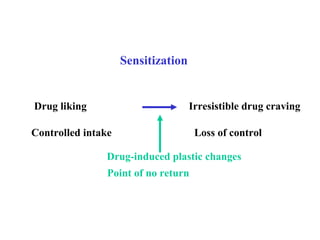
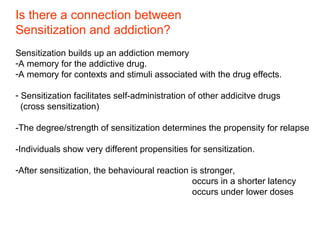
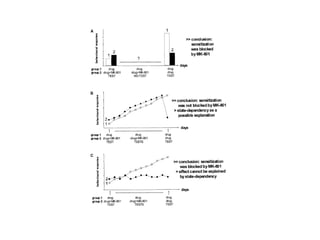
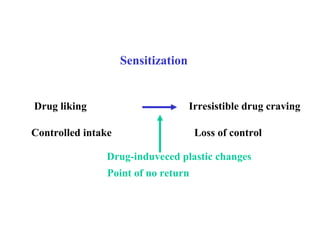
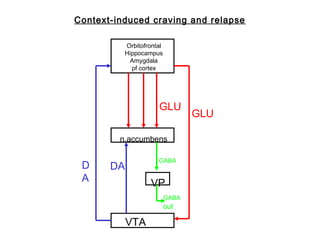
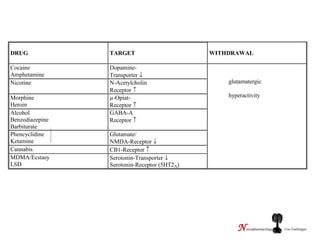
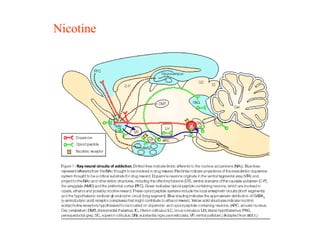
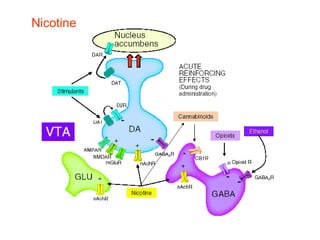
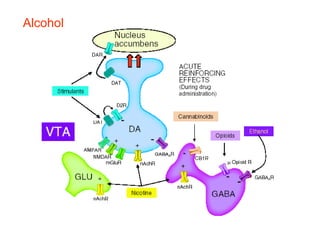
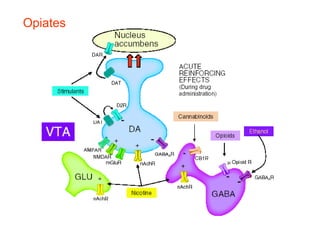
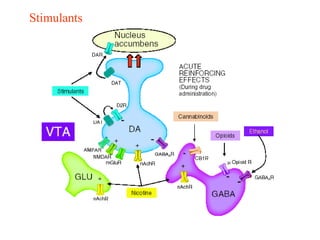
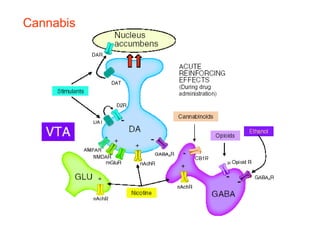
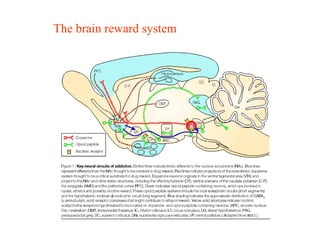
The brain reward system is activated by natural rewards to meet biological needs, but is also activated by addictive drugs even when no needs are present. Chronic drug use causes plastic changes in the brain that contribute to addiction. Glutamate signaling plays a key role in addiction learning and craving. Future anti-craving therapies aim to target drug-induced changes in neuronal networks specific to each addiction, moving toward individualized treatment approaches.