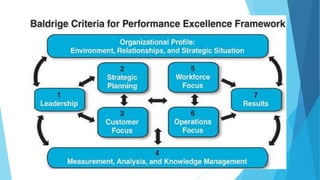
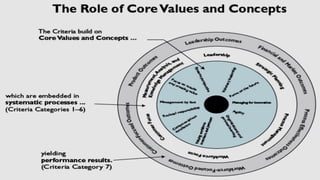
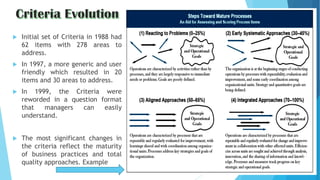
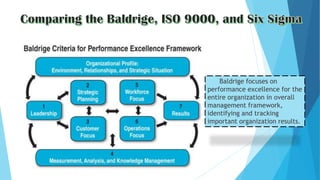
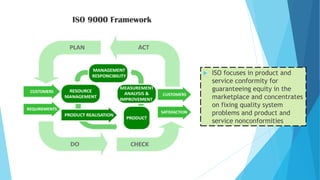
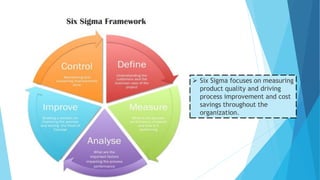
The document discusses the history and framework of the Malcolm Baldrige National Quality Award. It began in the 1980s in response to declining US productivity. The award recognizes organizational excellence and provides criteria for organizations to evaluate themselves. There are 7 criteria categories covering leadership, strategic planning, customer focus, and results. The application process is rigorous, involving multiple levels of review. Award winners are seen as models of innovation, leadership, and performance excellence. The Baldrige framework has influenced quality awards in other countries and raised global competitiveness.