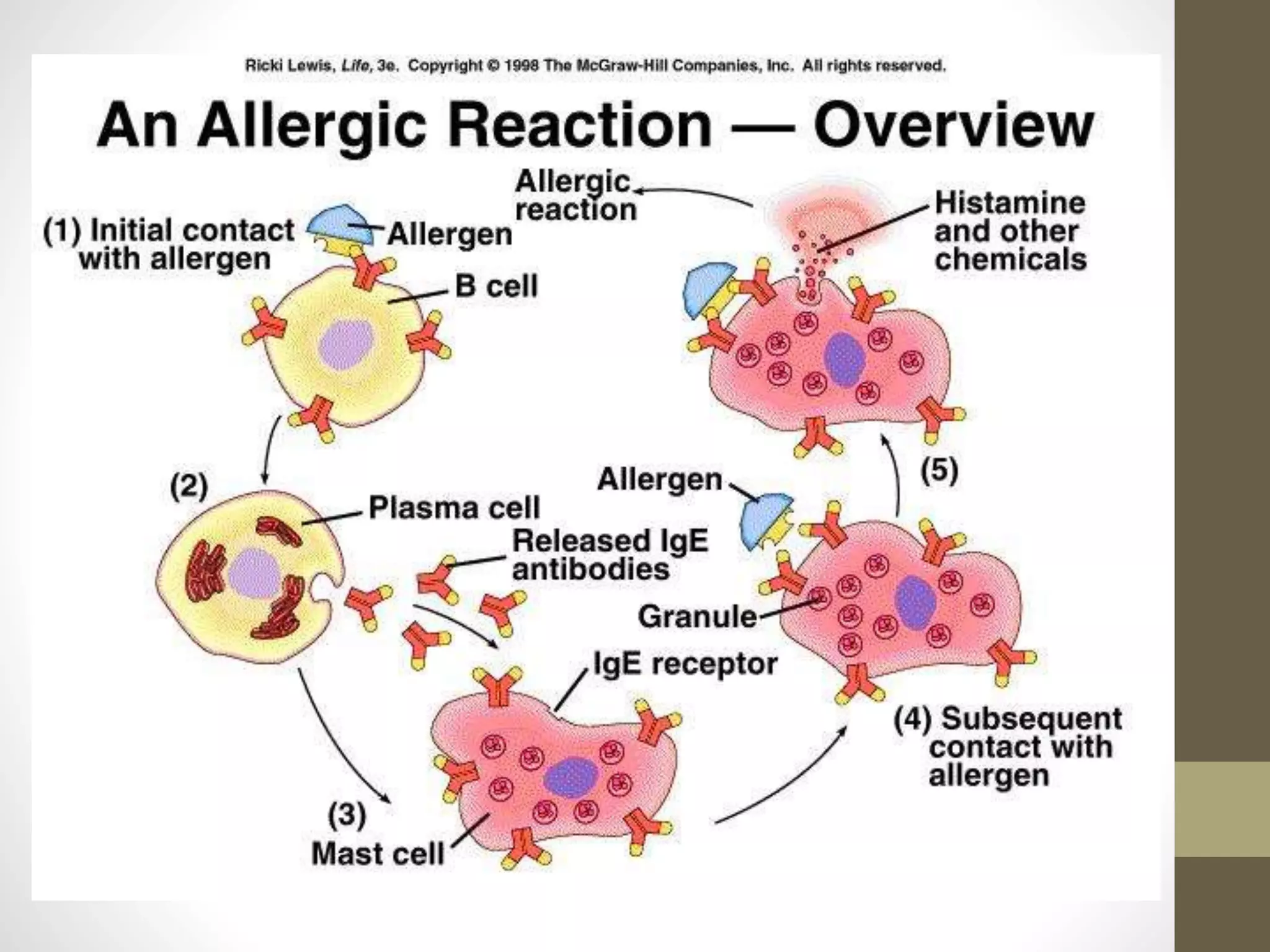
An allergic reaction to food occurs in two steps. The first exposure causes the immune system to produce IgE antibodies specific to the allergen. These attach to mast cells. The next exposure triggers the mast cells to release chemicals like histamine, causing symptoms ranging from mild to potentially life-threatening anaphylaxis. Common food allergies include eggs, milk, and wheat, which can cause symptoms like hives, vomiting, diarrhea and more. Management requires strict avoidance of the allergen and use of epinephrine for severe reactions. Cross-reactive allergies may also occur between similar foods like shellfish.