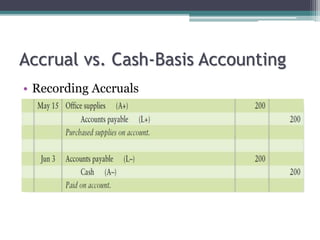
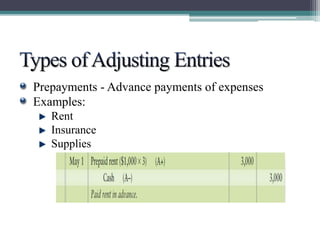
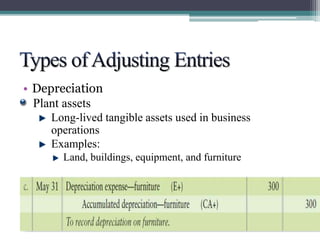
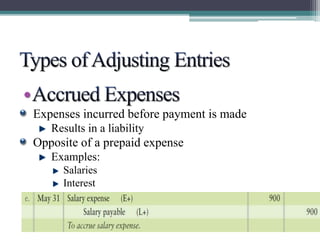
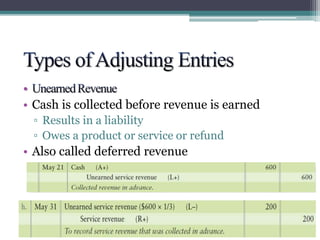
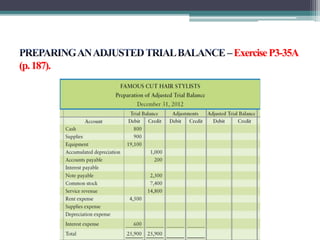
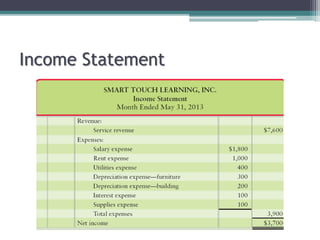
This document discusses the differences between cash basis and accrual basis accounting. Cash basis accounting records revenue when cash is received and expenses when cash is paid, while accrual basis accounting records revenue when it is earned and expenses when they are incurred. Accrual basis accounting is required under GAAP and is generally used by larger businesses. The document also discusses key accrual accounting concepts like recording accruals, the accounting period, when to record revenue and expenses, and preparing adjusting entries and an adjusted trial balance.