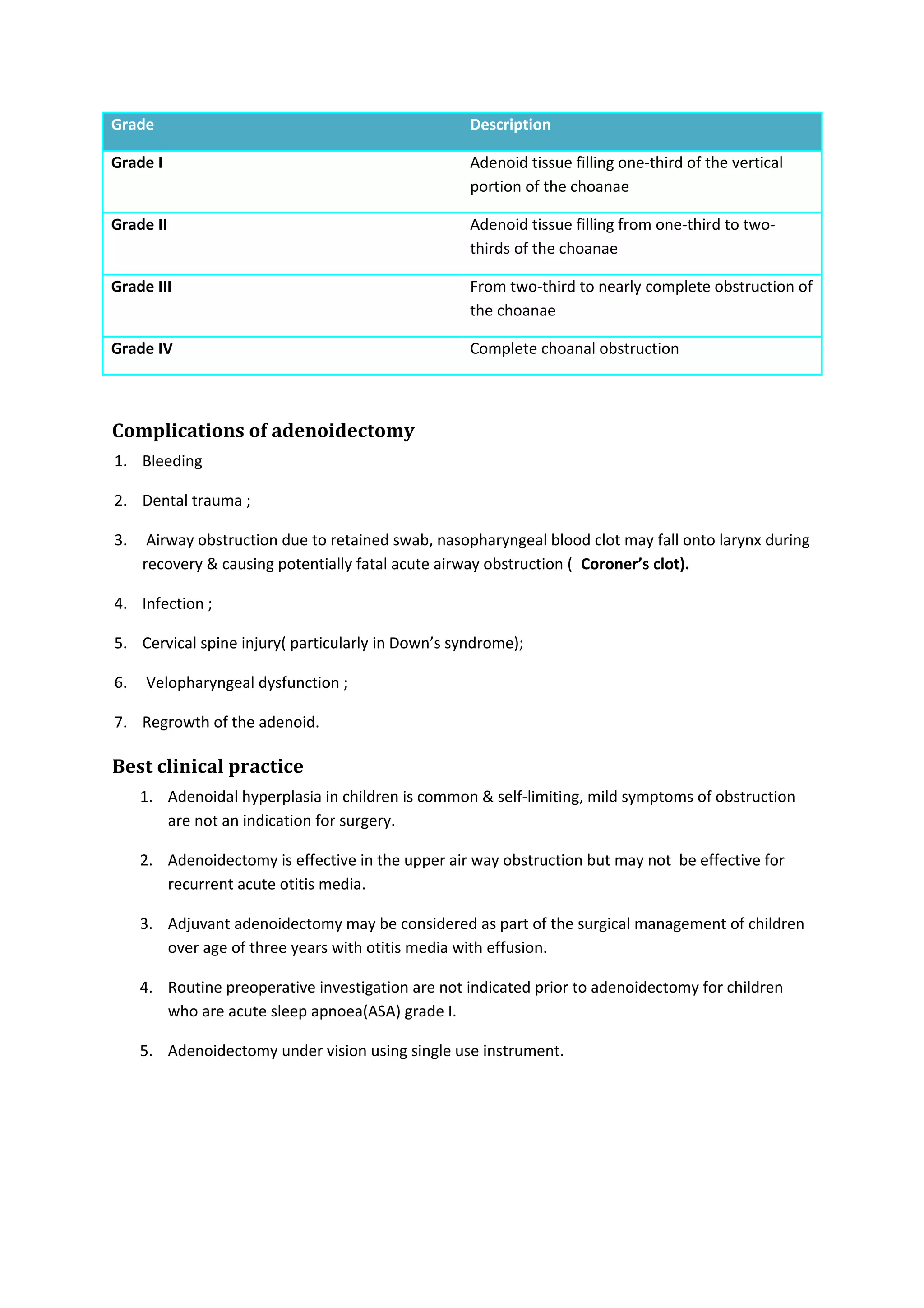
The document discusses the adenoid and adenoidectomy procedure. It covers the anatomy and function of the adenoid, including its role in immunity. It describes pathological effects like otitis media, upper airway obstruction, and rhinosinusitis. The assessment, management, and complications of adenoidectomy are outlined. While adenoidectomy is effective for upper airway obstruction and otitis media with effusion, its efficacy for other issues like recurrent ear infections, sleep apnea, and sinusitis requires more research. Mild adenoid hypertrophy does not always require surgery.