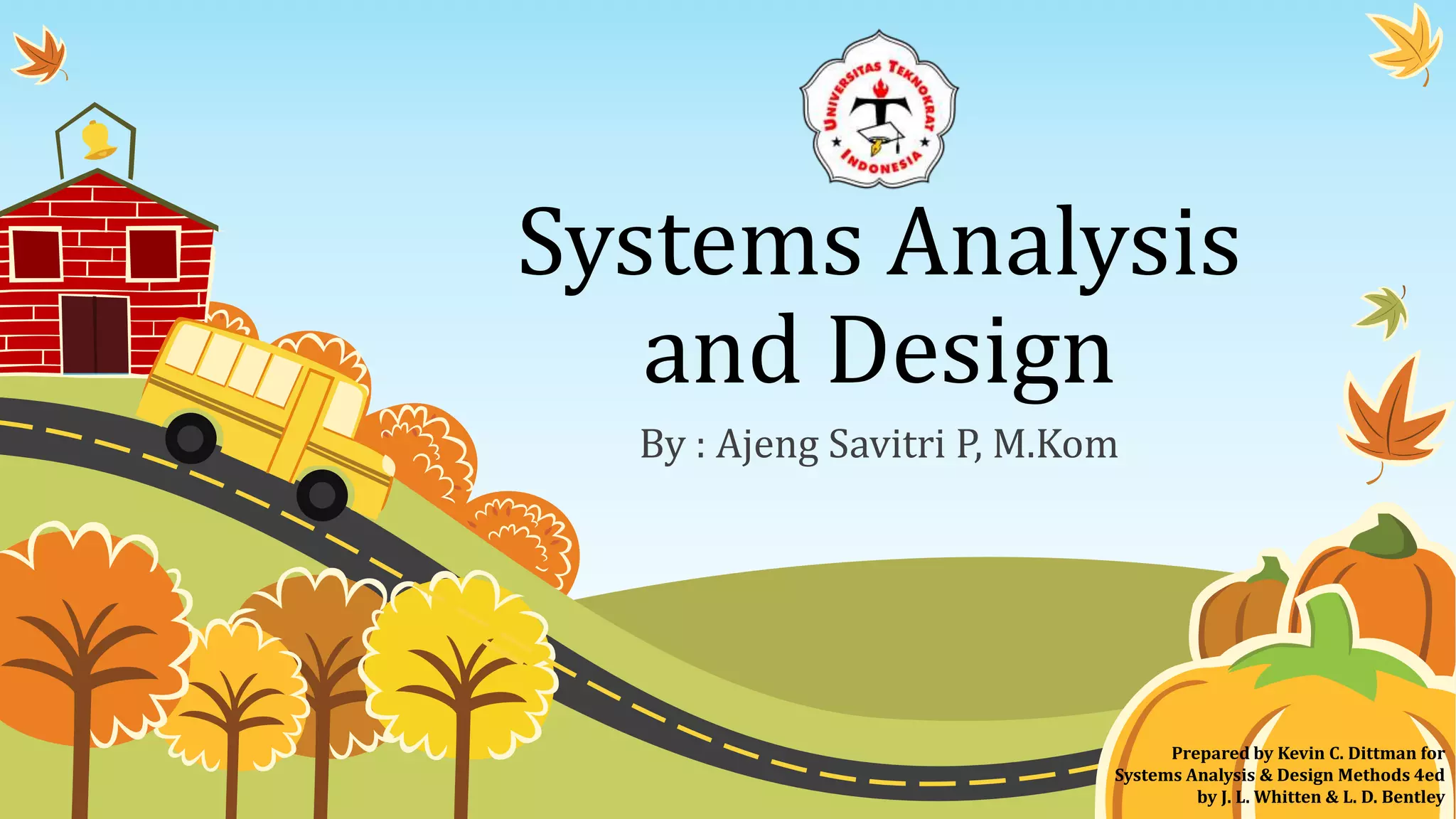
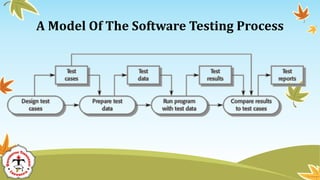
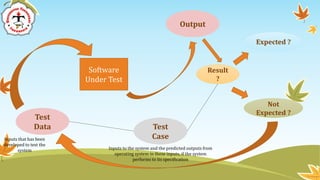
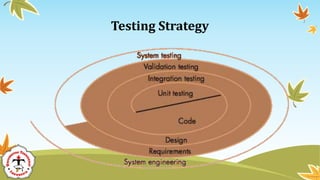
The document discusses software testing strategies and methods. It begins by defining software testing as executing a program with artificial data to check results for errors or anomalies. It then discusses testing goals of validating that software meets requirements and discovering defects. Different testing types are covered, including black box testing which focuses on functional requirements without viewing internal program structure. Specific black box techniques like equivalence partitioning, boundary value analysis, and robustness testing are described. The document emphasizes planning a thorough testing strategy to improve software quality.