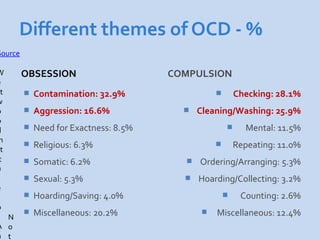
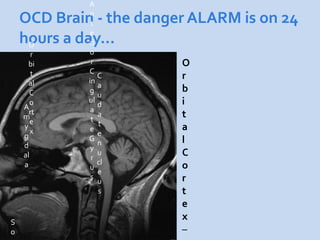
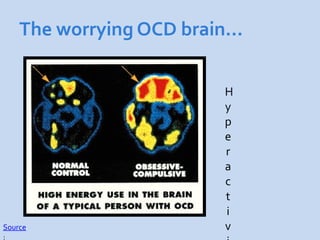
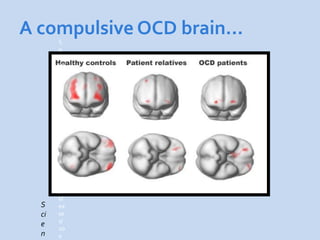
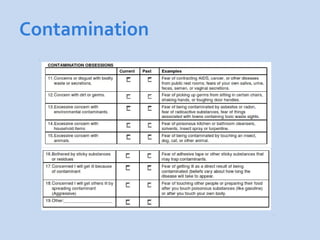
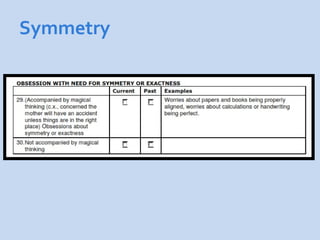
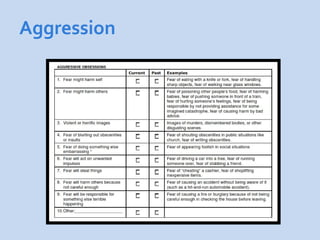
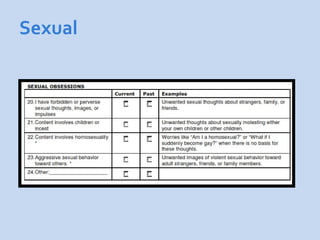
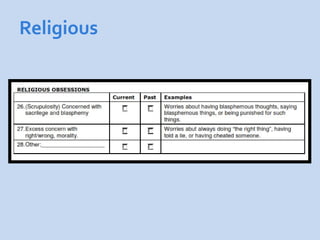
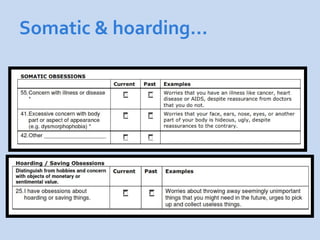
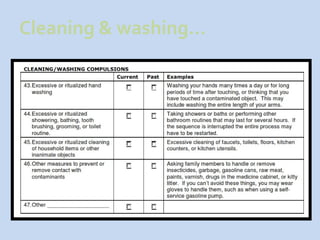
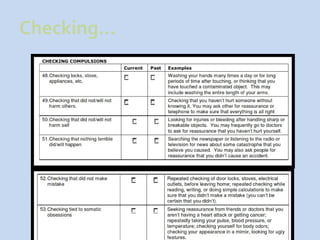
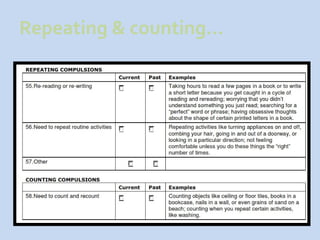
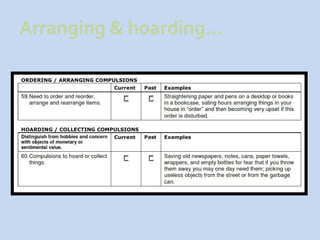
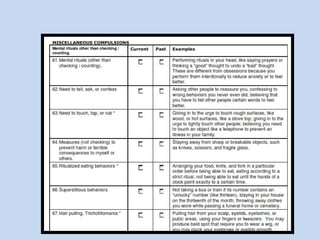
This document is a presentation about obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD) given by Dr. Phang Cheng Kar. It defines OCD as having distressing, repetitive obsessions and compulsions to neutralize them. Common obsessions include contamination, aggression, and symmetry, while common compulsions are cleaning, checking, and repeating rituals. The causes of OCD may include genetics, brain chemistry imbalances, and stress. Treatments discussed are medication like SSRIs and psychological therapies using exposure, mindfulness, and challenging irrational thoughts.