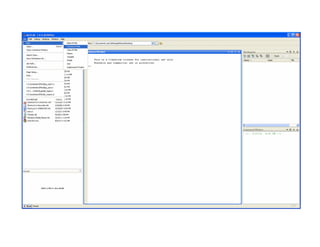
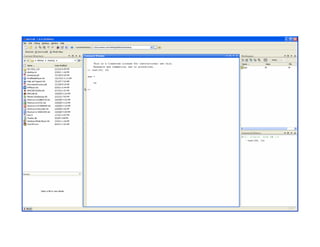
Computer vision involves acquiring, processing, analyzing and understanding images and video to extract numerical or symbolic information. It has applications in industrial inspection, medical imaging, surveillance, and more. It is related to fields like image processing, pattern recognition and computer graphics. MATLAB is a common platform used for computer vision development, allowing image processing, algorithms, and structured programming.











![array
• a collection of values represented by one
variable name
• one-dimensional array – vector
• two-dimensional array – matrix
>> a = [1 2 3 4 5]
a=
1 2 3 4 5 Row vector
>>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/test1552-120328124626-phpapp02/85/Test-12-320.jpg)
![>> a = [1;2;3;4;5] >> a = [1 2 3 4 5]'
a= a=
1 1 Use single quote
2 2 as transpose
3 3 operator
4 4
5 5
>> >>
Column vector](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/test1552-120328124626-phpapp02/85/Test-13-320.jpg)
![>> A = [1 2 3; 4 5 6; 7 8 9] >> A = [1 2 3
A= 456
1 2 3 7 8 9]
4 5 6 A=
7 8 9 1 2 3
>> 4 5 6
7 8 9
>>
Press Enter key
to separate the rows](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/test1552-120328124626-phpapp02/85/Test-14-320.jpg)