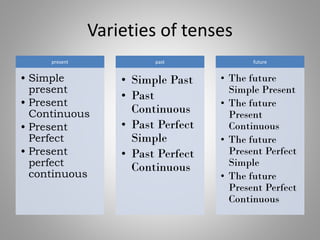
This document provides an overview of tense in English grammar, emphasizing its role in indicating the time of actions or states as expressed by verbs. It categorizes verbs into types, including regular and irregular verbs, and includes examples of auxiliary verbs. Additionally, various forms of tenses are outlined, including present, past, and future categories.