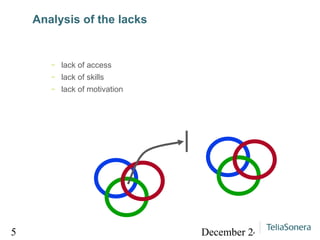
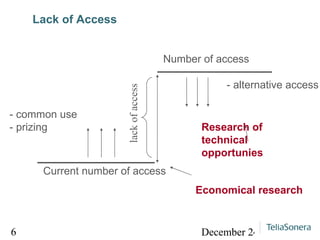
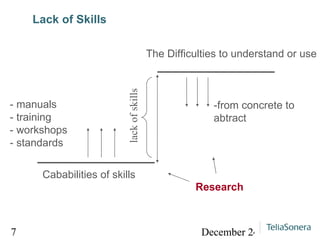
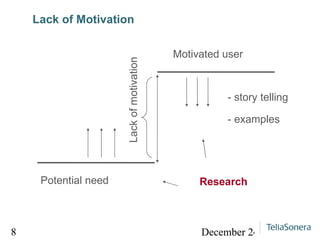
Digital balance refers to achieving balance between digital technology, the environment, and human society, while digital divide refers to the lack of balance between them. The document analyzes lacks of access, skills, and motivation that can lead to a digital divide. It suggests researching technical opportunities, skills capabilities, and motivating users to strengthen social relationships and achieve a digital balance where services are available and useful to all.