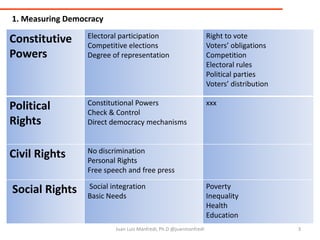
Dr. Juan Luis Manfredi Sánchez discusses measuring democracy and technology. He explains that information has become abundant due to digital technology, bringing benefits but also challenges. When measuring technology, indexes consider the information society, economic, and social dimensions. Key laws around the growth of processing power, bandwidth, and network value are described. Mixing democracy and technology requires considering infrastructure, costs, policy, education, innovation, and more. The digital divide refers to gaps between those who do and do not have access to technology, which can impact development and society.