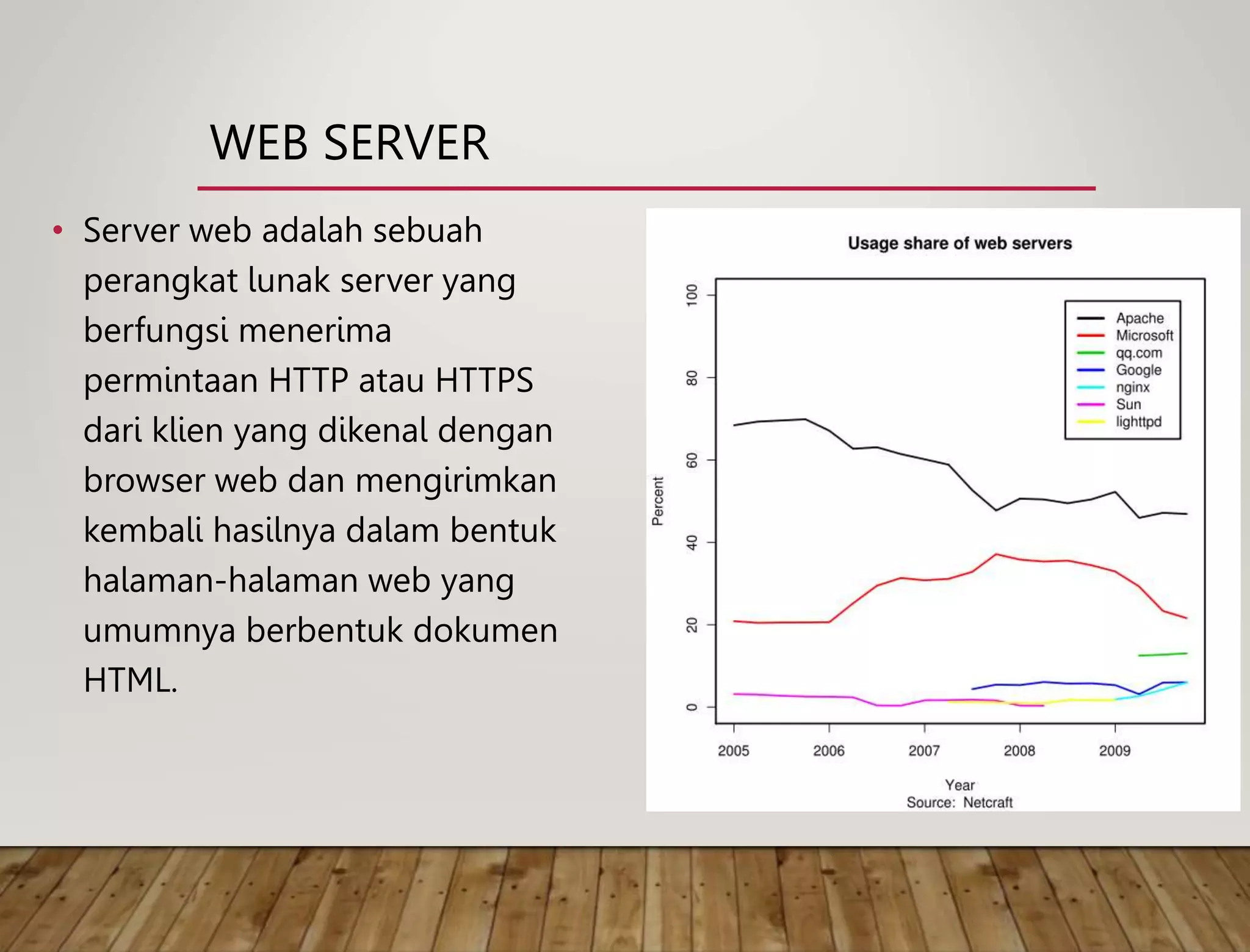
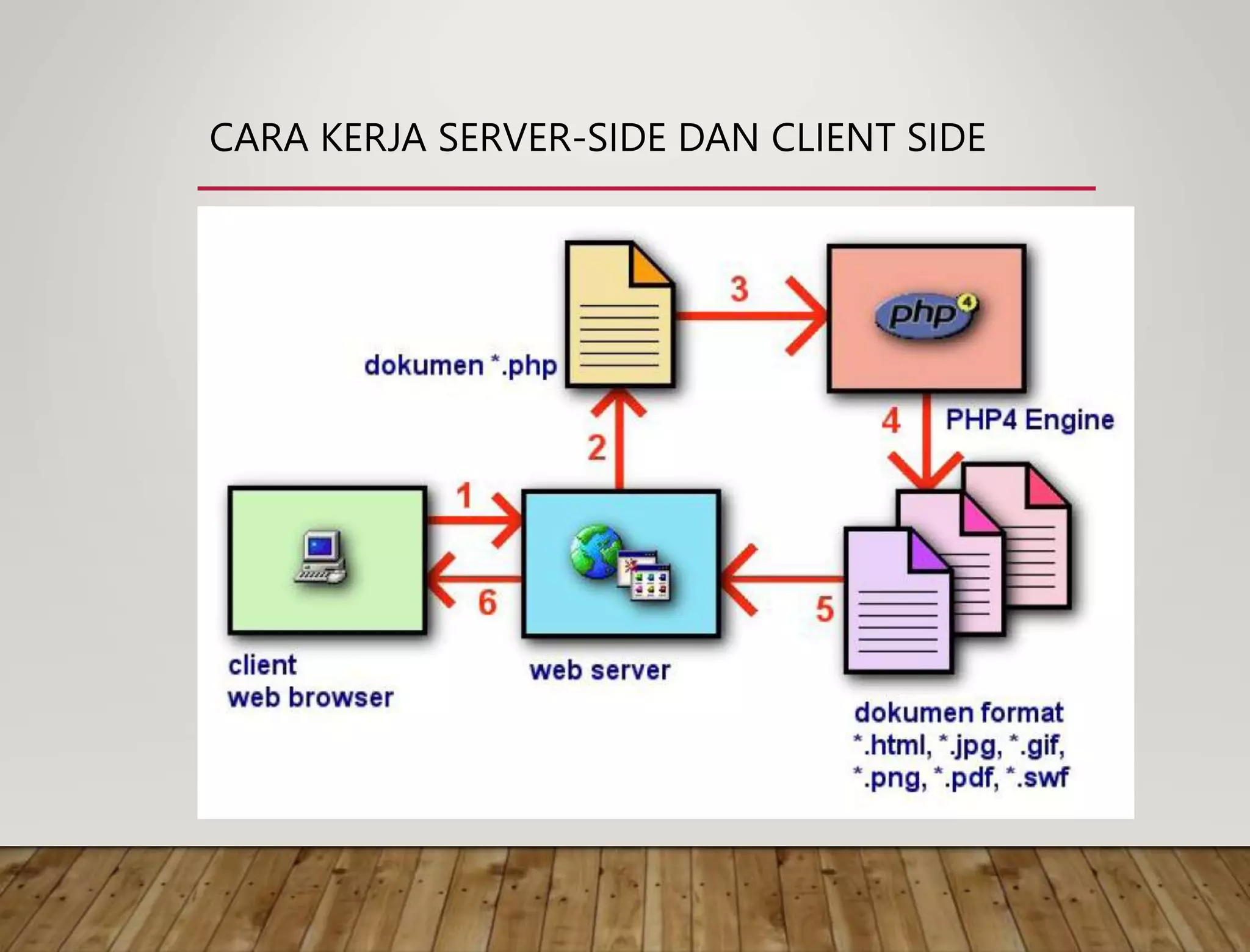
This document discusses technologies used in website applications such as HTML, CSS, JavaScript, PHP and frameworks. It also discusses common questions about the web and how the web works. The key difference between the internet and the world wide web is explained, with the internet being the underlying network and infrastructure, while the web is software and documents accessed via HTTP. A brief history of the internet and growth of the web is provided.