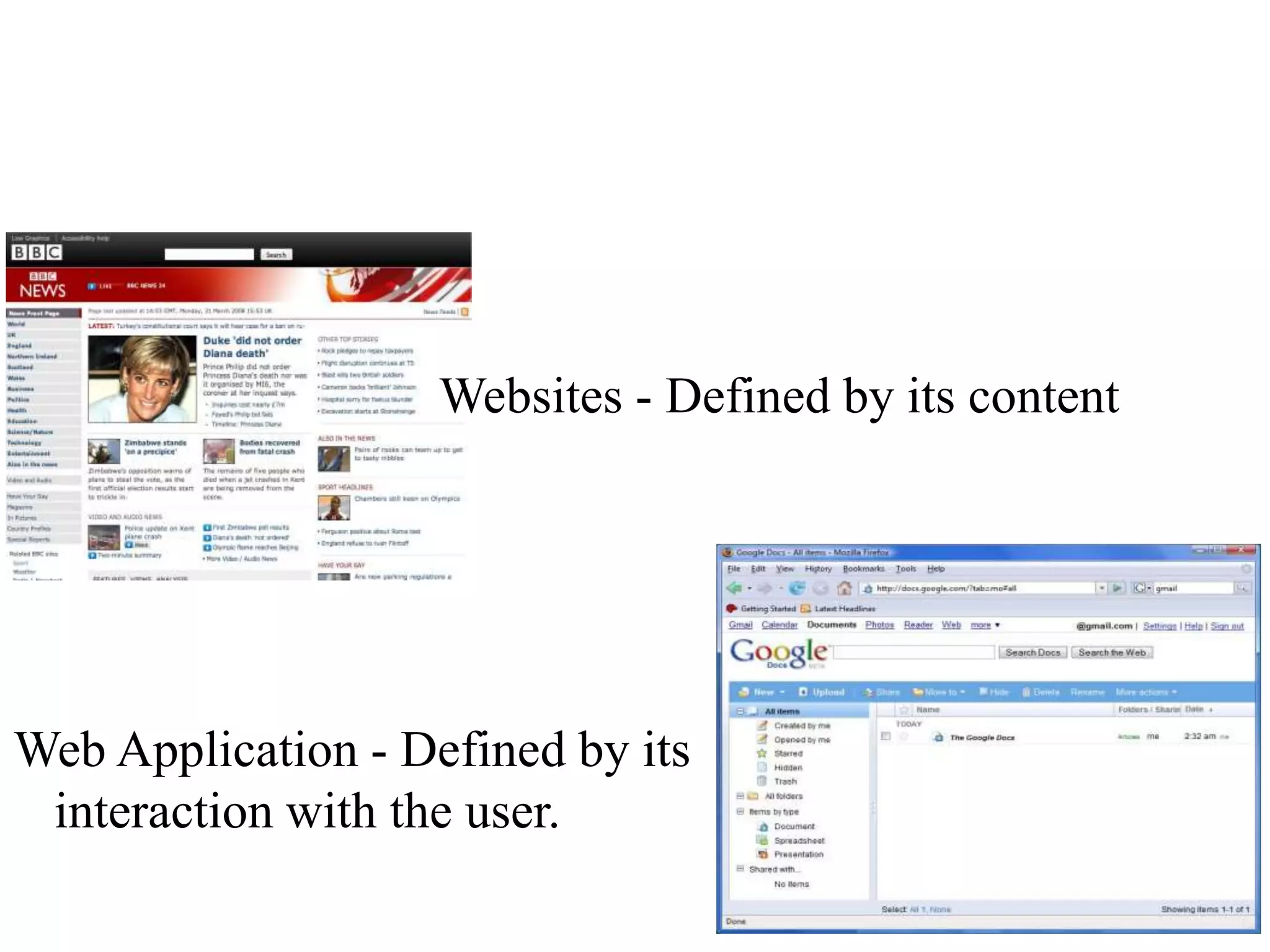
This document summarizes the evolution of front end technologies from the invention of the World Wide Web to modern web applications. It describes how Tim Berners-Lee invented HTML as a publishing language and HTTP as a protocol for linking documents. The development of Mosaic browser and JavaScript enabled interactive web pages. Style sheets and the DOM API allowed formatting and programmatic access to pages. Now, web applications are defined by user interaction rather than just content.