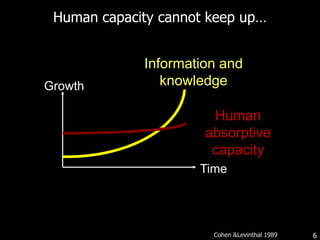
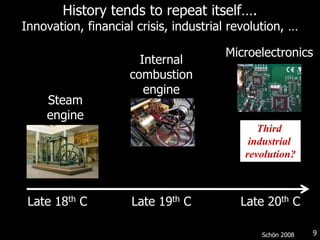
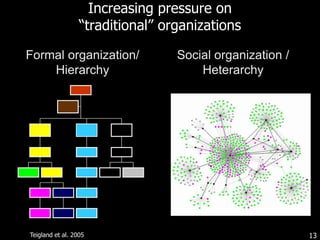
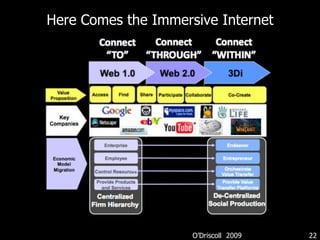
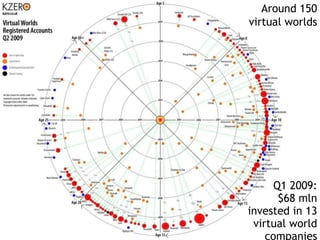
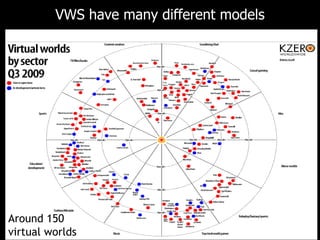
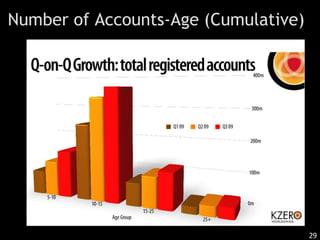
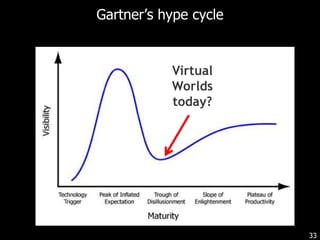
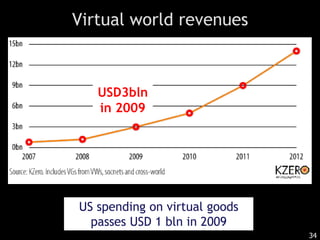
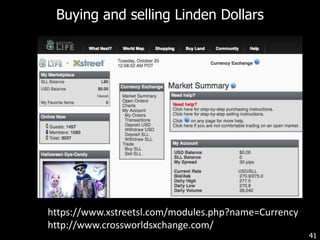
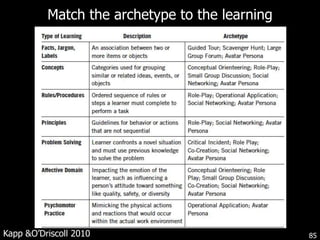
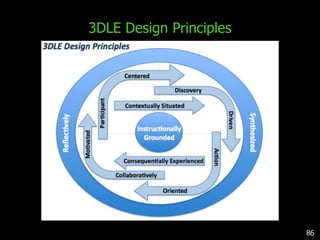
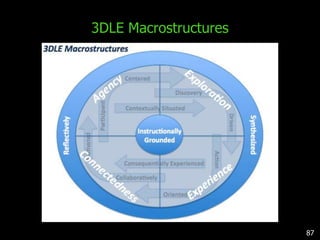
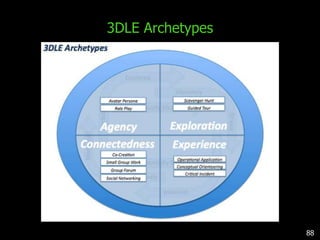
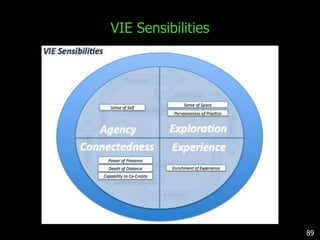
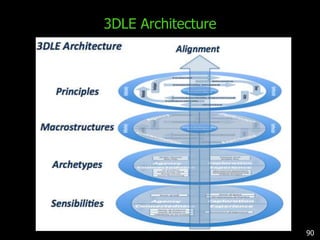
This document discusses bringing education and collaboration into virtual worlds like Second Life. It provides an introduction to virtual worlds and education/collaboration in them. It also highlights Tony O'Driscoll's new book "Learning in 3D" and how the University of Texas has established a presence in Second Life for educational purposes.