This document discusses how technology and problem-based learning can increase student engagement. It first defines student engagement and discusses factors that influence it such as student motivation, engagement in classrooms, socio-political context, and family background. It then explains problem-based learning and how it puts students in an active problem-solving role. Next, it discusses how technology such as interactive learning platforms can promote independence. The document concludes by describing an English course created by the author that incorporates technology and problem-based learning modules to tie into research on increasing student engagement.






![Fall 2015 Allison Hughes | ITEC 800 | Dr. Donohue11
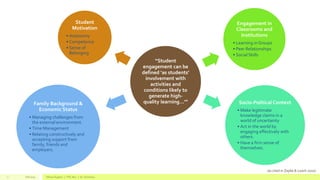
Engagement in Classrooms and Institutions
“…[A] multimodal learning environment which affords
interaction with content and among learners as well as
collaboration and reflection across collocated and
networked learning spaces may be able to provide
additional support for student-centered problem-based
pedagogies” (as cited in Ioannou 2015).
“’We took pictures of specific artifacts and moments using
our tablets or smartphones, we looked at them at the end
of each tutorial and chose a couple to upload on
Facebook; they helped us keep a record of our progress
and recall information and parts of the process’” (as cited
in Ioannou 2015).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16f37d76-0716-4ad8-8986-4eab14ec1e36-160125190955/85/Technology-Problem-Based-Learning-in-Action-11-320.jpg)
![Fall 2015 Allison Hughes | ITEC 800 | Dr. Donohue13
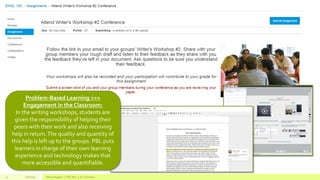
Socio-Political Context
“Researchers working on the rapidly developing sciences
of pedagogy and instructional design are clear that
improved learning outcomes take place in a more
mentor-like environment that allows the student to
experiment, fail, be guided to the right path and
subsequently learn to master a subject or a process”
(Bertrand 2010).
“…[S]ocial media platforms may make learning more
ludic and thus enable more learners to take in the
information that may change their present cognitive
status into a new, reflection-based type of knowledge
that may be applied in new situations” (Mondahl &
Razmerita 2009)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/16f37d76-0716-4ad8-8986-4eab14ec1e36-160125190955/85/Technology-Problem-Based-Learning-in-Action-13-320.jpg)