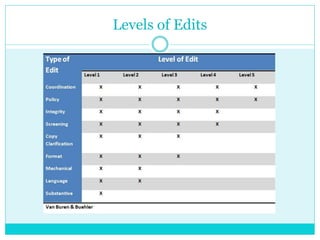
Technical editing involves editing scientific, engineering, medical, or other complex documents for both language and content. It requires specialized knowledge of language usage, information presentation, and the subject matter of the documents. To be a technical editor, one needs expertise in style guides, editing tools, and the mechanics of language. Technical editors perform various types of edits at different levels, from rush edits with a focus on comprehension to standard and revision edits involving comprehensive review and major changes. Key skills include copyediting to correct grammar, punctuation and style, as well as comprehensive editing to evaluate content, organization, design and accommodate the needs of readers.