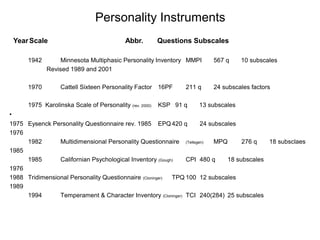
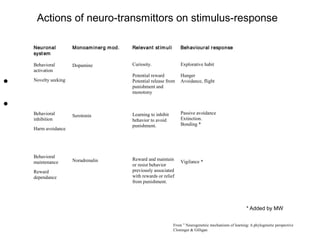
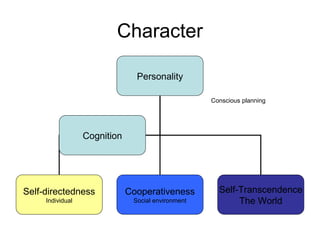
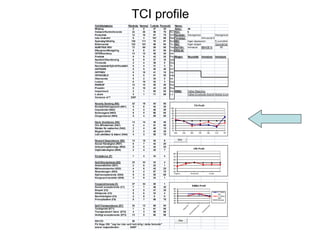
This document provides information about various theories and models of personality and temperament. It discusses early theories from the 1930s-1950s linking physical body types to personality. It then summarizes various trait theories from the 1920s-1970s and biological models of temperament from the 1970s-1980s. The document also describes several widely used personality questionnaires and provides an example profile from the Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI).