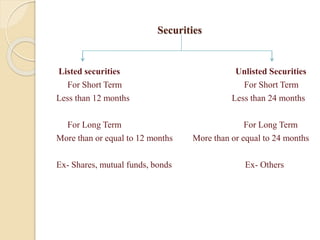
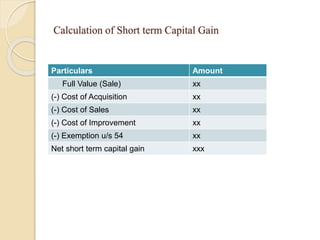
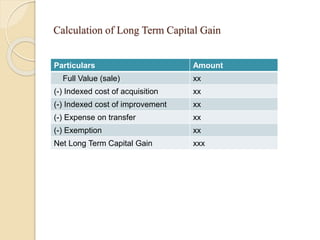
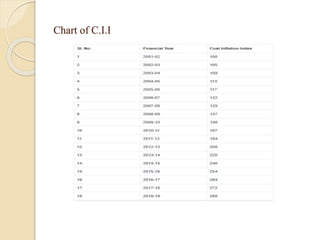
This document discusses capital gains and the taxation of capital assets in India. It defines capital gain as the profit from selling an investment or property at a higher price than its purchase price. It distinguishes between short-term capital assets held for less than 36 months and long-term capital assets held for more than 36 months. The document provides examples of calculating short-term and long-term capital gains, including indexed cost and exemptions. It includes a case study demonstrating how capital gains exemptions work when reinvesting profits into a new residential property.