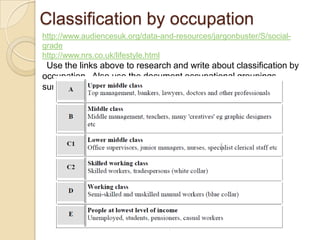
This document provides guidance on classifying audiences for media products. It discusses several ways that audiences can be classified, including by standard occupation, lifestyle or psychographics, postcode or geodemographics, age, gender, and sexual orientation. For each classification, the document instructs the reader to research the topic, provide examples, and write a report explaining what each classification means. It emphasizes structuring the report in Microsoft Word and including illustrations and detailed examples.