This document discusses modularity and composition of language specifications. It describes how language extensions can be added to a "host" language in a modular way through tools like ableP. The key points are:
1) ableP allows users to choose extensions independently and composes them with the Promela host language to create a custom translator.
2) Developing extensible language frameworks requires addressing composable syntax and semantics through techniques like context-aware scanning and modular attribute grammar analyses.
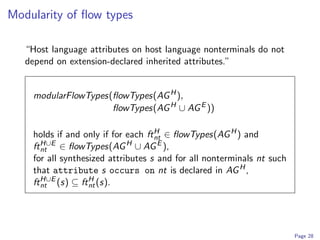
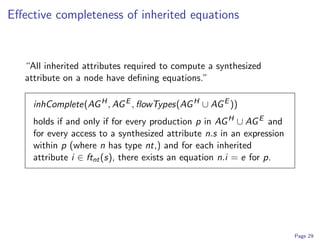
3) Modular analyses like determinism and completeness checking ensure the composed language specification is well-defined and will result in a working translator. This allows extensions to be developed independently and composed automatically.






![Developing language extensions
Two primary challenges:
1. composable syntax — enables building a parser
context-aware scanning [GPCE’07]
modular determinism analysis [PLDI’09]
Copper
2. composable semantics — analysis and translations
attribute grammars with forwarding, collections and
higher-order attributes
set union of specification components
sets of productions, non-terminals, attributes
sets of attribute defining equations, on a production
sets of equations contributing values to a single attribute
modular well-definedness analysis [SLE’12a]
monolithic termination analysis [SLE’12b]
Silver
Page 7](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-7-320.jpg)
![Context aware scanning
Scanner recognizes only tokens valid for current “context”
keeps embedded sub-languages, in a sense, separate
Consider:
chan in, out;
for i in a { a[i] = i*i ; }
Two terminal symbols that match “in”.
terminal IN ’in’ ;
terminal ID /[a-zA-Z ][a-zA-Z 0-9]*/
submits to {promela kwd };
terminal FOR ’for’ lexer classes {promela kwd };
Page 8](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-8-320.jpg)
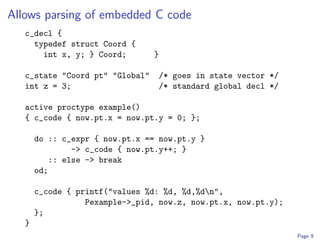

![Adding ETCH-like semantic analysis.
grammar edu:umn:cs:melt:ableP:extensions:typeChecking ;
synthesized attribute typerep::TypeRep
occurs on Expr, Decls ;
aspect production varRef
e::Expr ::= id::ID
{ e.typerep = ... retrieve from declaration
found in e.env ... ; }
aspect production defaultAssign
s::Stmt ::= lhs::Expr rhs::Expr
{ s.errors <- if isCompatible(lhs.typerep, rhs.typerep)
then [ ]
else [ mkError ("Incompatible types ...") ];
}
Page 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-11-320.jpg)
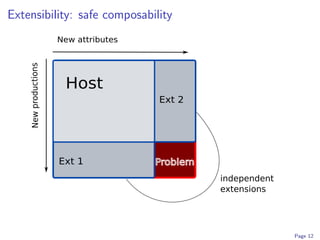
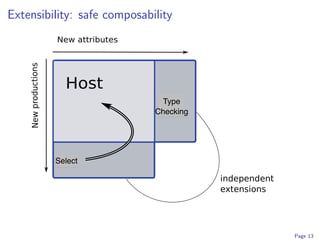
![Extensions get undefined semantics from host translation.
grammar edu:umn:cs:melt:ableP:extensions:enhancedSelect ;
abstract production selectFrom
s::Stmt ::= sl::’select’ v::Expr es::Exprs
{
s.pp = "select ( " ++ v.pp ++ ":" ++ es.pp ++ " ); n" ;
s.errors := v.errors ++ es.errors ++
if ... check that all expressions in ’es’ have
same type as ’v’ ...
then [ mkError ("Error: select statement " ++
"requires same type ... ") ]
else [ ] ;
forwards to ifStmt( mkOptions (v, es) ) ;
}
Page 14](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-14-320.jpg)





![Modular determinism analysis for grammars, 2009
1 2 i
GH ∪ GE ∪ GE ∪ ... ∪ GE
1 1
isComposable(GH , GE ) ∧ conflictFree(GH ∪ GE ) holds
2 2
isComposable(GH , GE ) ∧ conflictFree(GH ∪ GE ) holds
i i
isComposable(GH , GE ) ∧ conflictFree(GH ∪ GE ) holds
1 2
these imply conflictFree(GH ∪ GE ∪ GE ∪ ...) holds
i
( ∀i ∈ [1, n].isComposable(GH , GE ) ∧
i
conflictFree(GH ∪ {GE )} )
1 n
=⇒ conflictFree(GH ∪ {GE , . . . , GE })
Some restrictions to extension introduced syntax apply, of
course.
Page 20](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-20-320.jpg)
![Modular completeness analysis for attribute grammars
1 2 i
AGH ∪ AGE ∪ AGE ∪ ... ∪ AGE
1
modComplete(AGH ∪ AGE ) holds
2
modComplete(AGH ∪ AGE ) holds
i
modComplete(AGH ∪ AGE ) holds
1 2
these imply complete(AGH ∪ AGE ∪ AGE ∪ ...) holds
(∀i ∈ [1, n].modComplete(AG H , AG iE ))
1 n
=⇒ complete(AG H ∪ {AGE , ..., AGE }).
similarly for non-circularity of the AG
Again, some restrictions on extensions.
Page 21](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-21-320.jpg)














![[GPCE’07] Eric Van Wyk and August Schwerdfeger.
Context-aware scanning for parsing extensible
languages.
In Intl. Conf. on Generative Programming and
Component Engineering, (GPCE). ACM Press,
October 2007.
[PLDI’09] August Schwerdfeger and Eric Van Wyk.
Verifiable composition of deterministic grammars.
In Proc. of ACM SIGPLAN Conference on
Programming Language Design and Implementation
(PLDI). ACM Press, June 2009.
Page 39](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-39-320.jpg)
![[SLE’12a] Ted Kaminski and Eric Van Wyk.
Modular well-definedness analysis for attribute
grammars.
In Proceedings of 5th the International Conference
on Software Language Engineering (SLE 2012),
LNCS. Springer-Verlag, September 2012.
To appear.
[SLE’12b] Lijesh Krishnan and Eric Van Wyk.
Termination analysis for higher-order attribute
grammars.
In Proceedings of 5th the International Conference
on Software Language Engineering (SLE 2012),
LNCS. Springer-Verlag, September 2012.
To appear.
Page 40](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/vanwyklundcs-120930093223-phpapp02/85/Talk-Lund-University-CS-Department-40-320.jpg)