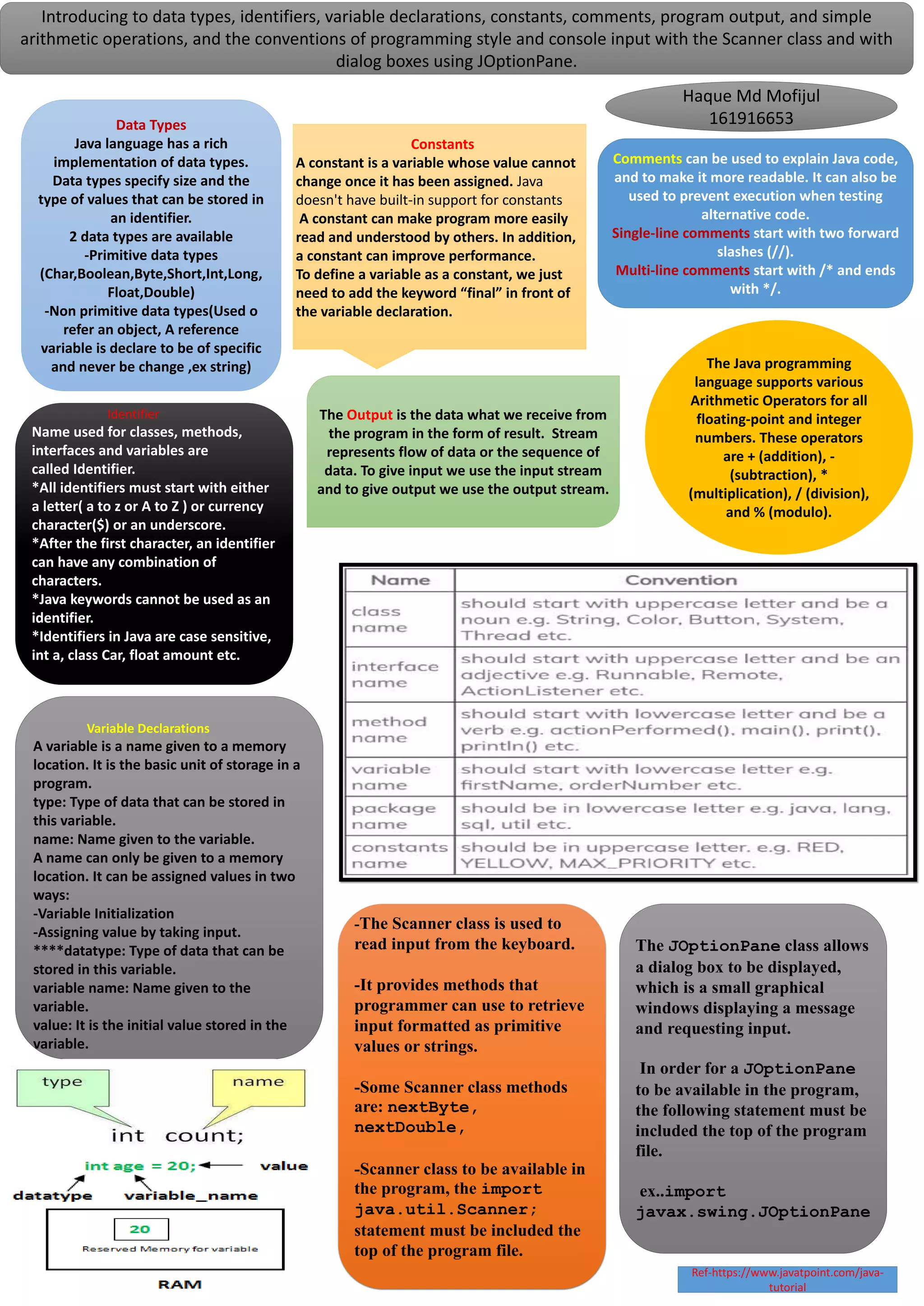
This document introduces key concepts in Java programming including data types, identifiers, variable declarations, constants, comments, arithmetic operations, input/output, and the Scanner and JOptionPane classes. It defines identifiers as names for classes, methods, and variables that must start with a letter or underscore. It describes primitive and non-primitive data types. It explains that variables store values in memory locations and are declared with a type and name. Constants are variables that cannot change value once assigned. Comments are used to explain code. The Scanner class reads input and JOptionPane displays dialog boxes.