This document discusses technological advancements in international business and technology transfer. It covers the following key points:
1. Firms are compelled to internationalize due to globalization and technological advances that reduce costs and enable small firms to operate globally. Advances like the internet open up global markets.
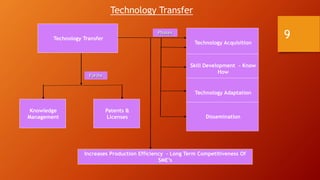
2. Technology transfer involves transferring technologies developed by one organization to other entities to exploit its potential benefits. It discusses different forms and phases of technology transfer.
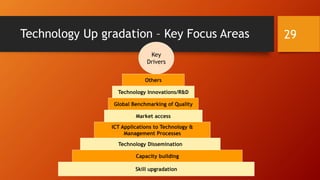
3. Developing countries face challenges in technology competitiveness like lack of indigenous innovation, inadequate infrastructure and skills, and difficulties acquiring and adapting new technologies due to costs and rapid changes. Effective technology transfer can help address these issues.