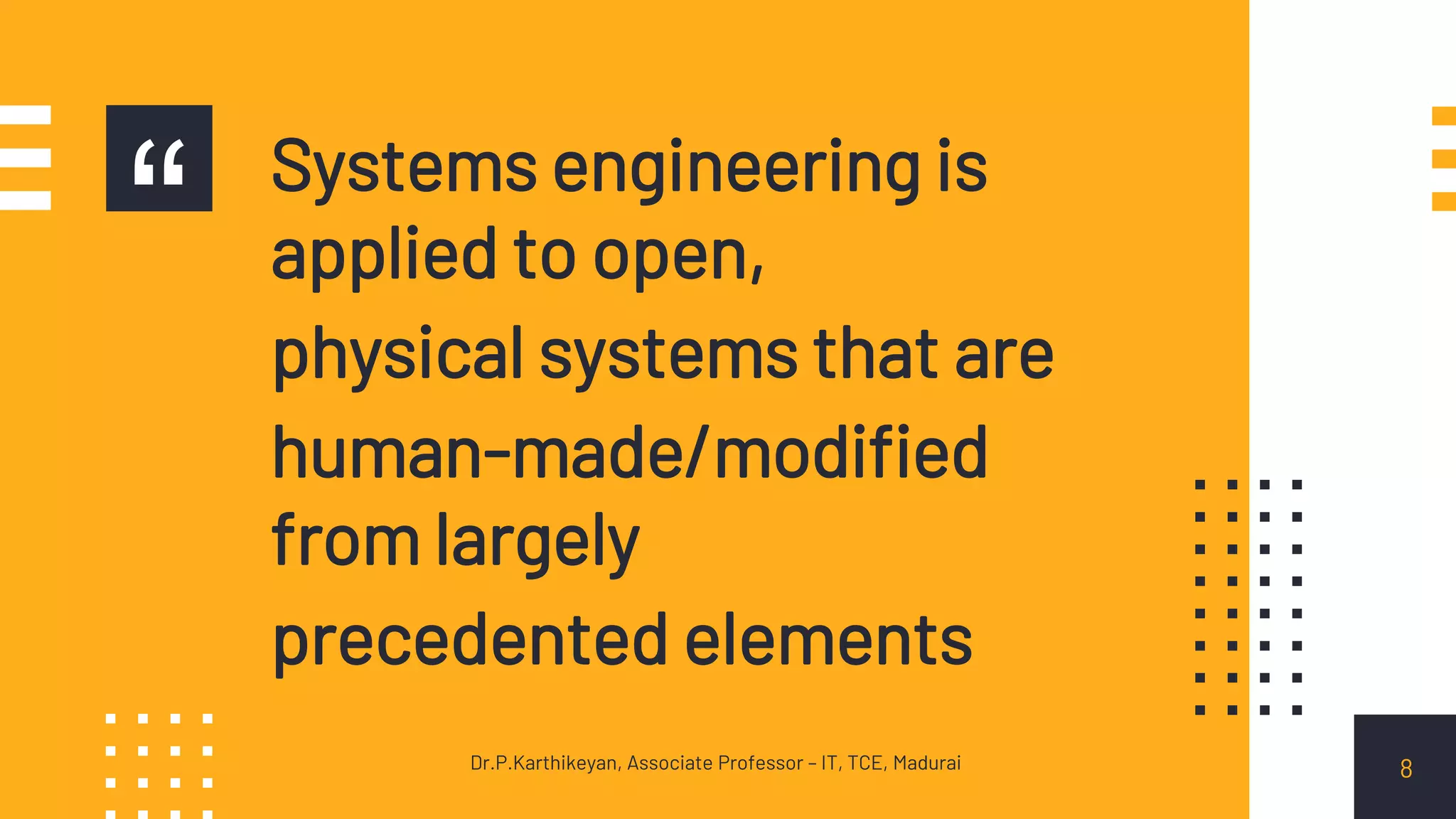
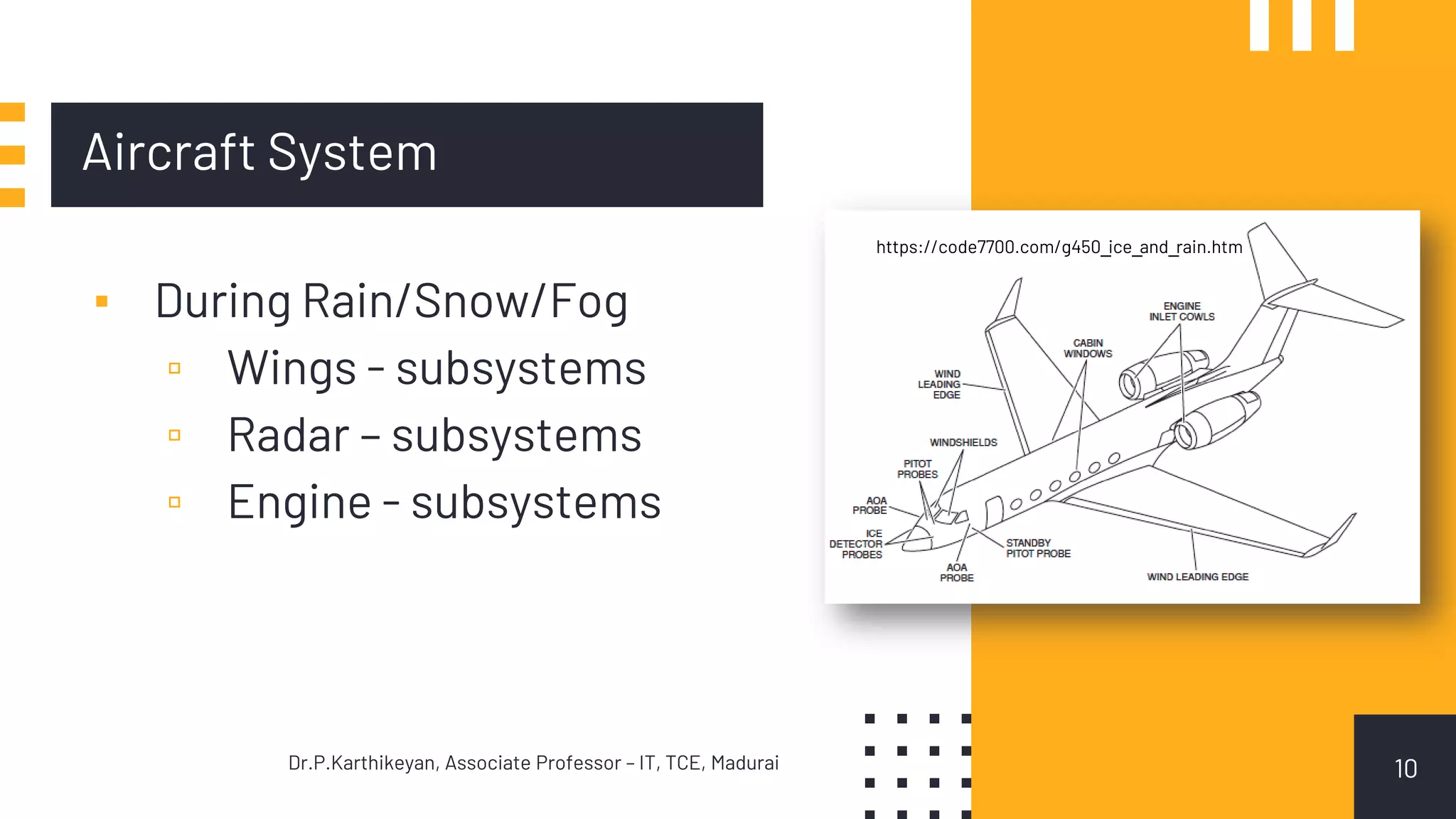
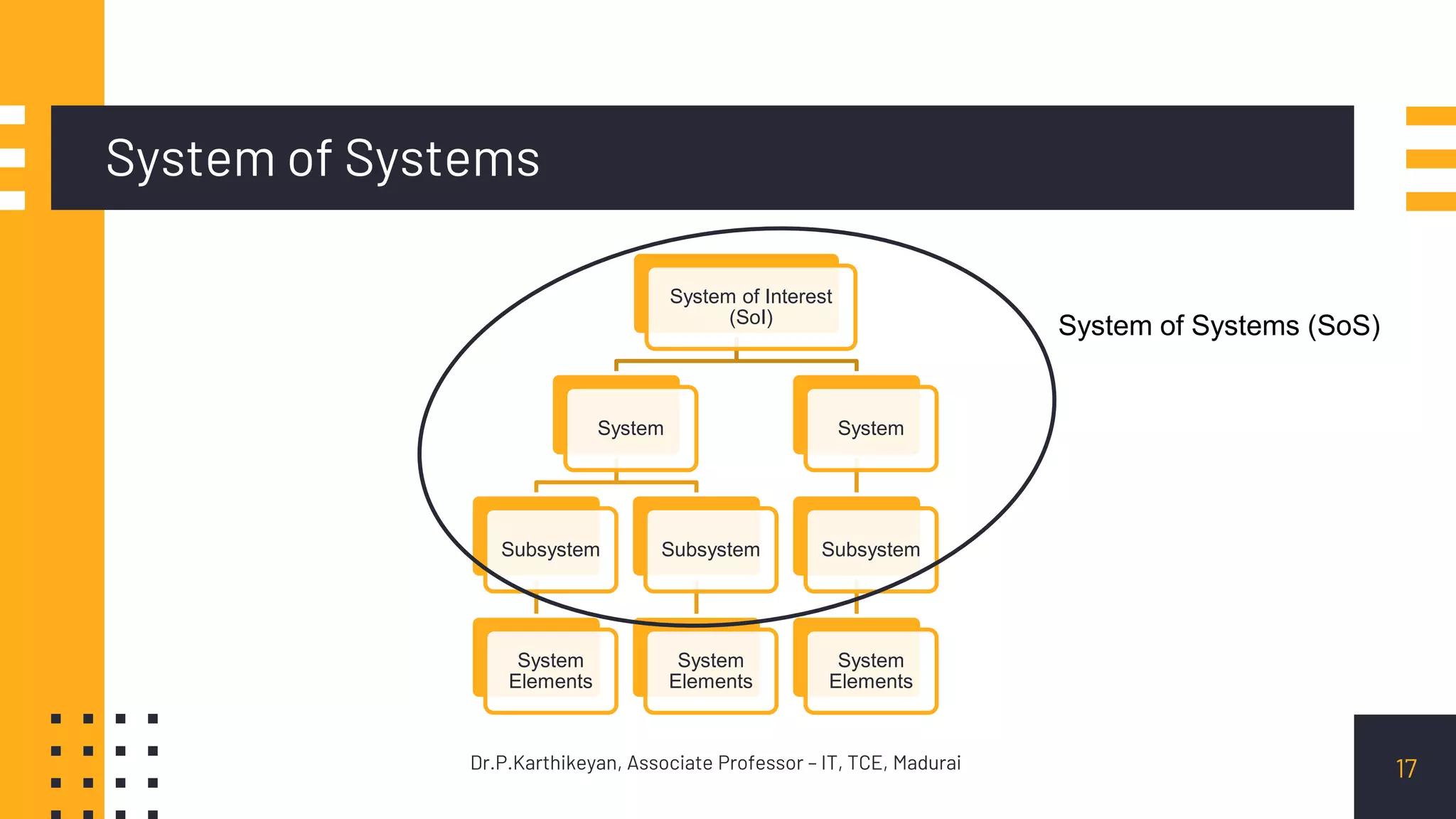
The document describes various types of systems. It states that systems engineering is applied to open, physical systems that are human-made or modified from largely precedented elements. It provides examples of different types of systems, including:
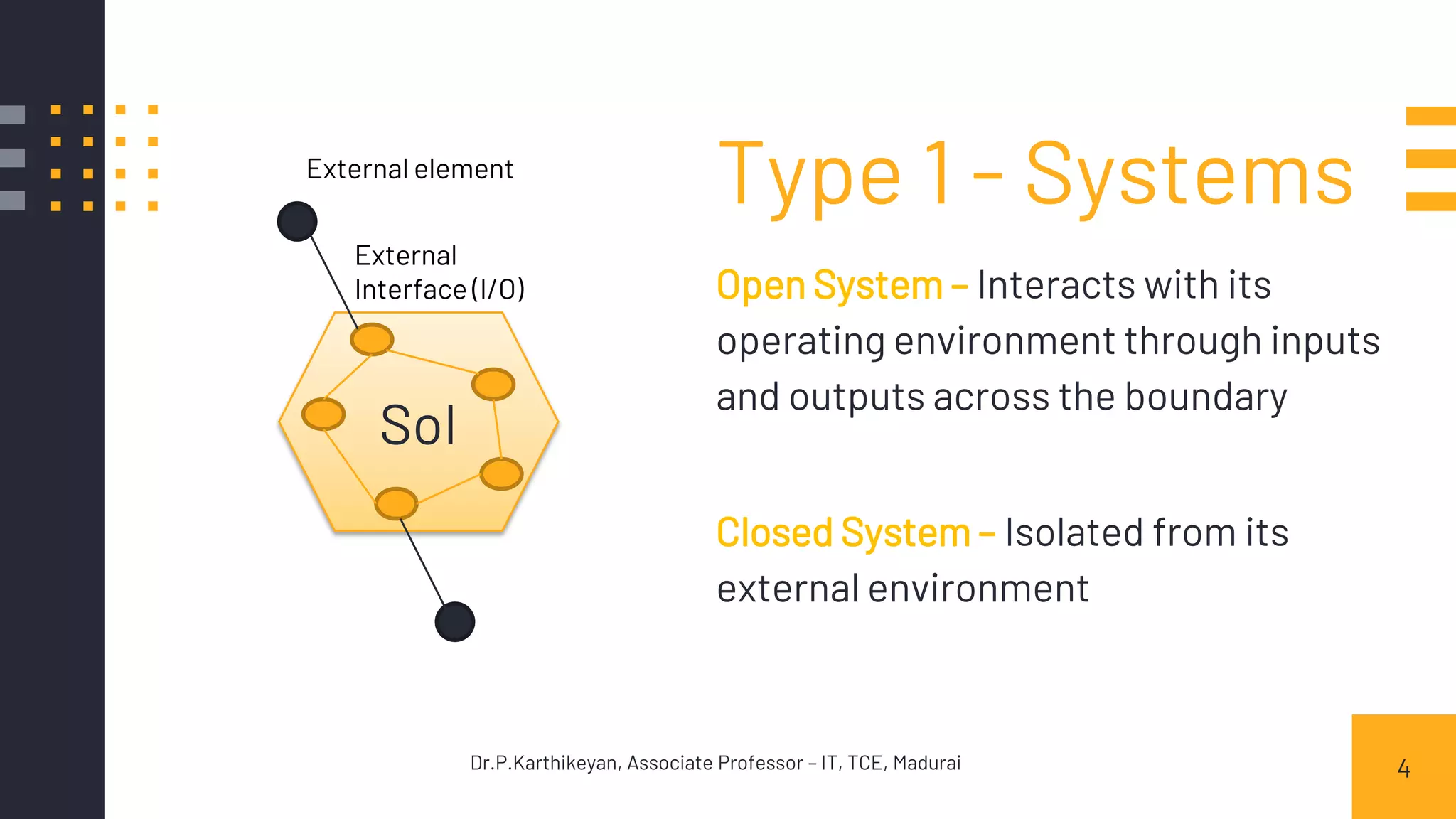
- Open systems that interact with their environment and closed systems that are isolated
- Natural, human-made, and human-modified systems
- Physical and conceptual systems
- Precedented systems that have been produced before and unprecedented systems requiring research
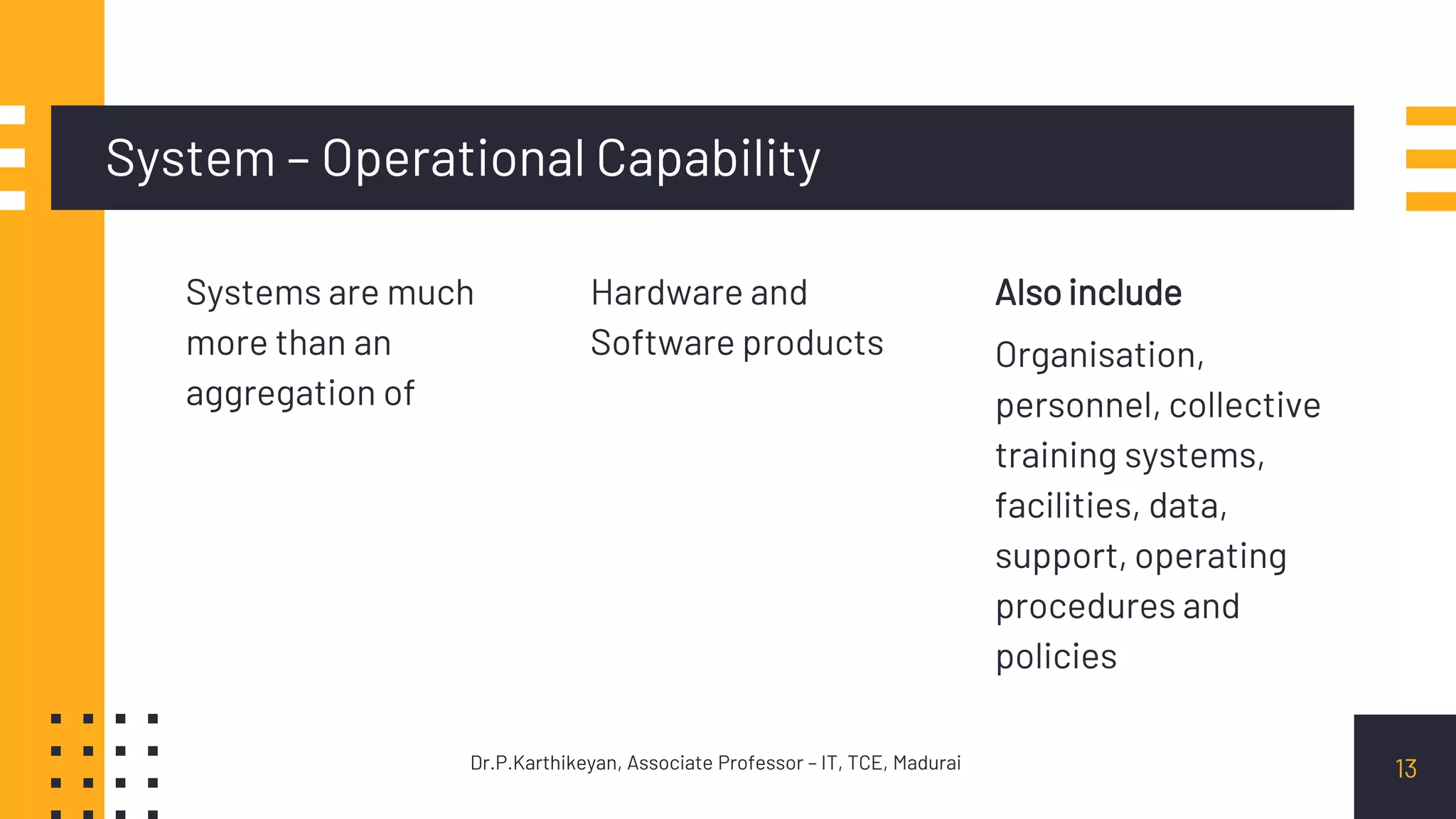
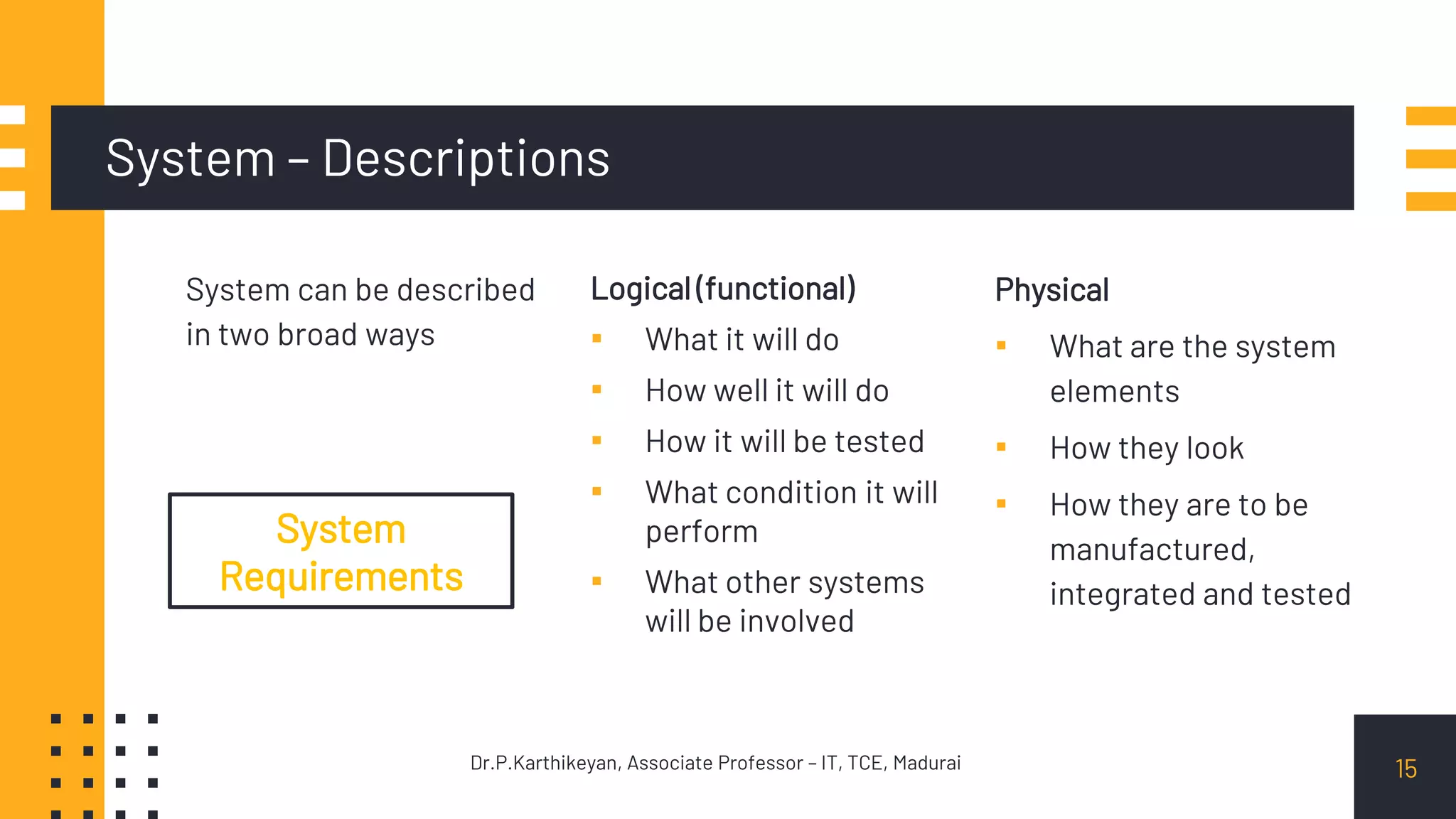
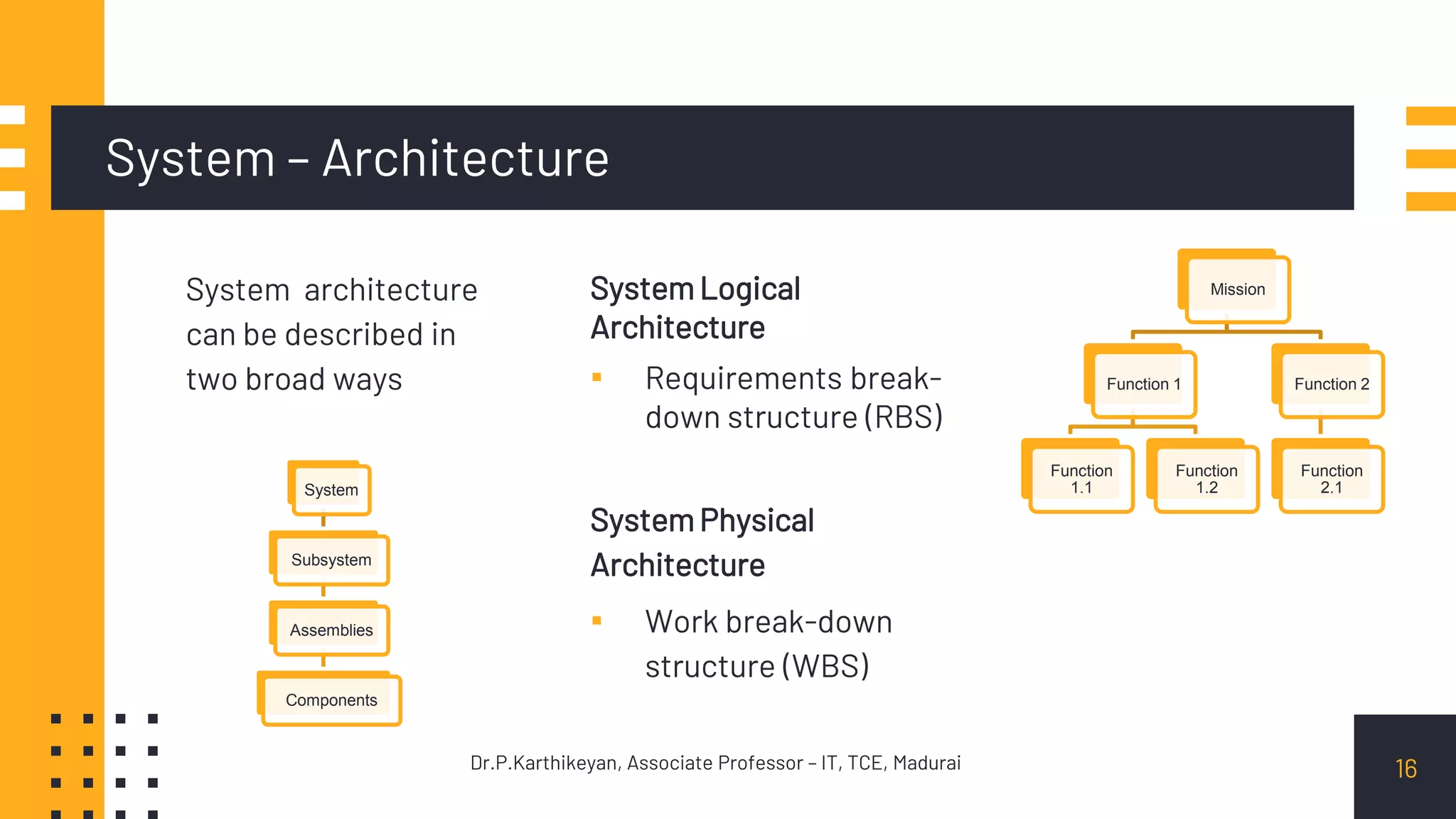
It discusses systems in terms of their capabilities and operational aspects beyond just hardware and software, such as organization, personnel, facilities, data, and procedures. Systems can be described logically in terms of functions and physically in terms of their elements. System