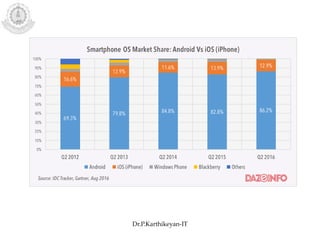
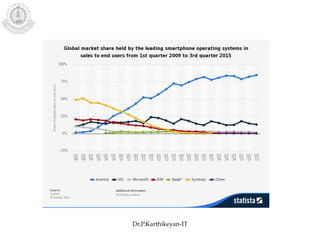
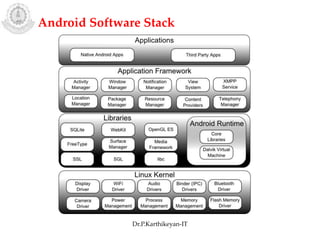
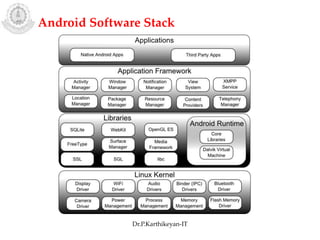
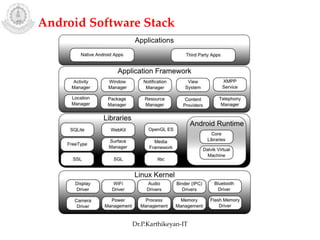
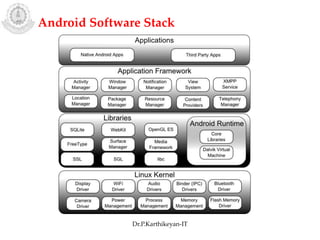
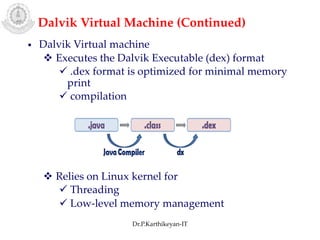
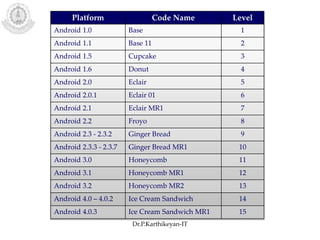
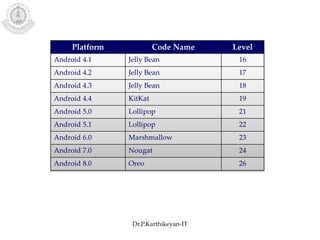
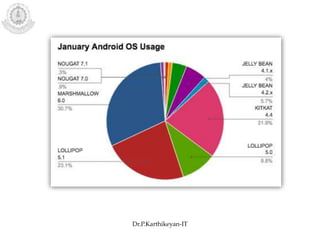
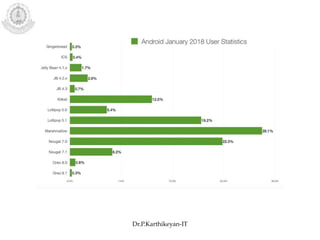
The document discusses mobile operating systems and Android application development. It provides an overview of mobile OS characteristics like multitasking and power management. Current mobile OSs mentioned include Android, iOS, Blackberry and Windows Mobile. Android is described as being developed by Google based on Linux, using Java and a Dalvik virtual machine. The Android software stack is explained, including its applications, framework, libraries and runtime. Tools for Android app development in Eclipse and Android Studio are also listed.