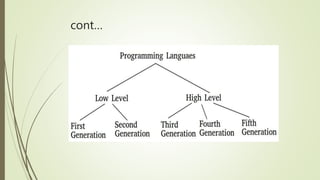
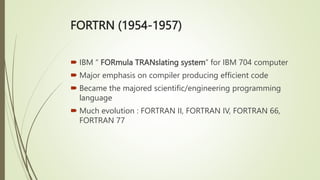
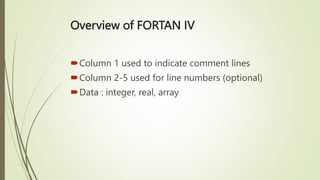
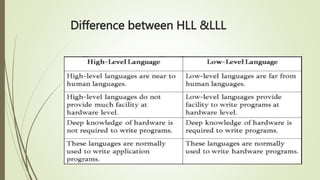
System software directly interacts with hardware and manages devices to perform background tasks for application software. It includes operating systems, compilers, linkers and loaders. Application software is developed for specific tasks like word processing, spreadsheets, web browsing. Common types of application software include office suites, web browsers, games. Programming languages have evolved from low-level machine languages to modern high-level languages that are closer to human languages like C++, Java, Python. The best language depends on the specific task.