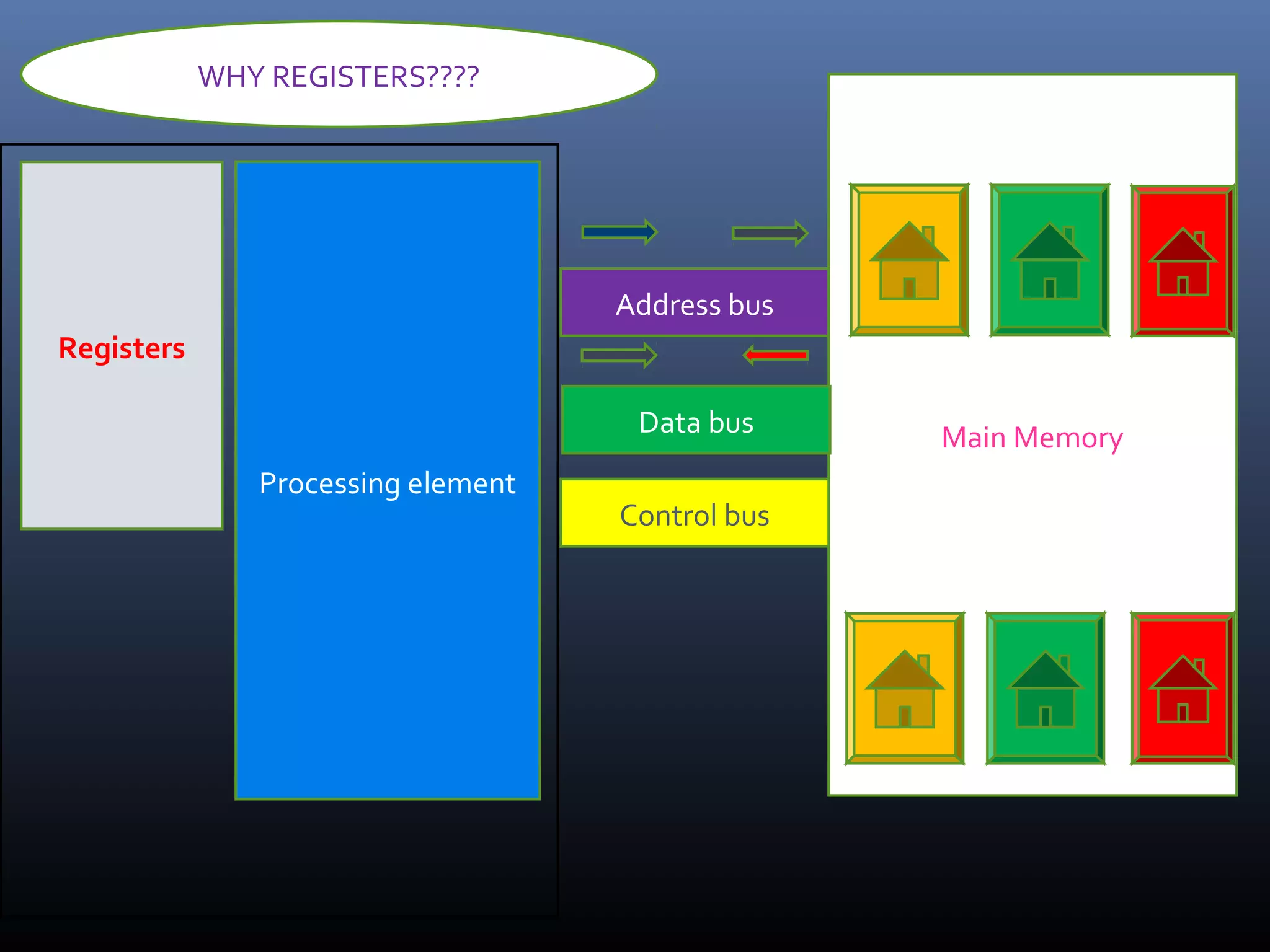
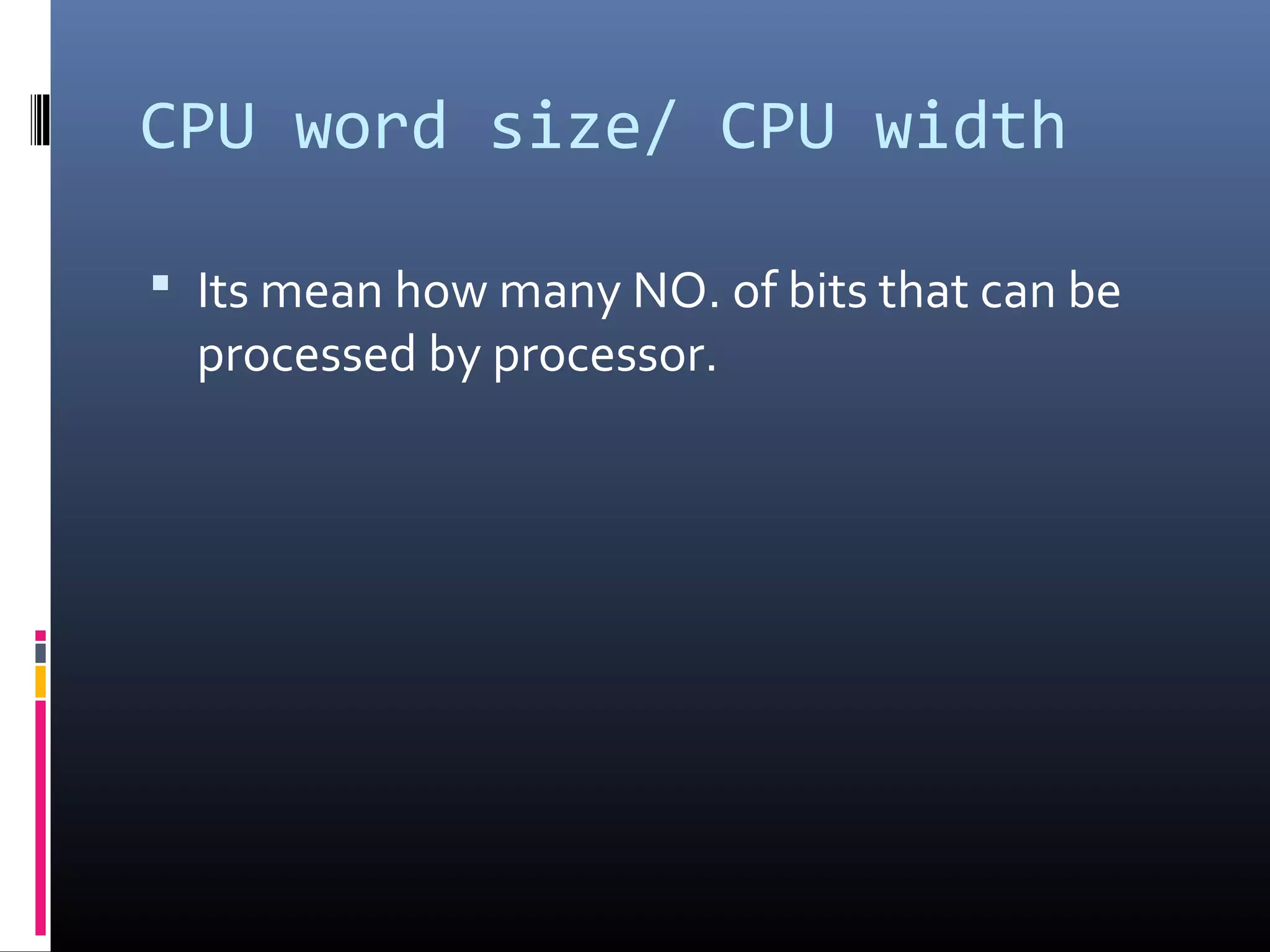
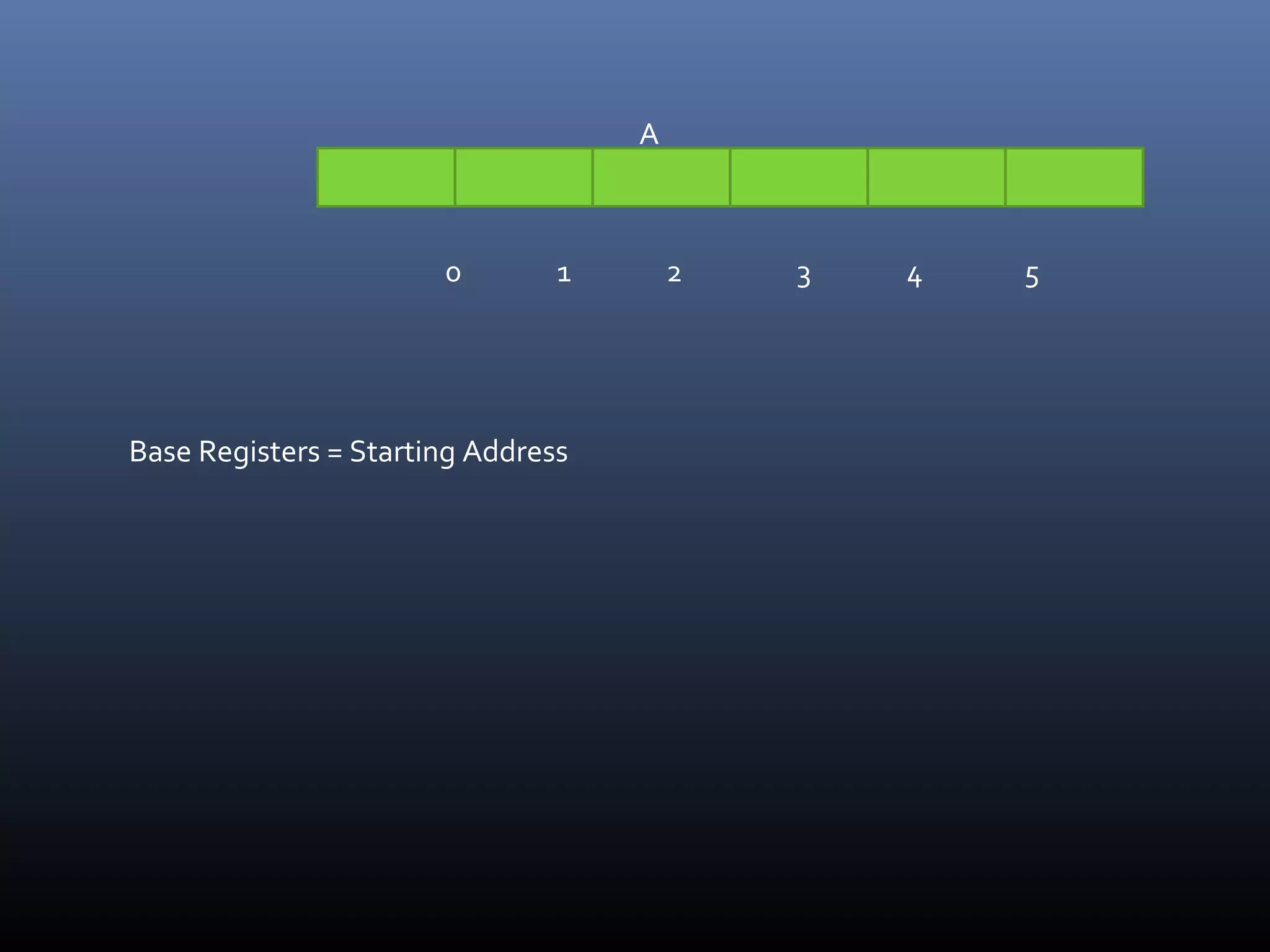
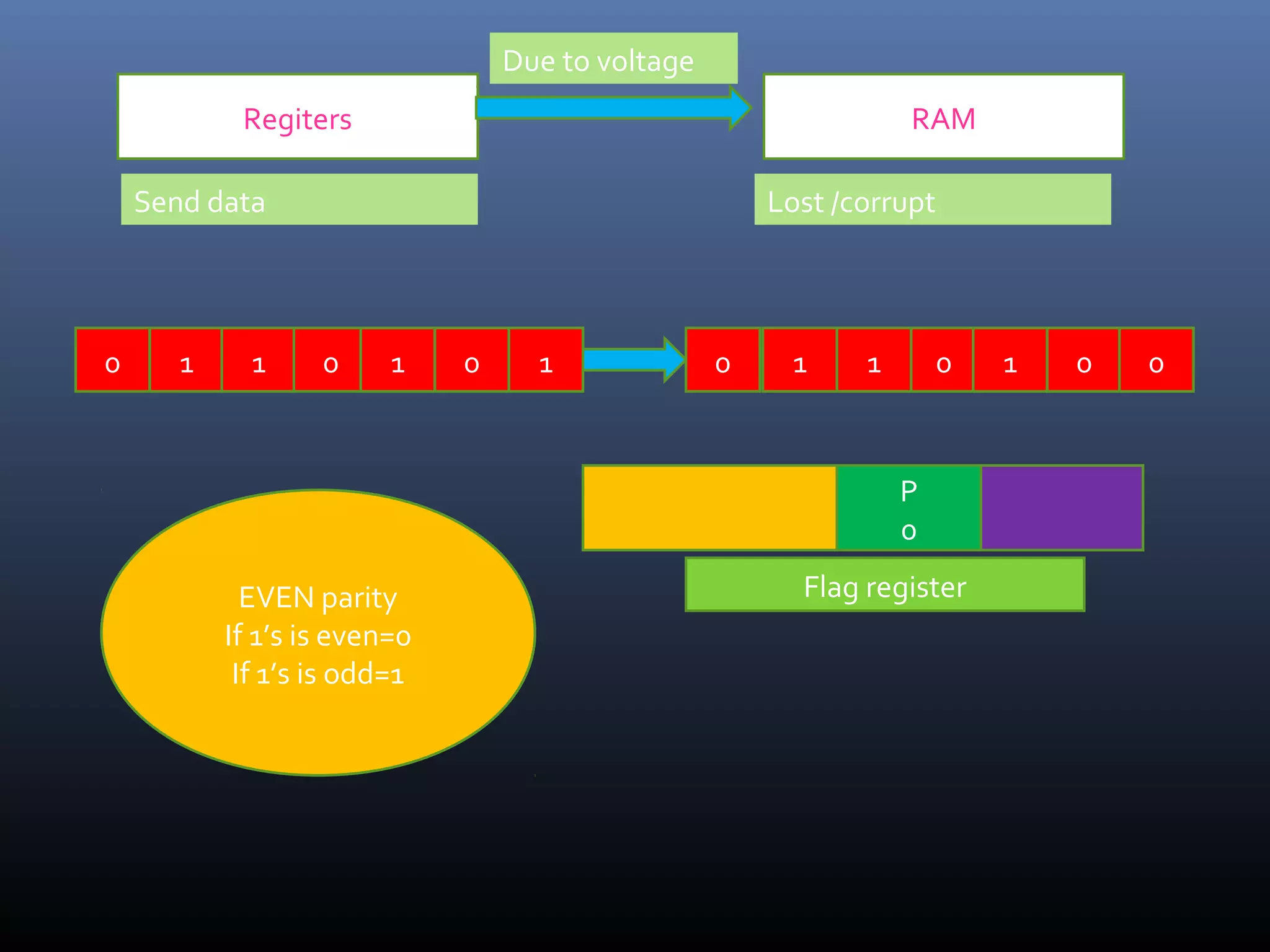
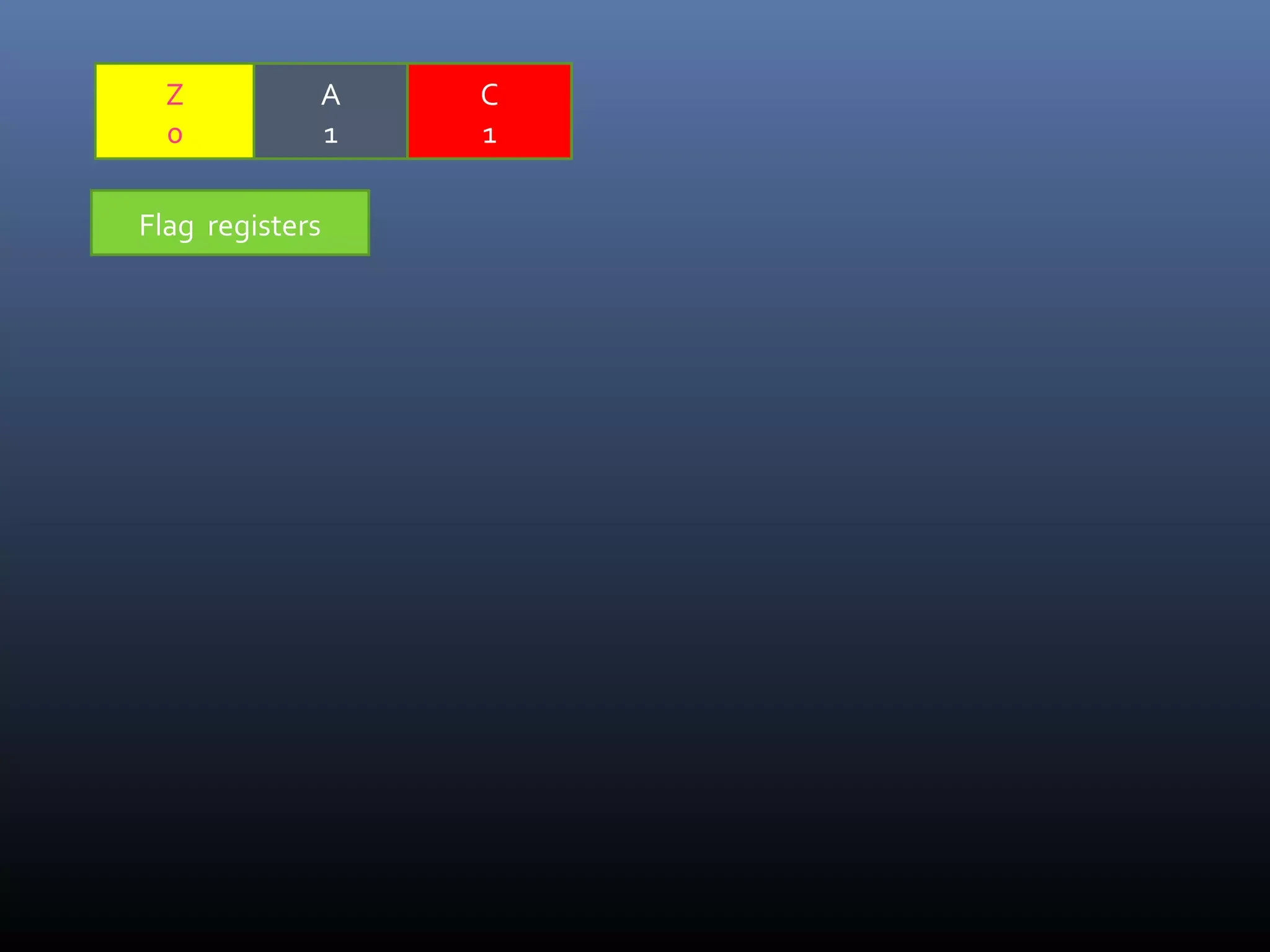
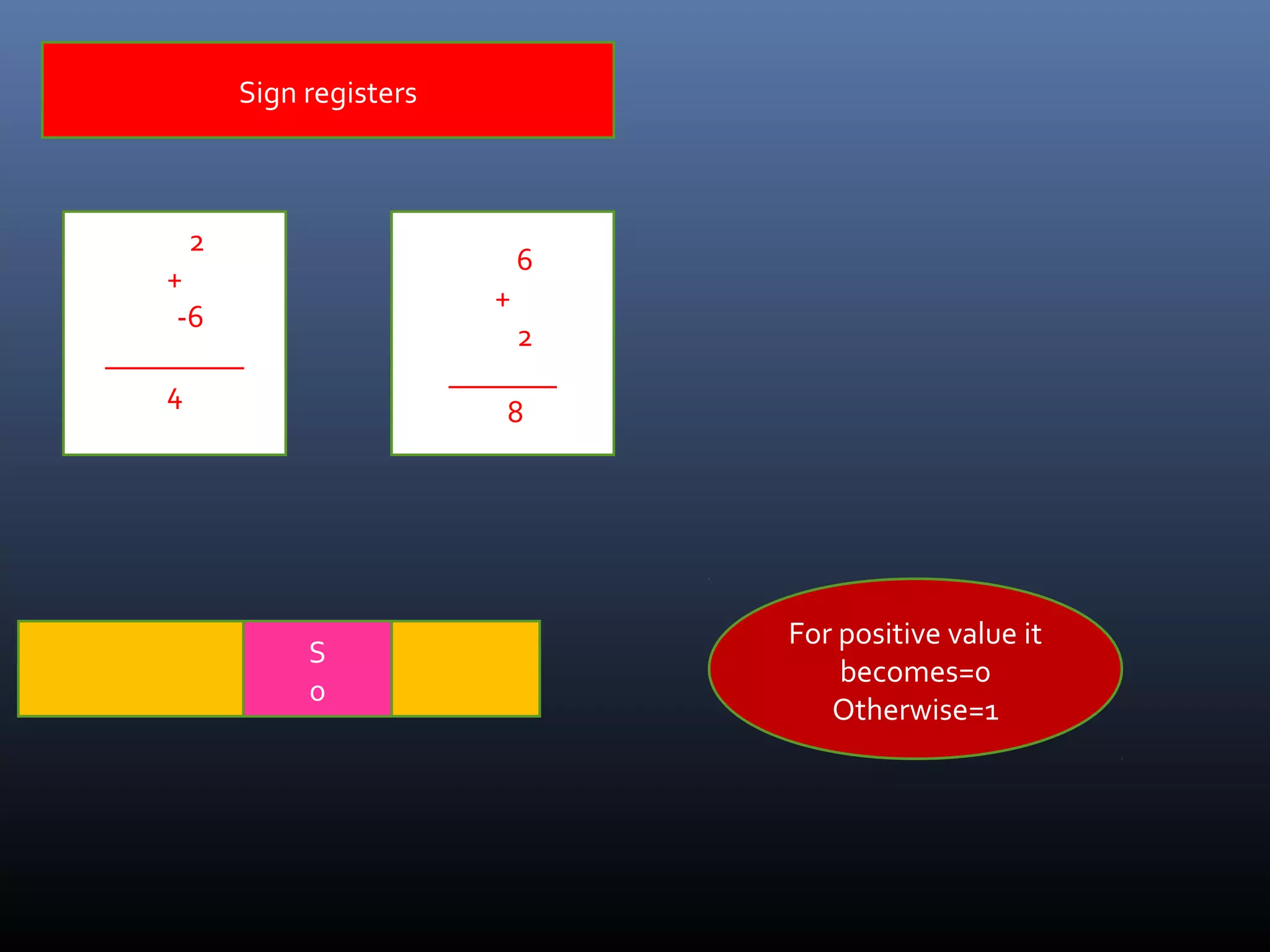
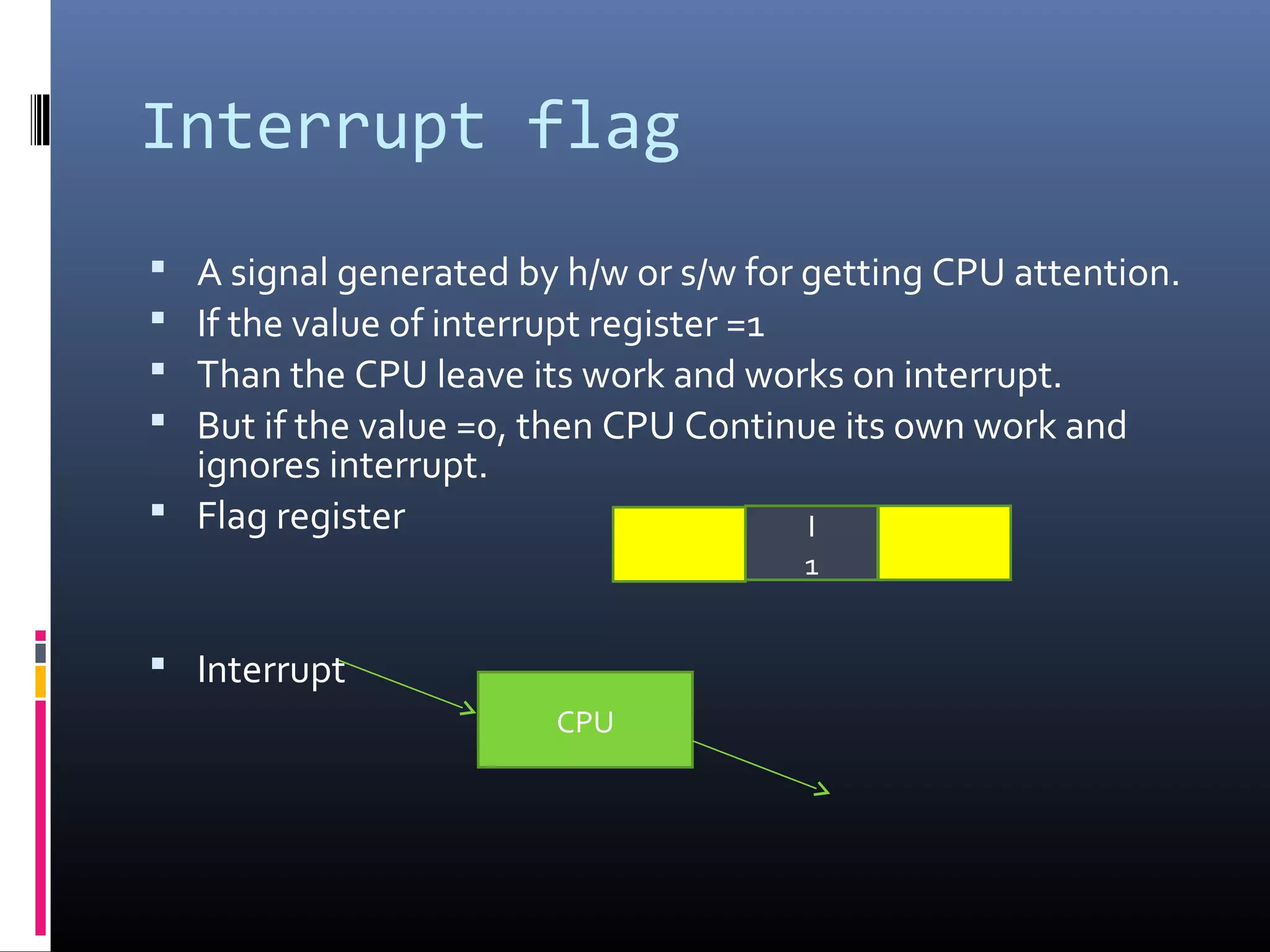
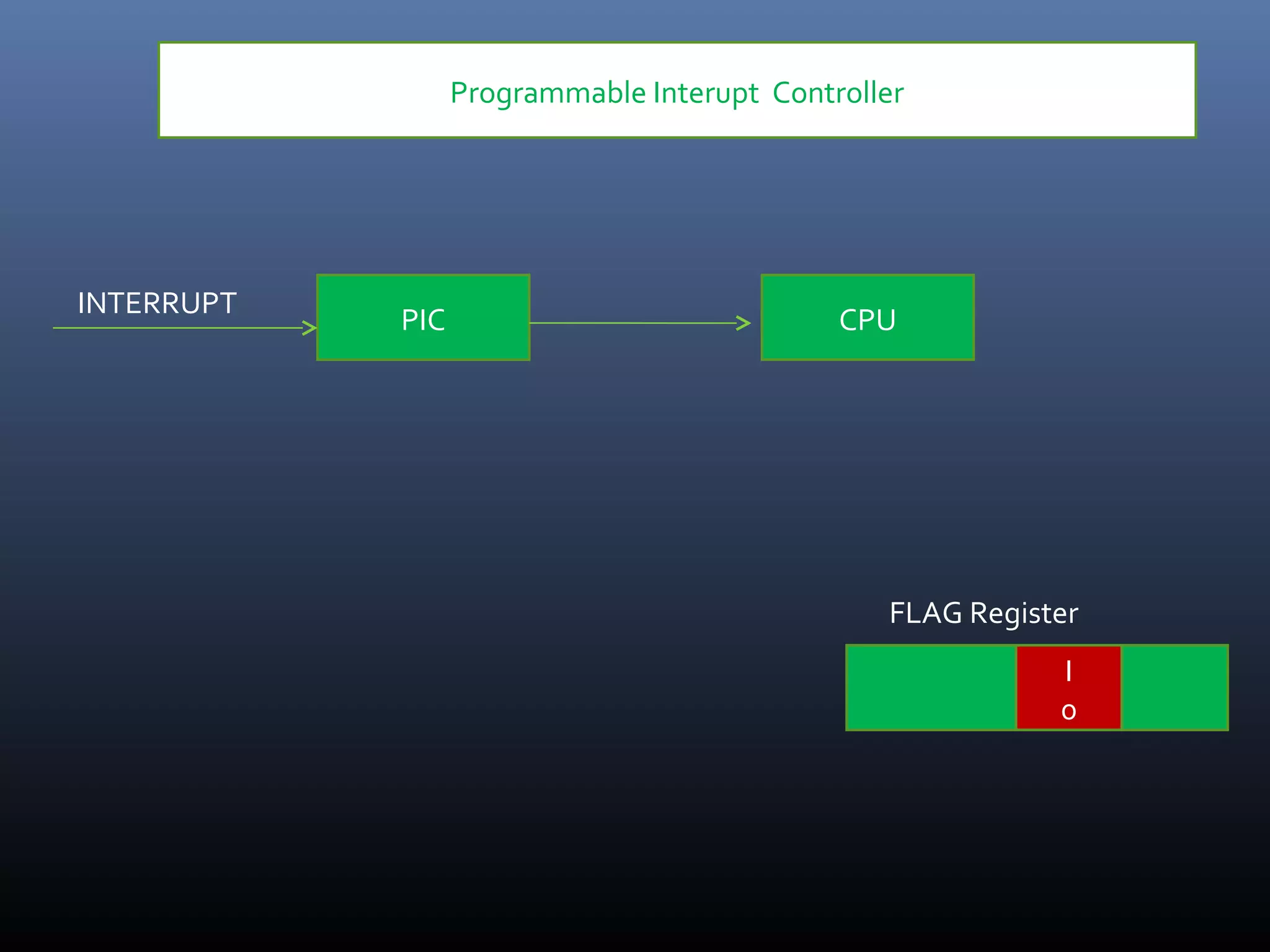
The document discusses register types in computer processors, focusing on general-purpose and special-purpose registers. It explains the function of various flag registers such as carry, parity, zero, and overflow flags, detailing their roles in processing and error detection. Additionally, it covers aspects like direction flags and the trap flag for debugging purposes.