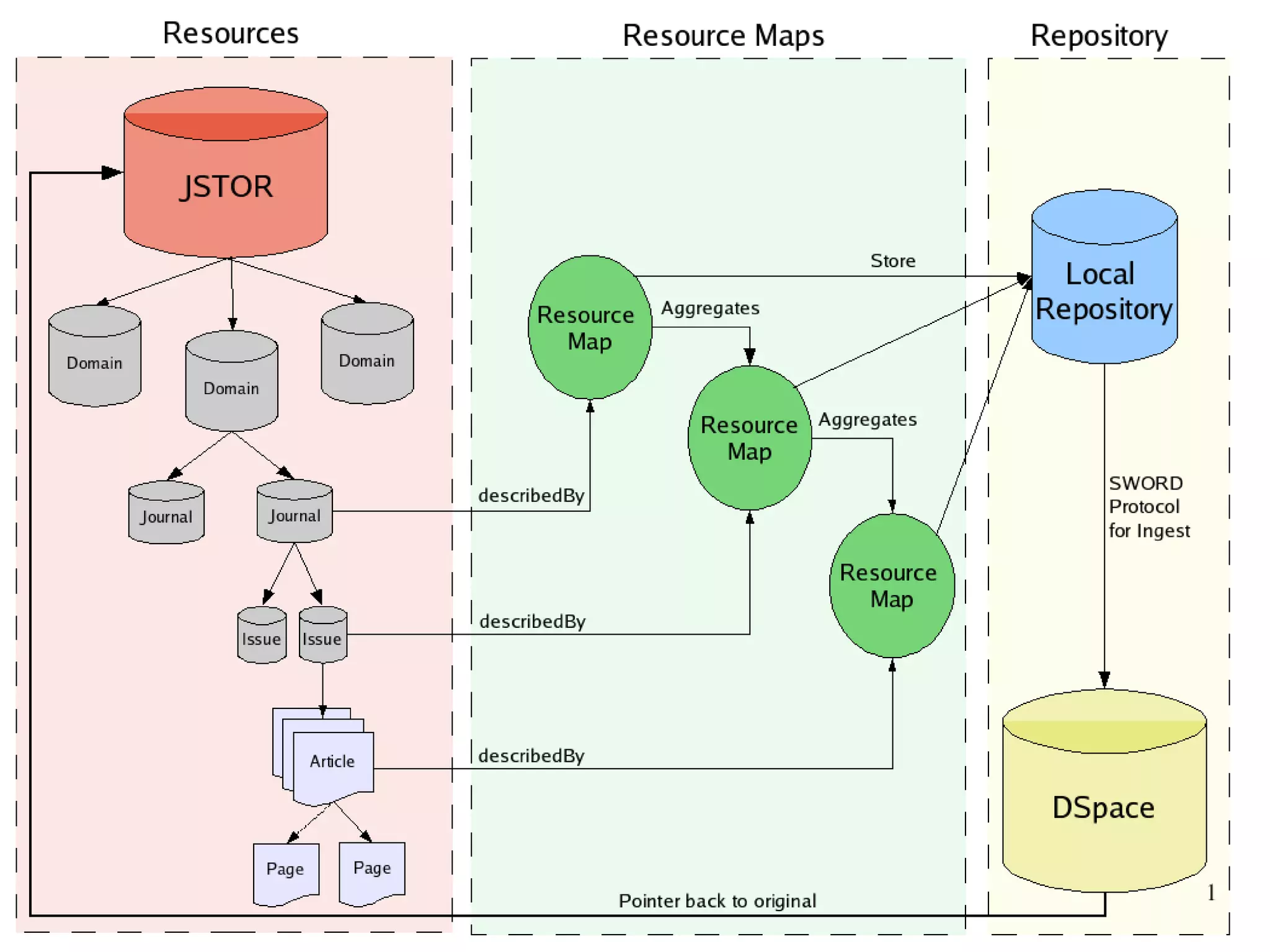
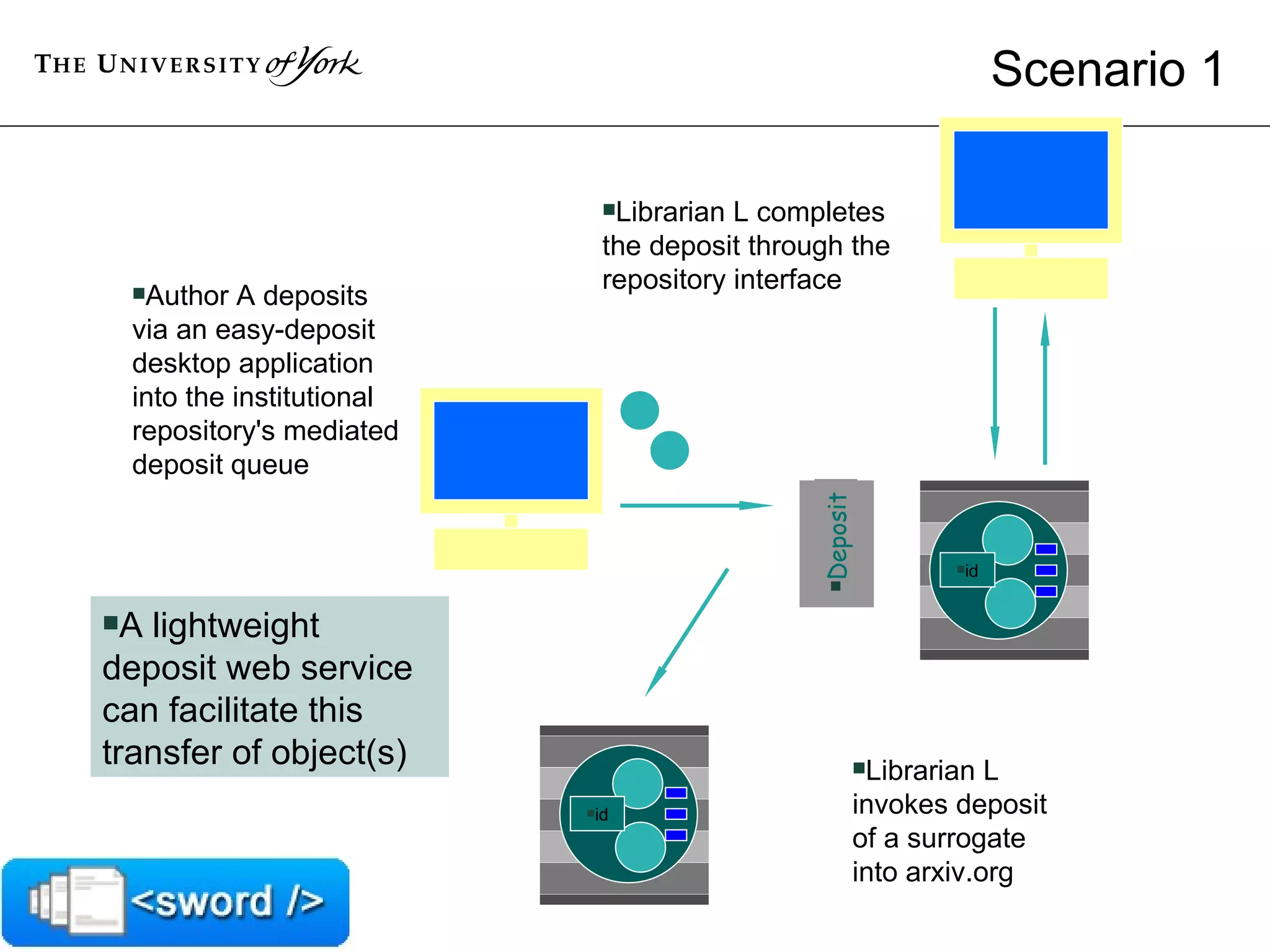
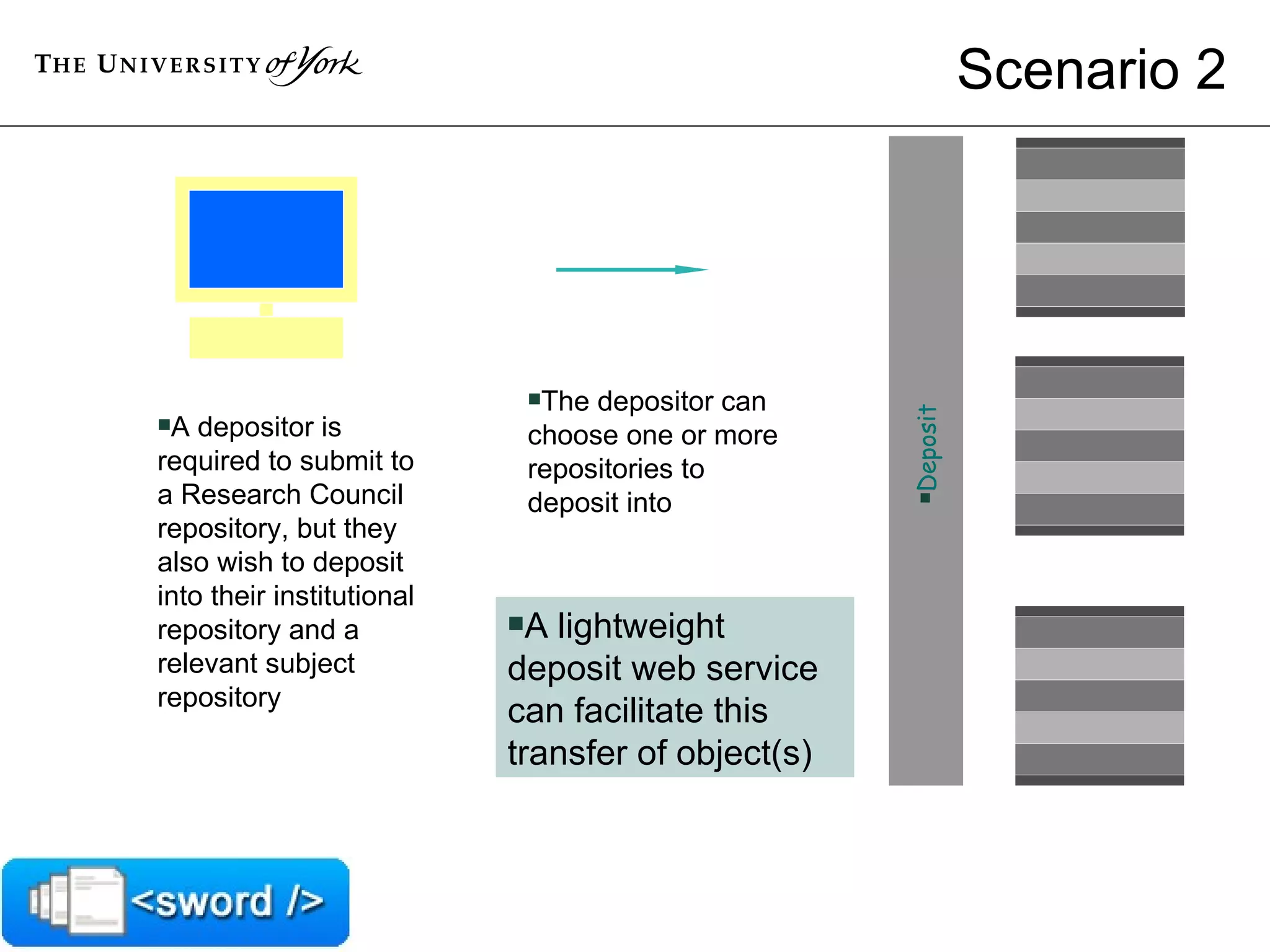
The document discusses SWORD, a protocol for depositing content into repositories. It aims to lower barriers to deposit by providing a standard mechanism. SWORD is based on the Atom Publishing Protocol and supports depositing packages and mediated deposit. Implementations exist for repositories like DSpace, EPrints and Fedora, as well as client tools. The document provides an overview of how SWORD works and some use cases.















![More Info and Contact SWORD Website: http://www.swordapp.org General queries: Adrian Stevenson [email_address] Technical queries: sword sourceforge list [email_address]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/sword-bl-09031-090327105033-phpapp01/75/Sword-Bl-0903-1-26-2048.jpg)