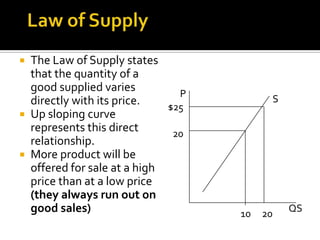
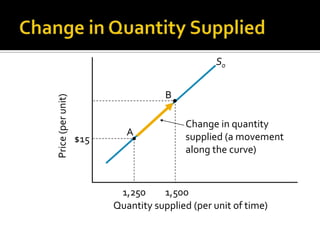
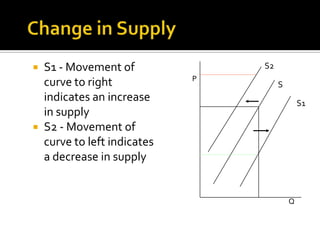
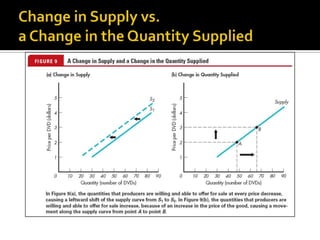
The document discusses the law of supply and factors that cause the supply curve to shift. It explains that the law of supply states that quantity supplied rises with price, as higher prices increase producer profits and allow firms to cover higher costs. It then provides examples of factors that can cause the supply curve to shift left or right, such as changes in input costs, technology, taxes, subsidies, and expectations about future prices. Government regulations can also impact supply.