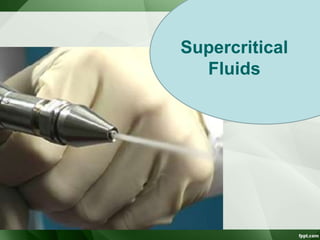
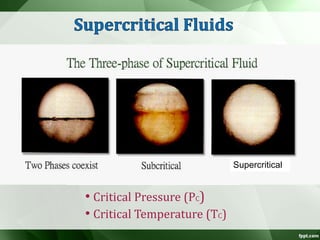
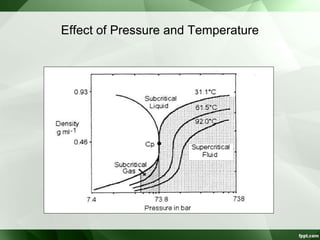
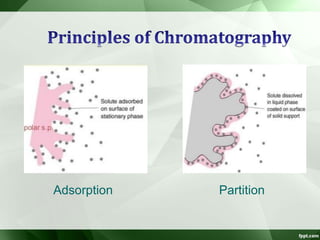
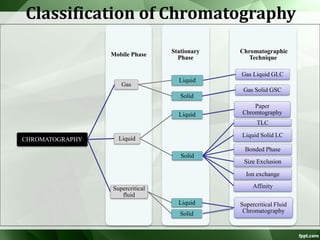
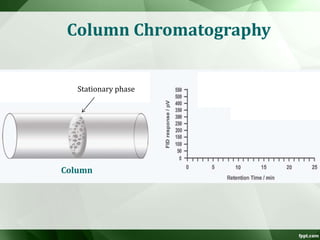
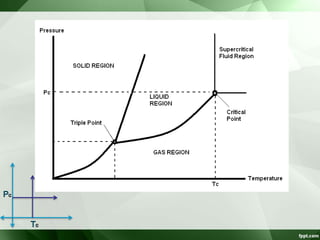
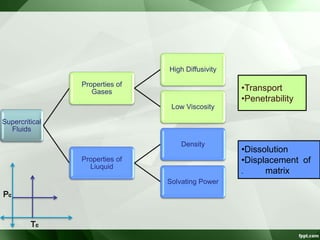
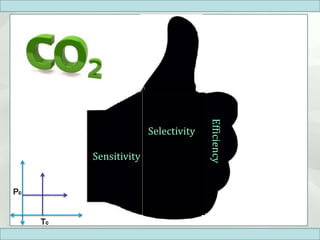
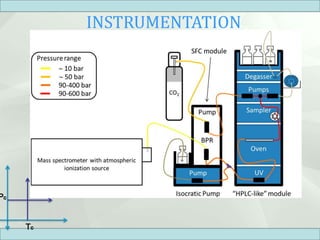
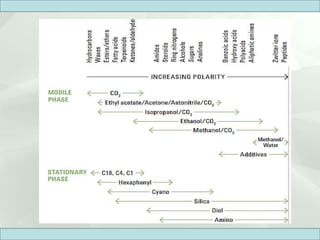
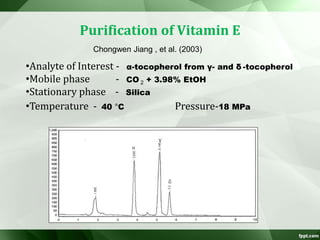
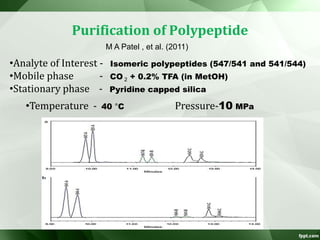
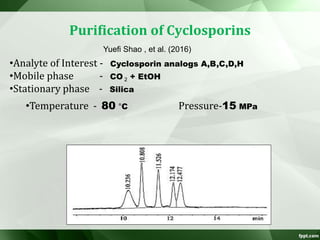
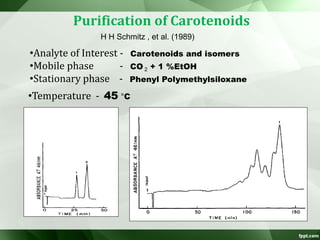
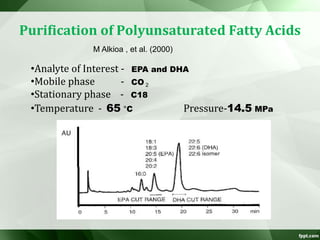
The document discusses supercritical fluid chromatography (SFC), highlighting its principles, instrumentation, advantages, challenges, and applications in the biotechnology field. It details the properties of supercritical fluids, the classification of chromatographic techniques, and case studies on the purification of various compounds using SFC. The document also lists key manufacturers and specific examples of applications in the pharmaceutical industry and biotechnology.