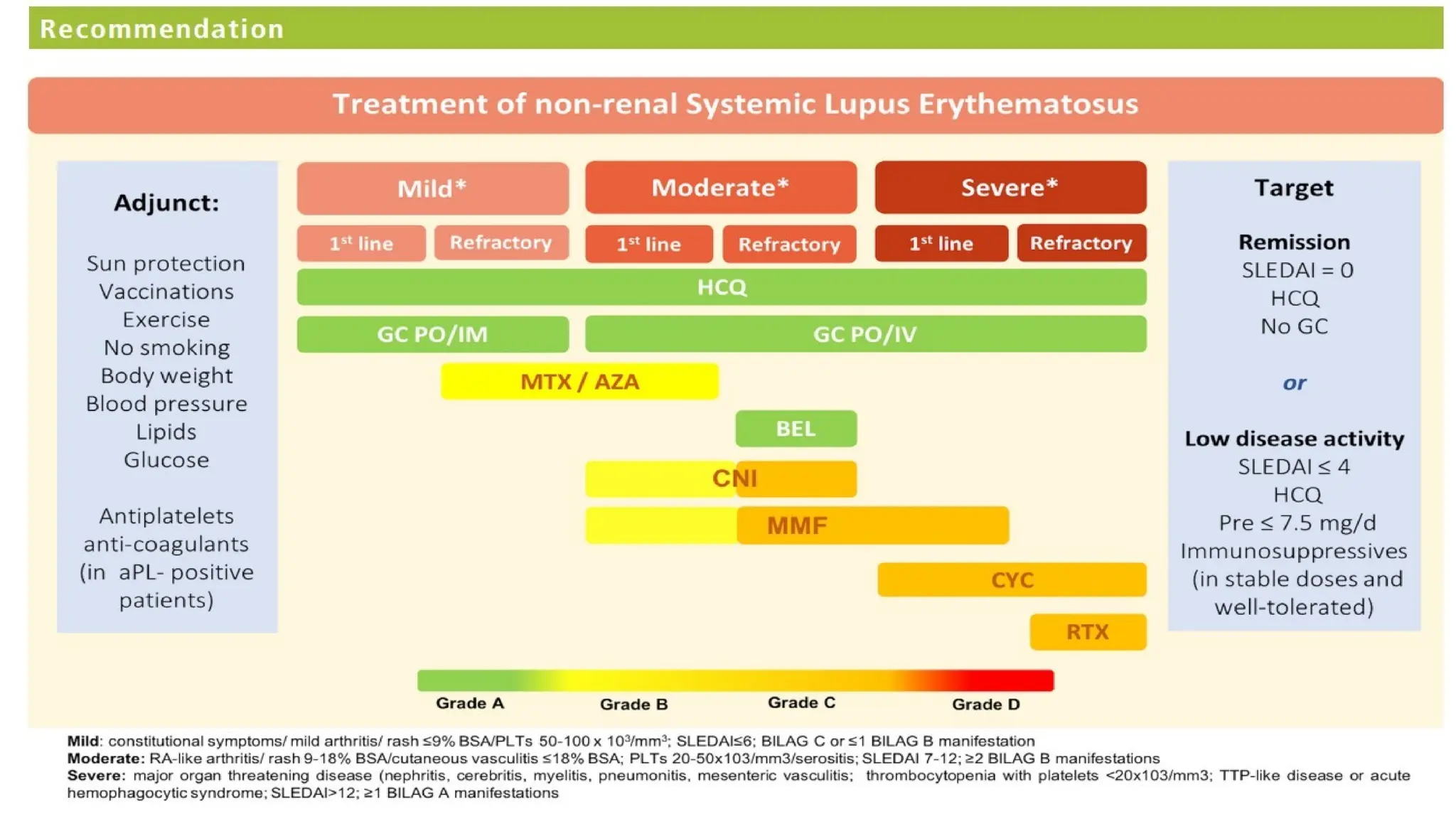
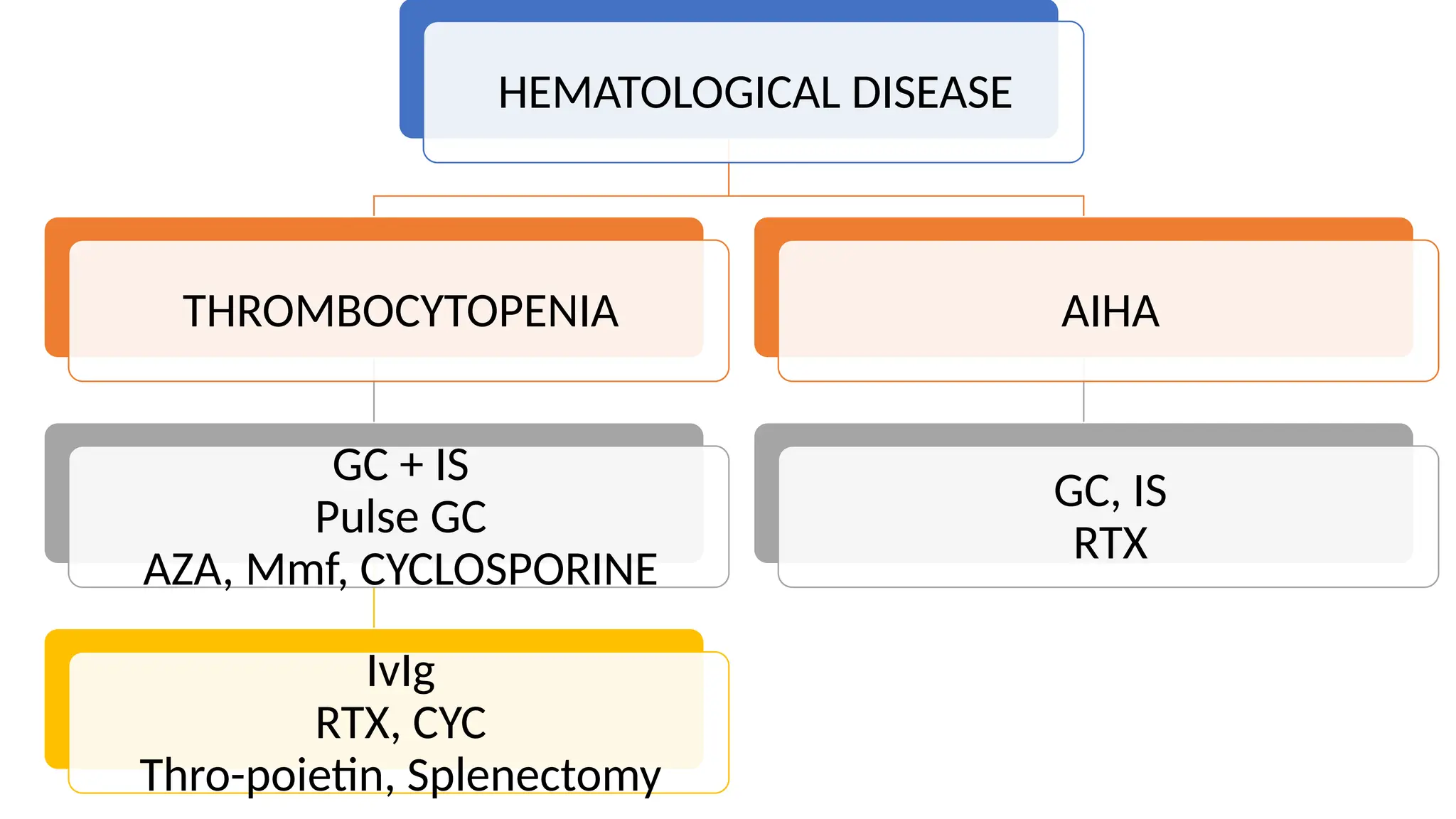
The 2019 update for SLE management emphasizes the goals of therapy aiming for low disease activity and remission, with recommended treatments including hydroxychloroquine for all patients, and various immunosuppressants based on disease severity. Key changes from the 2008 guidelines include increased use of hydroxychloroquine, reduced reliance on glucocorticoids, and specific treatment strategies for lupus nephritis and neuropsychiatric lupus. The document also highlights the importance of monitoring proteinuria instead of hematuria for follow-up in lupus nephritis cases.