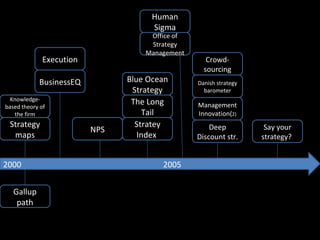
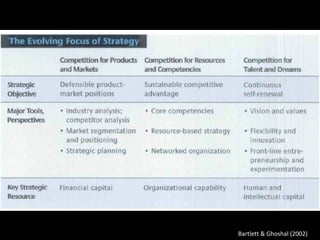
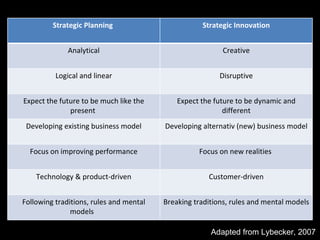
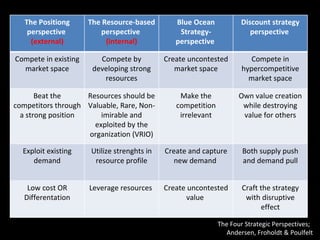
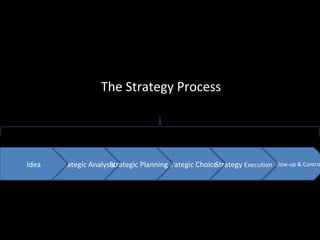
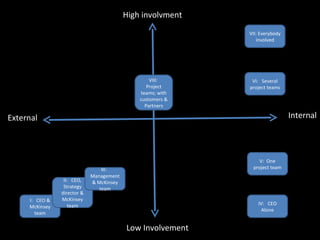
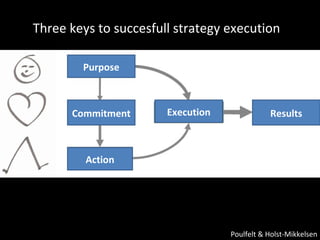
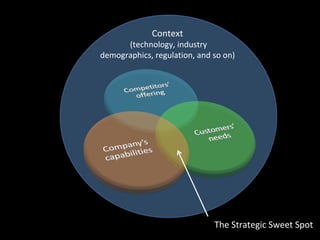
The document is a presentation on strategic management delivered by Christian Rangen at Copenhagen Business School in February 2010. It explores various definitions of strategy, historical developments in strategic management, and key perspectives and concepts such as competitive advantage, strategy execution, and the importance of alignment within organizations. The presentation also emphasizes the evolving nature of strategy in dynamic business environments and the necessity of innovation and comprehensive understanding for effective strategic planning.