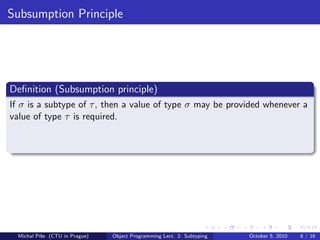
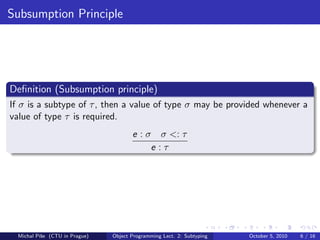
The document discusses polymorphism and subtyping in programming languages. It explains that languages can be monomorphic, where values have a single type, or polymorphic, where values can have multiple types. There are different types of polymorphism like universal, parametric, inclusion, overloading, and coercion. Subtyping allows a value of a subtype to be used wherever the supertype is expected. For subtyping to work, the subsumption and Liskov substitution principles must hold. The document also discusses how subtyping applies to constructed types like functions, records, references, arrays, and objects.