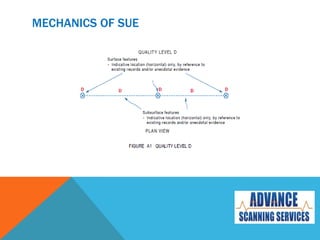
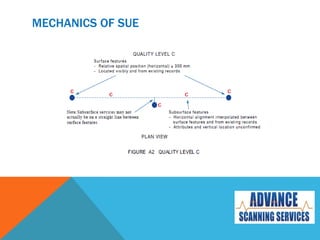
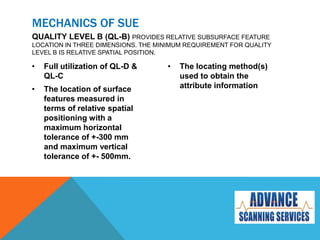
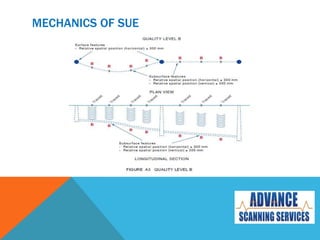
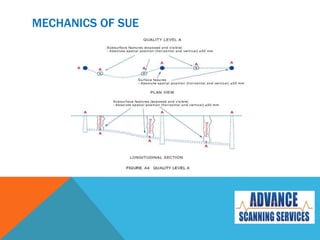
Subsurface Utility Engineering (SUE) is essential for managing risks related to underground utilities in infrastructure projects, helping to prevent damage to vital services and ensuring public safety. Australian standards define four quality levels of SUE, ranging from basic information (Quality Level D) to precise identification (Quality Level A). Utilizing SUE effectively minimizes project delays, design errors, and associated costs, ultimately safeguarding lives and the environment.