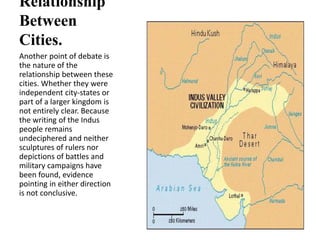
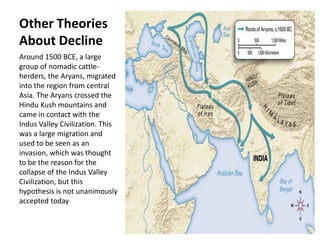
The Indus Valley Civilization was one of the earliest civilizations in South Asia, located along the Indus River valley. Two major cities, Mohenjo-Daro and Harappa, displayed advanced urban planning with wells, drainage systems, and comparable social conditions to Sumeria. While the writing system remains undeciphered, evidence suggests contact with Mesopotamian civilizations. The civilization began declining around 1800 BCE as the Saraswati River dried up, and many theorize nomadic Aryan migrants contributed to its collapse as they settled the region and their languages came to dominate.