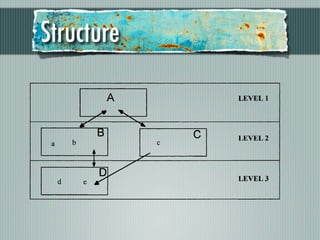
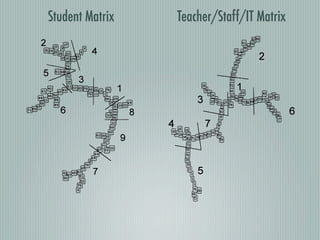
The document discusses a study where subjects were asked to categorize information items in a hierarchical structure. The subjects received cards describing each item and had to organize them into categories and higher-order categories. This was done to find the natural hierarchical structure. Subjects were allowed to place items in multiple categories, showing direct connections between items and categories that break the hierarchical structure.