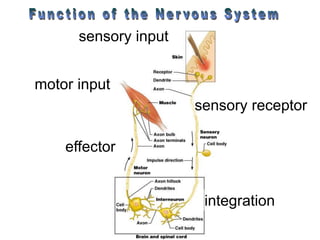
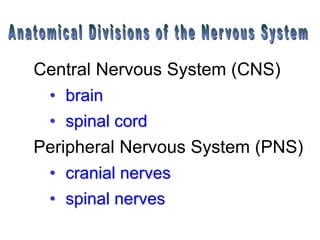
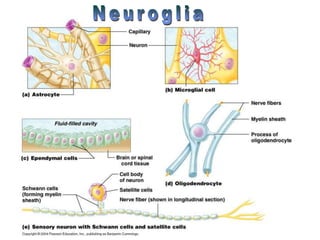
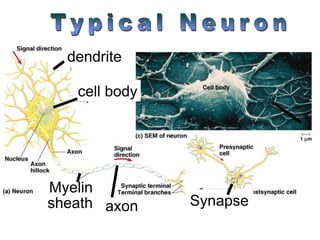
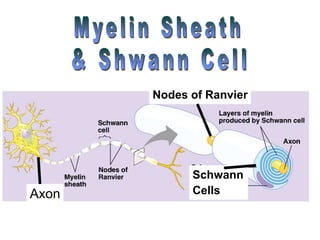
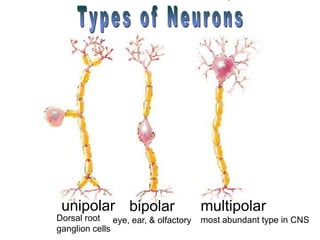
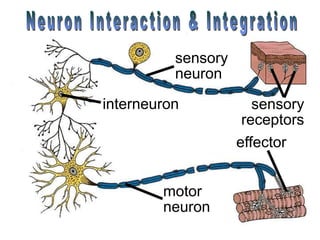
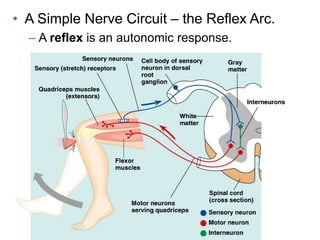
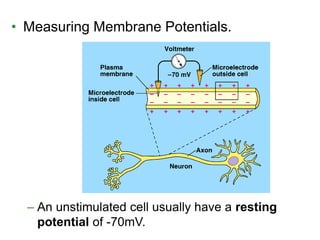
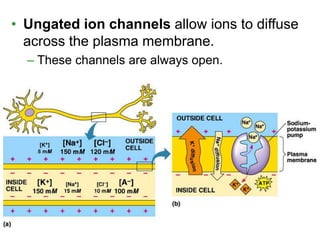
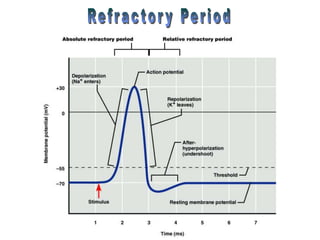
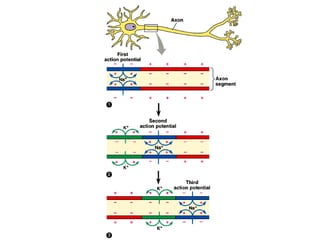
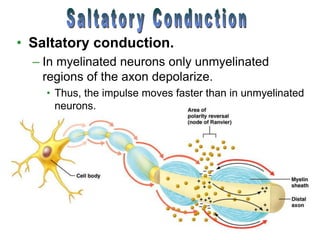
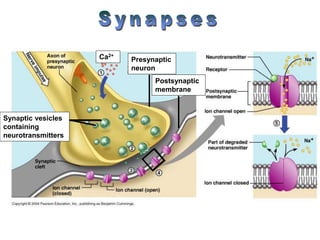
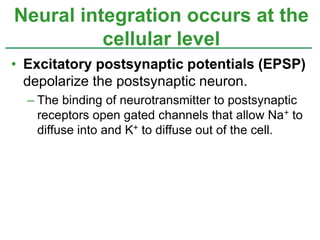
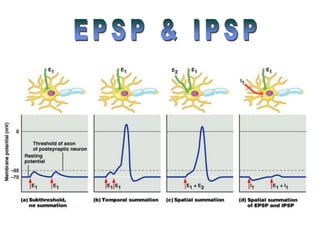
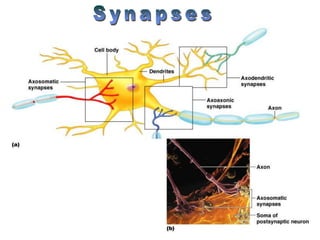
The document summarizes the structure and function of the nervous system. It describes how sensory receptors detect stimuli and transmit sensory information to the central nervous system via sensory neurons. The central nervous system, which includes the brain and spinal cord, then integrates this information and can initiate motor responses via motor neurons to the effectors. It explains key cellular structures like neurons, synapses, and myelination that allow rapid signal transmission. The reflex arc is provided as a simple example of a nerve circuit involving sensory and motor neurons. Finally, it outlines how electrical and chemical signals propagate through the nervous system and the roles of different neurotransmitters.