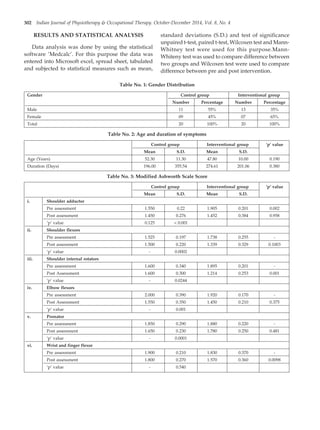
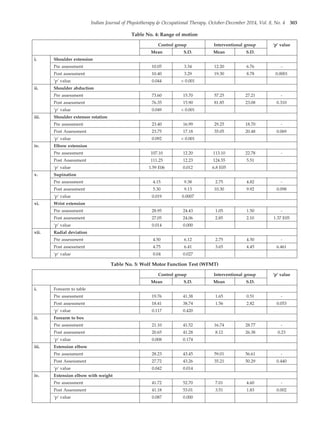
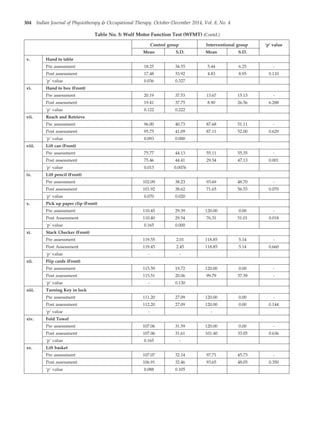
The document summarizes a randomized controlled trial that assessed the effectiveness of arm ergometer training for improving spasticity, range of motion, and motor control in patients with sub-acute and chronic stroke. 40 patients were divided into two groups - one that received conventional therapy alone and one that received conventional therapy plus arm ergometer training. The results showed that the group receiving arm ergometer training in addition to conventional therapy had significantly greater reductions in spasticity, as well as greater improvements in range of motion and gross motor function compared to the conventional therapy alone group. The study concluded that conventional therapy combined with arm ergometer treatment was effective for reducing spasticity and improving motor outcomes in sub-acute and chronic stroke