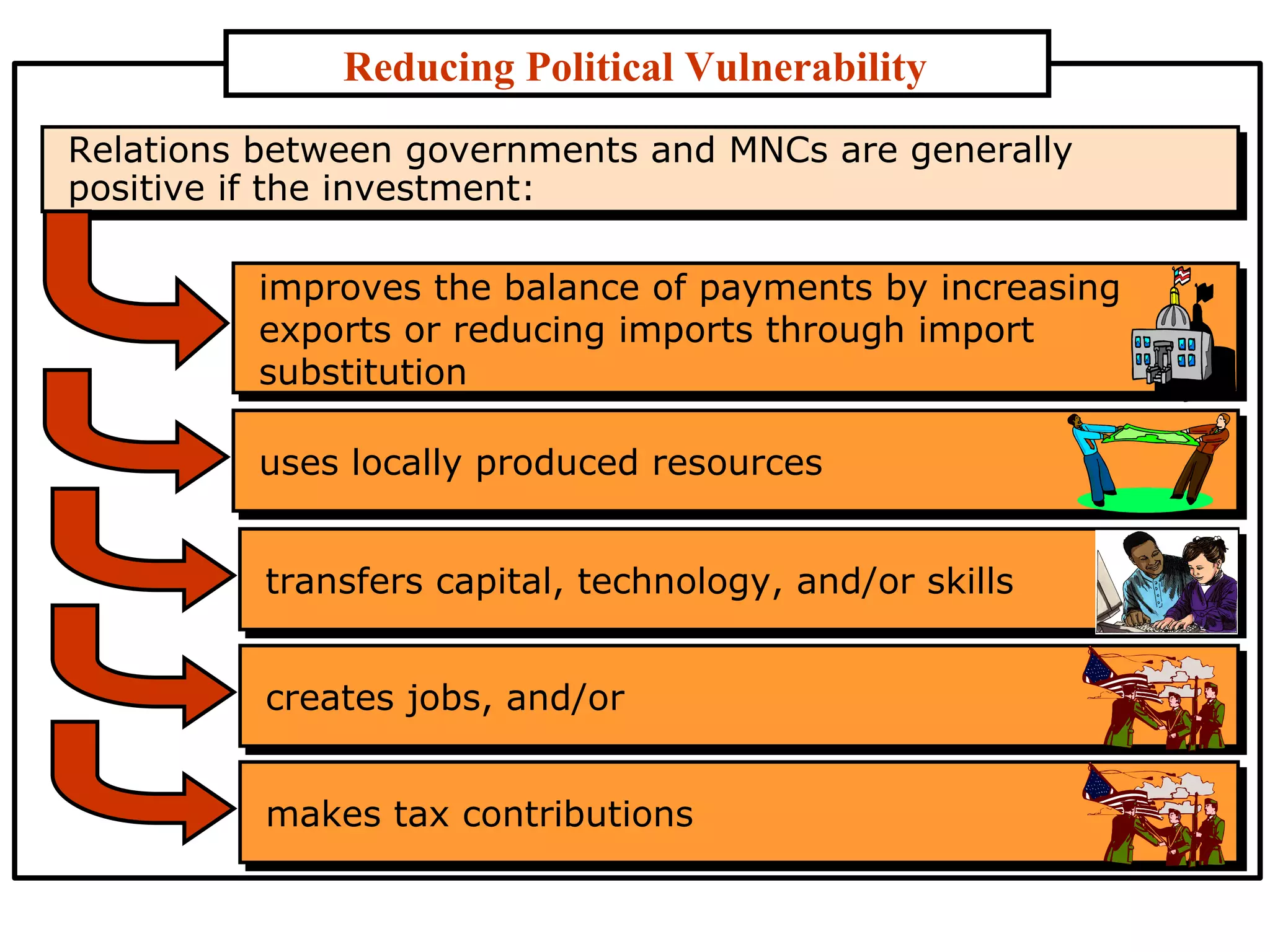
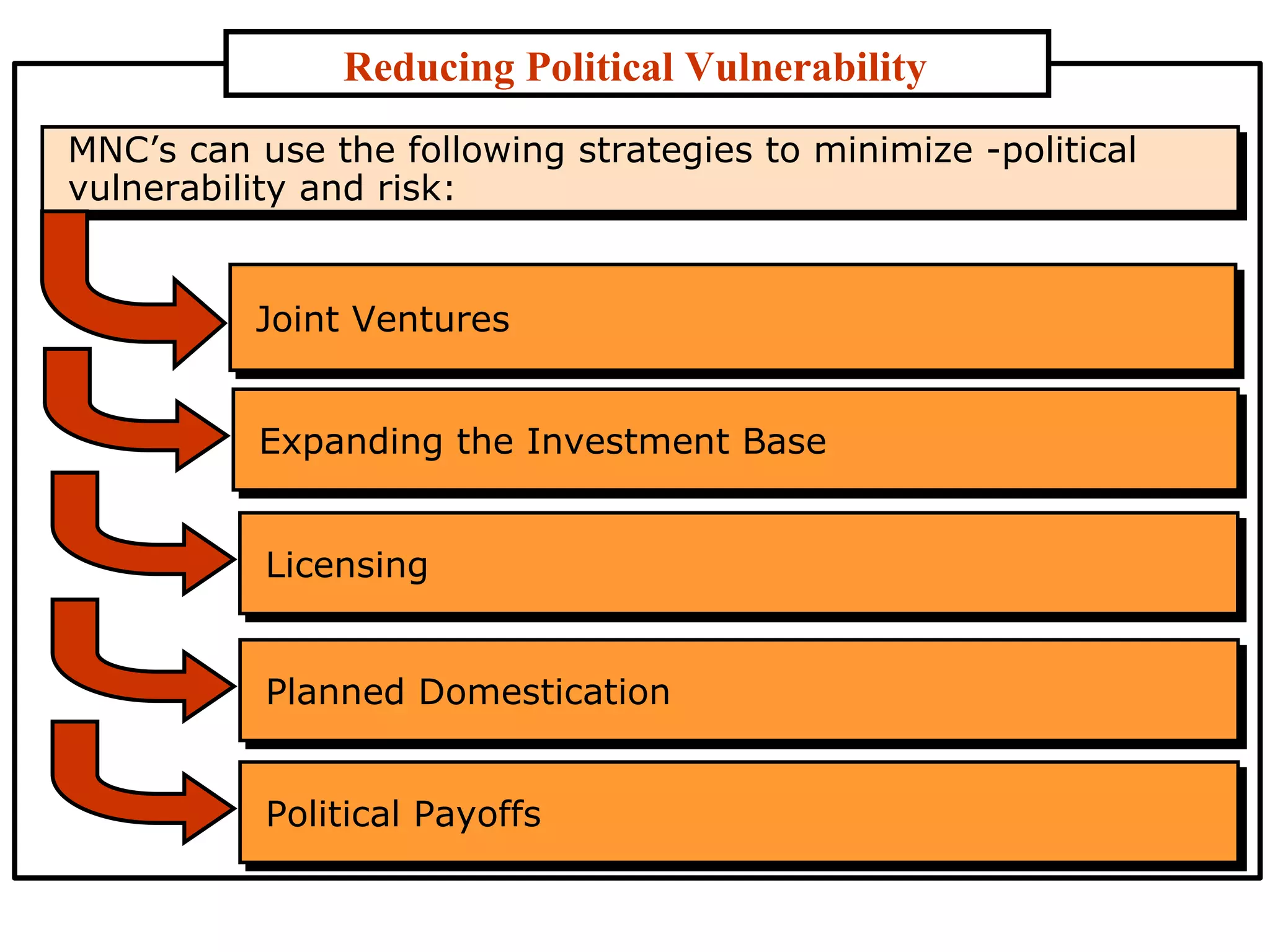
The document discusses the political environment as a critical concern for international business. It covers topics such as sovereignty of nations, stability of government policies, nationalism, political risks, assessing and reducing political vulnerability. Government philosophies and policies can shift with changes in government or pressure from groups. Nationalism may increase restrictions on imports and foreign investment. Businesses must consider risks like confiscation of assets, economic policy changes, and political and social activists when operating globally.