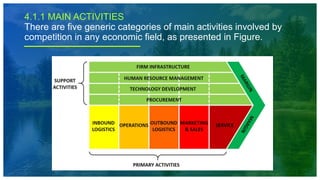
This document discusses strategy development in international trade and value chain analysis. It describes reasons for developing an international business strategy, including improved communication, globalization of markets, following competition, and availability of market information. It also explains Porter's classification of value chain activities into main activities and support activities. Main activities include inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, marketing and sales, and service. Support activities comprise procurement, technology development, human resource management, and firm infrastructure. The document outlines factors influencing international business locations and different production layouts used by companies. It stresses the importance of conducting a value chain analysis before economic analysis.